Marcelino Almeida
POp-GS: Next Best View in 3D-Gaussian Splatting with P-Optimality
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel algorithm for quantifying uncertainty and information gained within 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) through P-Optimality. While 3D-GS has proven to be a useful world model with high-quality rasterizations, it does not natively quantify uncertainty. Quantifying uncertainty in parameters of 3D-GS is necessary to understand the information gained from acquiring new images as in active perception, or identify redundant images which can be removed from memory due to resource constraints in online 3D-GS SLAM. We propose to quantify uncertainty and information gain in 3D-GS by reformulating the problem through the lens of optimal experimental design, which is a classical solution to measuring information gain. By restructuring information quantification of 3D-GS through optimal experimental design, we arrive at multiple solutions, of which T-Optimality and D-Optimality perform the best quantitatively and qualitatively as measured on two popular datasets. Additionally, we propose a block diagonal approximation of the 3D-GS uncertainty, which provides a measure of correlation for computing more accurate information gain, at the expense of a greater computation cost.
Modeling Uncertainty in 3D Gaussian Splatting through Continuous Semantic Splatting
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel algorithm for probabilistically updating and rasterizing semantic maps within 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS). Although previous methods have introduced algorithms which learn to rasterize features in 3D-GS for enhanced scene understanding, 3D-GS can fail without warning which presents a challenge for safety-critical robotic applications. To address this gap, we propose a method which advances the literature of continuous semantic mapping from voxels to ellipsoids, combining the precise structure of 3D-GS with the ability to quantify uncertainty of probabilistic robotic maps. Given a set of images, our algorithm performs a probabilistic semantic update directly on the 3D ellipsoids to obtain an expectation and variance through the use of conjugate priors. We also propose a probabilistic rasterization which returns per-pixel segmentation predictions with quantifiable uncertainty. We compare our method with similar probabilistic voxel-based methods to verify our extension to 3D ellipsoids, and perform ablation studies on uncertainty quantification and temporal smoothing.
The Role of Compute in Autonomous Aerial Vehicles
Jun 24, 2019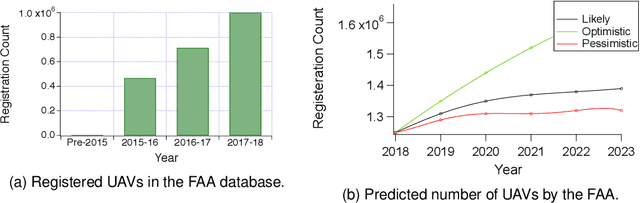
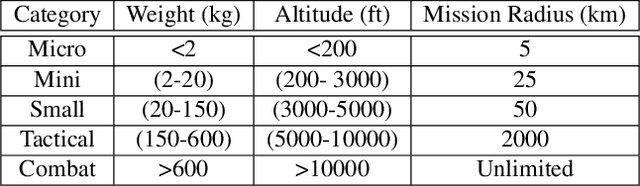

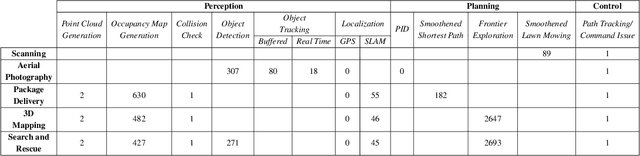
Abstract:Autonomous-mobile cyber-physical machines are part of our future. Specifically, unmanned-aerial-vehicles have seen a resurgence in activity with use-cases such as package delivery. These systems face many challenges such as their low-endurance caused by limited onboard-energy, hence, improving the mission-time and energy are of importance. Such improvements traditionally are delivered through better algorithms. But our premise is that more powerful and efficient onboard-compute should also address the problem. This paper investigates how the compute subsystem, in a cyber-physical mobile machine, such as a Micro Aerial Vehicle, impacts mission-time and energy. Specifically, we pose the question as what is the role of computing for cyber-physical mobile robots? We show that compute and motion are tightly intertwined, hence a close examination of cyber and physical processes and their impact on one another is necessary. We show different impact paths through which compute impacts mission-metrics and examine them using analytical models, simulation, and end-to-end benchmarking. To enable similar studies, we open sourced MAVBench, our tool-set consisting of a closed-loop simulator and a benchmark suite. Our investigations show cyber-physical co-design, a methodology where robot's cyber and physical processes/quantities are developed with one another consideration, similar to hardware-software co-design, is necessary for optimal robot design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge