Jinsun Park
OceanSplat: Object-aware Gaussian Splatting with Trinocular View Consistency for Underwater Scene Reconstruction
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We introduce OceanSplat, a novel 3D Gaussian Splatting-based approach for accurately representing 3D geometry in underwater scenes. To overcome multi-view inconsistencies caused by underwater optical degradation, our method enforces trinocular view consistency by rendering horizontally and vertically translated camera views relative to each input view and aligning them via inverse warping. Furthermore, these translated camera views are used to derive a synthetic epipolar depth prior through triangulation, which serves as a self-supervised depth regularizer. These geometric constraints facilitate the spatial optimization of 3D Gaussians and preserve scene structure in underwater environments. We also propose a depth-aware alpha adjustment that modulates the opacity of 3D Gaussians during early training based on their $z$-component and viewing direction, deterring the formation of medium-induced primitives. With our contributions, 3D Gaussians are disentangled from the scattering medium, enabling robust representation of object geometry and significantly reducing floating artifacts in reconstructed underwater scenes. Experiments on real-world underwater and simulated scenes demonstrate that OceanSplat substantially outperforms existing methods for both scene reconstruction and restoration in scattering media.
All-day Depth Completion via Thermal-LiDAR Fusion
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Depth completion, which estimates dense depth from sparse LiDAR and RGB images, has demonstrated outstanding performance in well-lit conditions. However, due to the limitations of RGB sensors, existing methods often struggle to achieve reliable performance in harsh environments, such as heavy rain and low-light conditions. Furthermore, we observe that ground truth depth maps often suffer from large missing measurements in adverse weather conditions such as heavy rain, leading to insufficient supervision. In contrast, thermal cameras are known for providing clear and reliable visibility in such conditions, yet research on thermal-LiDAR depth completion remains underexplored. Moreover, the characteristics of thermal images, such as blurriness, low contrast, and noise, bring unclear depth boundary problems. To address these challenges, we first evaluate the feasibility and robustness of thermal-LiDAR depth completion across diverse lighting (eg., well-lit, low-light), weather (eg., clear-sky, rainy), and environment (eg., indoor, outdoor) conditions, by conducting extensive benchmarks on the MS$^2$ and ViViD datasets. In addition, we propose a framework that utilizes COntrastive learning and Pseudo-Supervision (COPS) to enhance depth boundary clarity and improve completion accuracy by leveraging a depth foundation model in two key ways. First, COPS enforces a depth-aware contrastive loss between different depth points by mining positive and negative samples using a monocular depth foundation model to sharpen depth boundaries. Second, it mitigates the issue of incomplete supervision from ground truth depth maps by leveraging foundation model predictions as dense depth priors. We also provide in-depth analyses of the key challenges in thermal-LiDAR depth completion to aid in understanding the task and encourage future research.
Deep Depth Estimation from Thermal Image: Dataset, Benchmark, and Challenges
Mar 28, 2025



Abstract:Achieving robust and accurate spatial perception under adverse weather and lighting conditions is crucial for the high-level autonomy of self-driving vehicles and robots. However, existing perception algorithms relying on the visible spectrum are highly affected by weather and lighting conditions. A long-wave infrared camera (i.e., thermal imaging camera) can be a potential solution to achieve high-level robustness. However, the absence of large-scale datasets and standardized benchmarks remains a significant bottleneck to progress in active research for robust visual perception from thermal images. To this end, this manuscript provides a large-scale Multi-Spectral Stereo (MS$^2$) dataset that consists of stereo RGB, stereo NIR, stereo thermal, stereo LiDAR data, and GNSS/IMU information along with semi-dense depth ground truth. MS$^2$ dataset includes 162K synchronized multi-modal data pairs captured across diverse locations (e.g., urban city, residential area, campus, and high-way road) at different times (e.g., morning, daytime, and nighttime) and under various weather conditions (e.g., clear-sky, cloudy, and rainy). Secondly, we conduct a thorough evaluation of monocular and stereo depth estimation networks across RGB, NIR, and thermal modalities to establish standardized benchmark results on MS$^2$ depth test sets (e.g., day, night, and rainy). Lastly, we provide in-depth analyses and discuss the challenges revealed by the benchmark results, such as the performance variability for each modality under adverse conditions, domain shift between different sensor modalities, and potential research direction for thermal perception. Our dataset and source code are publicly available at https://sites.google.com/view/multi-spectral-stereo-dataset and https://github.com/UkcheolShin/SupDepth4Thermal.
Federated Domain Generalization with Data-free On-server Gradient Matching
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Domain Generalization (DG) aims to learn from multiple known source domains a model that can generalize well to unknown target domains. One of the key approaches in DG is training an encoder which generates domain-invariant representations. However, this approach is not applicable in Federated Domain Generalization (FDG), where data from various domains are distributed across different clients. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach, dubbed Federated Learning via On-server Matching Gradient (FedOMG), which can \emph{efficiently leverage domain information from distributed domains}. Specifically, we utilize the local gradients as information about the distributed models to find an invariant gradient direction across all domains through gradient inner product maximization. The advantages are two-fold: 1) FedOMG can aggregate the characteristics of distributed models on the centralized server without incurring any additional communication cost, and 2) FedOMG is orthogonal to many existing FL/FDG methods, allowing for additional performance improvements by being seamlessly integrated with them. Extensive experimental evaluations on various settings to demonstrate the robustness of FedOMG compared to other FL/FDG baselines. Our method outperforms recent SOTA baselines on four FL benchmark datasets (MNIST, EMNIST, CIFAR-10, and CIFAR-100), and three FDG benchmark datasets (PACS, VLCS, and OfficeHome).
CMDA: Cross-Modal and Domain Adversarial Adaptation for LiDAR-Based 3D Object Detection
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Recent LiDAR-based 3D Object Detection (3DOD) methods show promising results, but they often do not generalize well to target domains outside the source (or training) data distribution. To reduce such domain gaps and thus to make 3DOD models more generalizable, we introduce a novel unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) method, called CMDA, which (i) leverages visual semantic cues from an image modality (i.e., camera images) as an effective semantic bridge to close the domain gap in the cross-modal Bird's Eye View (BEV) representations. Further, (ii) we also introduce a self-training-based learning strategy, wherein a model is adversarially trained to generate domain-invariant features, which disrupt the discrimination of whether a feature instance comes from a source or an unseen target domain. Overall, our CMDA framework guides the 3DOD model to generate highly informative and domain-adaptive features for novel data distributions. In our extensive experiments with large-scale benchmarks, such as nuScenes, Waymo, and KITTI, those mentioned above provide significant performance gains for UDA tasks, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
Lightweight Alpha Matting Network Using Distillation-Based Channel Pruning
Oct 14, 2022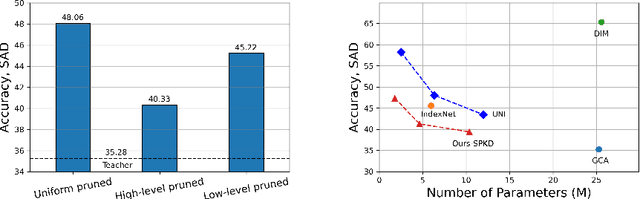
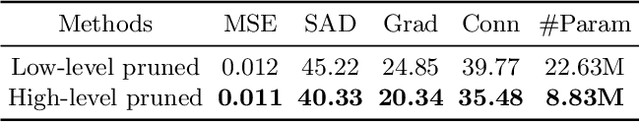
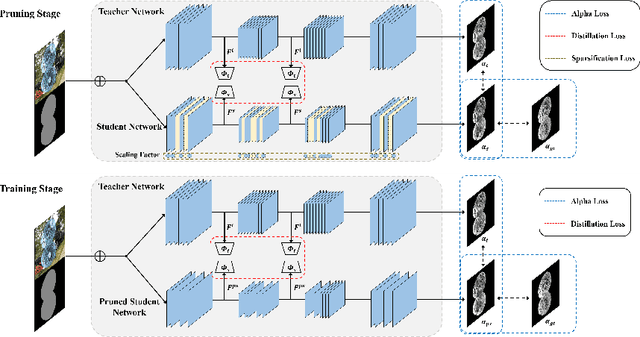
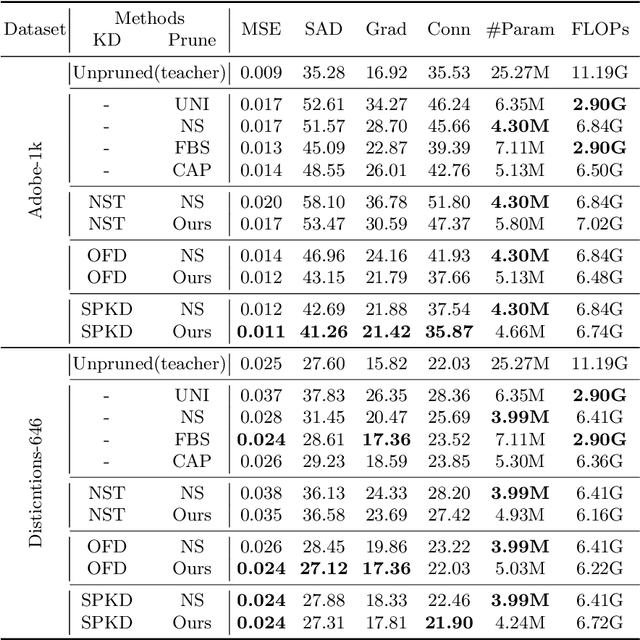
Abstract:Recently, alpha matting has received a lot of attention because of its usefulness in mobile applications such as selfies. Therefore, there has been a demand for a lightweight alpha matting model due to the limited computational resources of commercial portable devices. To this end, we suggest a distillation-based channel pruning method for the alpha matting networks. In the pruning step, we remove channels of a student network having fewer impacts on mimicking the knowledge of a teacher network. Then, the pruned lightweight student network is trained by the same distillation loss. A lightweight alpha matting model from the proposed method outperforms existing lightweight methods. To show superiority of our algorithm, we provide various quantitative and qualitative experiments with in-depth analyses. Furthermore, we demonstrate the versatility of the proposed distillation-based channel pruning method by applying it to semantic segmentation.
Source Domain Subset Sampling for Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation in Semantic Segmentation
May 03, 2022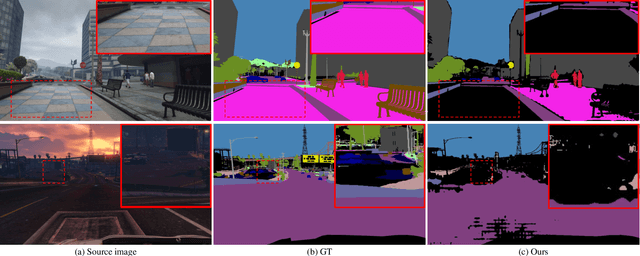
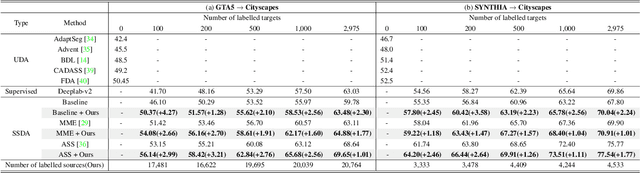

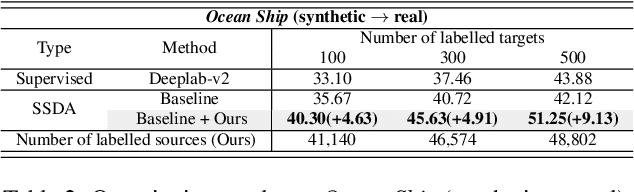
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce source domain subset sampling (SDSS) as a new perspective of semi-supervised domain adaptation. We propose domain adaptation by sampling and exploiting only a meaningful subset from source data for training. Our key assumption is that the entire source domain data may contain samples that are unhelpful for the adaptation. Therefore, the domain adaptation can benefit from a subset of source data composed solely of helpful and relevant samples. The proposed method effectively subsamples full source data to generate a small-scale meaningful subset. Therefore, training time is reduced, and performance is improved with our subsampled source data. To further verify the scalability of our method, we construct a new dataset called Ocean Ship, which comprises 500 real and 200K synthetic sample images with ground-truth labels. The SDSS achieved a state-of-the-art performance when applied on GTA5 to Cityscapes and SYNTHIA to Cityscapes public benchmark datasets and a 9.13 mIoU improvement on our Ocean Ship dataset over a baseline model.
Non-Local Spatial Propagation Network for Depth Completion
Jul 20, 2020
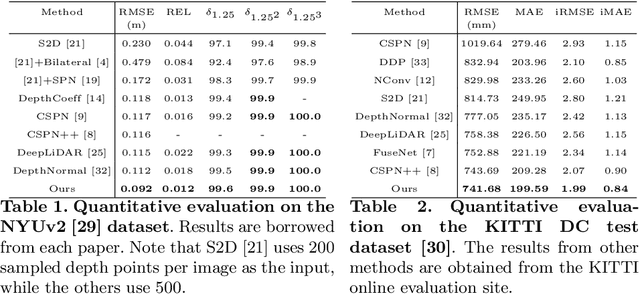
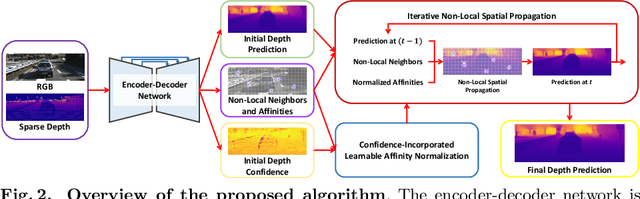
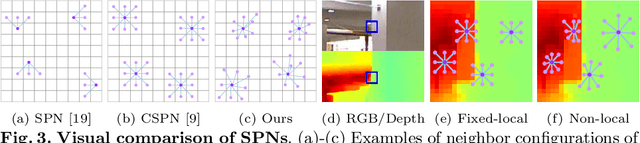
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a robust and efficient end-to-end non-local spatial propagation network for depth completion. The proposed network takes RGB and sparse depth images as inputs and estimates non-local neighbors and their affinities of each pixel, as well as an initial depth map with pixel-wise confidences. The initial depth prediction is then iteratively refined by its confidence and non-local spatial propagation procedure based on the predicted non-local neighbors and corresponding affinities. Unlike previous algorithms that utilize fixed-local neighbors, the proposed algorithm effectively avoids irrelevant local neighbors and concentrates on relevant non-local neighbors during propagation. In addition, we introduce a learnable affinity normalization to better learn the affinity combinations compared to conventional methods. The proposed algorithm is inherently robust to the mixed-depth problem on depth boundaries, which is one of the major issues for existing depth estimation/completion algorithms. Experimental results on indoor and outdoor datasets demonstrate that the proposed algorithm is superior to conventional algorithms in terms of depth completion accuracy and robustness to the mixed-depth problem. Our implementation is publicly available on the project page.
Propose-and-Attend Single Shot Detector
Jul 30, 2019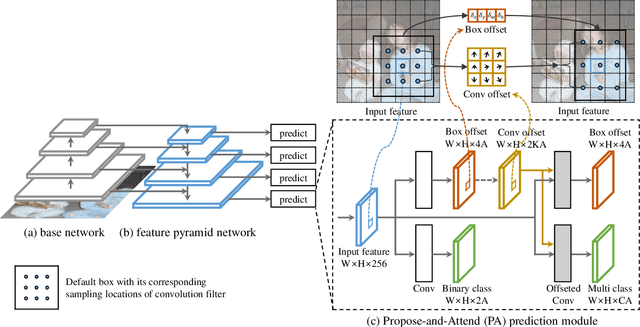
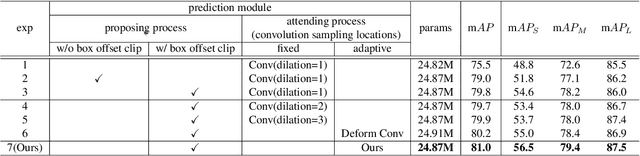
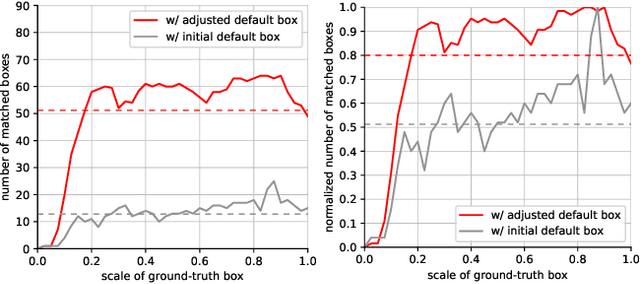
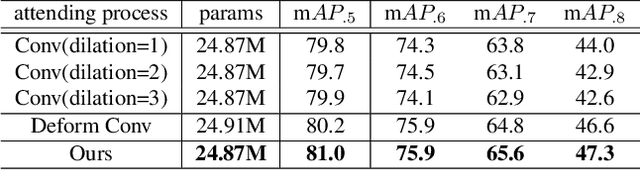
Abstract:We present a simple yet effective prediction module for a one-stage detector. The main process is conducted in a coarse-to-fine manner. First, the module roughly adjusts the default boxes to well capture the extent of target objects in an image. Second, given the adjusted boxes, the module aligns the receptive field of the convolution filters accordingly, not requiring any embedding layers. Both steps build a propose-and-attend mechanism, mimicking two-stage detectors in a highly efficient manner. To verify its effectiveness, we apply the proposed module to a basic one-stage detector SSD. Our final model achieves an accuracy comparable to that of state-of-the-art detectors while using a fraction of their model parameters and computational overheads. Moreover, we found that the proposed module has two strong applications. 1) The module can be successfully integrated into a lightweight backbone, further pushing the efficiency of the one-stage detector. 2) The module also allows train-from-scratch without relying on any sophisticated base networks as previous methods do.
Camera Exposure Control for Robust Robot Vision with Noise-Aware Image Quality Assessment
Jul 11, 2019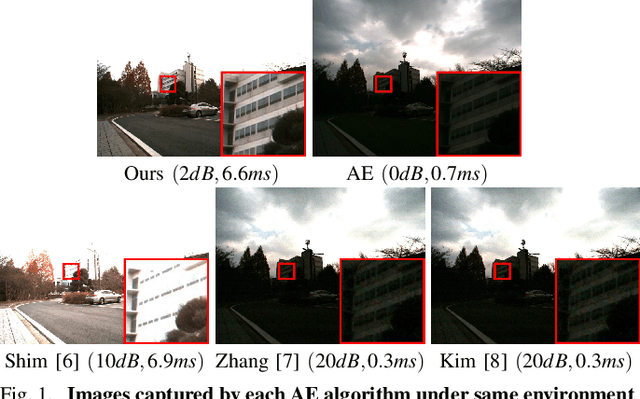
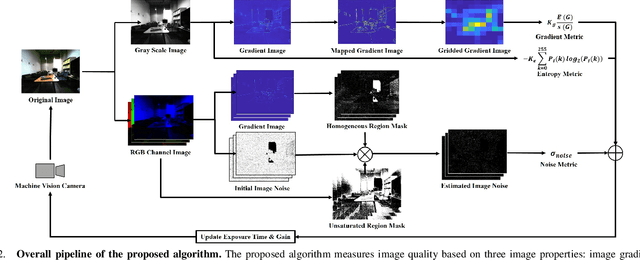


Abstract:In this paper, we propose a noise-aware exposure control algorithm for robust robot vision. Our method aims to capture the best-exposed image which can boost the performance of various computer vision and robotics tasks. For this purpose, we carefully design an image quality metric which captures complementary quality attributes and ensures light-weight computation. Specifically, our metric consists of a combination of image gradient, entropy, and noise metrics. The synergy of these measures allows preserving sharp edge and rich texture in the image while maintaining a low noise level. Using this novel metric, we propose a real-time and fully automatic exposure and gain control technique based on the Nelder-Mead method. To illustrate the effectiveness of our technique, a large set of experimental results demonstrates higher qualitative and quantitative performances when compared with conventional approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge