Jinkyu Kim
ALIGN: Advanced Query Initialization with LiDAR-Image Guidance for Occlusion-Robust 3D Object Detection
Dec 20, 2025



Abstract:Recent query-based 3D object detection methods using camera and LiDAR inputs have shown strong performance, but existing query initialization strategies,such as random sampling or BEV heatmap-based sampling, often result in inefficient query usage and reduced accuracy, particularly for occluded or crowded objects. To address this limitation, we propose ALIGN (Advanced query initialization with LiDAR and Image GuidaNce), a novel approach for occlusion-robust, object-aware query initialization. Our model consists of three key components: (i) Occlusion-aware Center Estimation (OCE), which integrates LiDAR geometry and image semantics to estimate object centers accurately (ii) Adaptive Neighbor Sampling (ANS), which generates object candidates from LiDAR clustering and supplements each object by sampling spatially and semantically aligned points around it and (iii) Dynamic Query Balancing (DQB), which adaptively balances queries between foreground and background regions. Our extensive experiments on the nuScenes benchmark demonstrate that ALIGN consistently improves performance across multiple state-of-the-art detectors, achieving gains of up to +0.9 mAP and +1.2 NDS, particularly in challenging scenes with occlusions or dense crowds. Our code will be publicly available upon publication.
Watermarking for Factuality: Guiding Vision-Language Models Toward Truth via Tri-layer Contrastive Decoding
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have recently shown promising results on various multimodal tasks, even achieving human-comparable performance in certain cases. Nevertheless, LVLMs remain prone to hallucinations -- they often rely heavily on a single modality or memorize training data without properly grounding their outputs. To address this, we propose a training-free, tri-layer contrastive decoding with watermarking, which proceeds in three steps: (1) select a mature layer and an amateur layer among the decoding layers, (2) identify a pivot layer using a watermark-related question to assess whether the layer is visually well-grounded, and (3) apply tri-layer contrastive decoding to generate the final output. Experiments on public benchmarks such as POPE, MME and AMBER demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in reducing hallucinations in LVLMs and generates more visually grounded responses.
SemanticControl: A Training-Free Approach for Handling Loosely Aligned Visual Conditions in ControlNet
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:ControlNet has enabled detailed spatial control in text-to-image diffusion models by incorporating additional visual conditions such as depth or edge maps. However, its effectiveness heavily depends on the availability of visual conditions that are precisely aligned with the generation goal specified by text prompt-a requirement that often fails in practice, especially for uncommon or imaginative scenes. For example, generating an image of a cat cooking in a specific pose may be infeasible due to the lack of suitable visual conditions. In contrast, structurally similar cues can often be found in more common settings-for instance, poses of humans cooking are widely available and can serve as rough visual guides. Unfortunately, existing ControlNet models struggle to use such loosely aligned visual conditions, often resulting in low text fidelity or visual artifacts. To address this limitation, we propose SemanticControl, a training-free method for effectively leveraging misaligned but semantically relevant visual conditions. Our approach adaptively suppresses the influence of the visual condition where it conflicts with the prompt, while strengthening guidance from the text. The key idea is to first run an auxiliary denoising process using a surrogate prompt aligned with the visual condition (e.g., "a human playing guitar" for a human pose condition) to extract informative attention masks, and then utilize these masks during the denoising of the actual target prompt (e.g., cat playing guitar). Experimental results demonstrate that our method improves performance under loosely aligned conditions across various conditions, including depth maps, edge maps, and human skeletons, outperforming existing baselines. Our code is available at https://mung3477.github.io/semantic-control.
LRSLAM: Low-rank Representation of Signed Distance Fields in Dense Visual SLAM System
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) has been crucial across various domains, including autonomous driving, mobile robotics, and mixed reality. Dense visual SLAM, leveraging RGB-D camera systems, offers advantages but faces challenges in achieving real-time performance, robustness, and scalability for large-scale scenes. Recent approaches utilizing neural implicit scene representations show promise but suffer from high computational costs and memory requirements. ESLAM introduced a plane-based tensor decomposition but still struggled with memory growth. Addressing these challenges, we propose a more efficient visual SLAM model, called LRSLAM, utilizing low-rank tensor decomposition methods. Our approach, leveraging the Six-axis and CP decompositions, achieves better convergence rates, memory efficiency, and reconstruction/localization quality than existing state-of-the-art approaches. Evaluation across diverse indoor RGB-D datasets demonstrates LRSLAM's superior performance in terms of parameter efficiency, processing time, and accuracy, retaining reconstruction and localization quality. Our code will be publicly available upon publication.
Mitigating Trade-off: Stream and Query-guided Aggregation for Efficient and Effective 3D Occupancy Prediction
Mar 28, 2025



Abstract:3D occupancy prediction has emerged as a key perception task for autonomous driving, as it reconstructs 3D environments to provide a comprehensive scene understanding. Recent studies focus on integrating spatiotemporal information obtained from past observations to improve prediction accuracy, using a multi-frame fusion approach that processes multiple past frames together. However, these methods struggle with a trade-off between efficiency and accuracy, which significantly limits their practicality. To mitigate this trade-off, we propose StreamOcc, a novel framework that aggregates spatio-temporal information in a stream-based manner. StreamOcc consists of two key components: (i) Stream-based Voxel Aggregation, which effectively accumulates past observations while minimizing computational costs, and (ii) Query-guided Aggregation, which recurrently aggregates instance-level features of dynamic objects into corresponding voxel features, refining fine-grained details of dynamic objects. Experiments on the Occ3D-nuScenes dataset show that StreamOcc achieves state-of-the-art performance in real-time settings, while reducing memory usage by more than 50% compared to previous methods.
3D Occupancy Prediction with Low-Resolution Queries via Prototype-aware View Transformation
Mar 19, 2025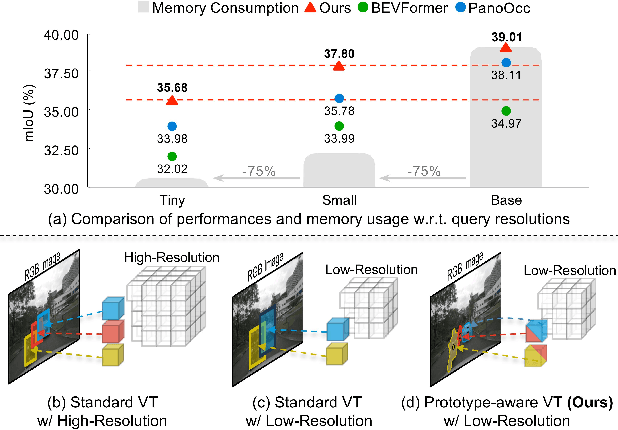
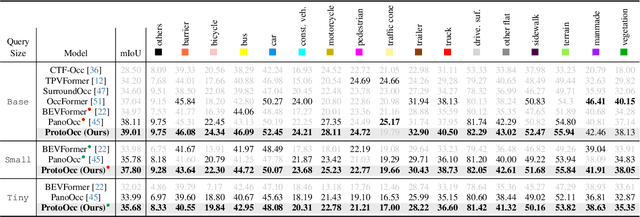
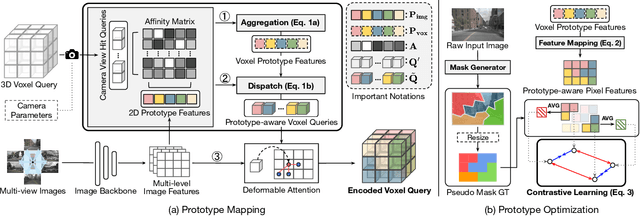
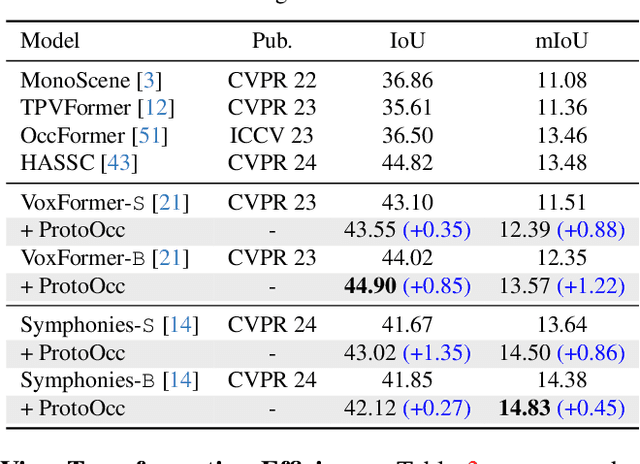
Abstract:The resolution of voxel queries significantly influences the quality of view transformation in camera-based 3D occupancy prediction. However, computational constraints and the practical necessity for real-time deployment require smaller query resolutions, which inevitably leads to an information loss. Therefore, it is essential to encode and preserve rich visual details within limited query sizes while ensuring a comprehensive representation of 3D occupancy. To this end, we introduce ProtoOcc, a novel occupancy network that leverages prototypes of clustered image segments in view transformation to enhance low-resolution context. In particular, the mapping of 2D prototypes onto 3D voxel queries encodes high-level visual geometries and complements the loss of spatial information from reduced query resolutions. Additionally, we design a multi-perspective decoding strategy to efficiently disentangle the densely compressed visual cues into a high-dimensional 3D occupancy scene. Experimental results on both Occ3D and SemanticKITTI benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, showing clear improvements over the baselines. More importantly, ProtoOcc achieves competitive performance against the baselines even with 75\% reduced voxel resolution.
GUIDE-CoT: Goal-driven and User-Informed Dynamic Estimation for Pedestrian Trajectory using Chain-of-Thought
Mar 10, 2025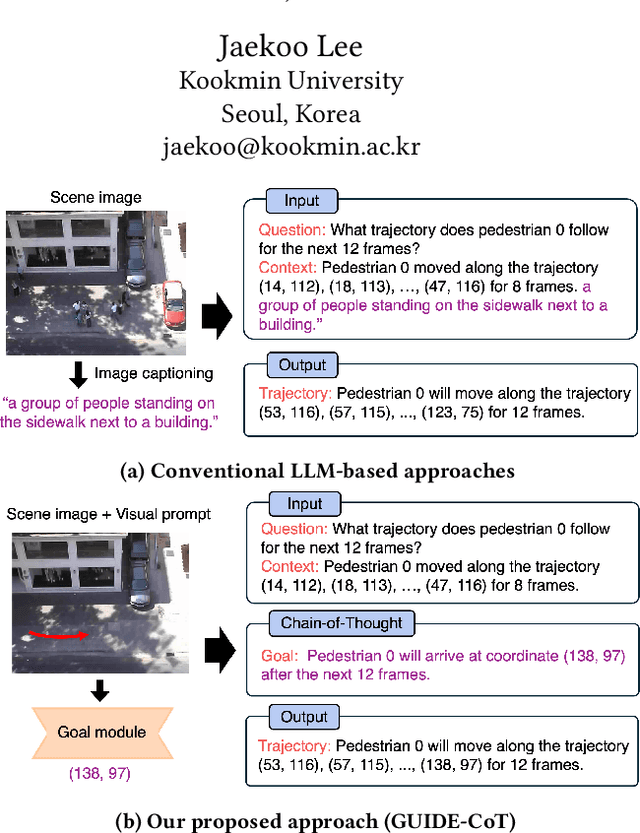

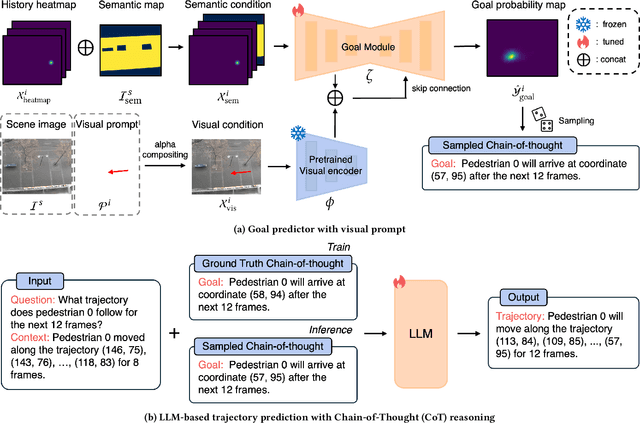

Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently shown impressive results in reasoning tasks, their application to pedestrian trajectory prediction remains challenging due to two key limitations: insufficient use of visual information and the difficulty of predicting entire trajectories. To address these challenges, we propose Goal-driven and User-Informed Dynamic Estimation for pedestrian trajectory using Chain-of-Thought (GUIDE-CoT). Our approach integrates two innovative modules: (1) a goal-oriented visual prompt, which enhances goal prediction accuracy combining visual prompts with a pretrained visual encoder, and (2) a chain-of-thought (CoT) LLM for trajectory generation, which generates realistic trajectories toward the predicted goal. Moreover, our method introduces controllable trajectory generation, allowing for flexible and user-guided modifications to the predicted paths. Through extensive experiments on the ETH/UCY benchmark datasets, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, delivering both high accuracy and greater adaptability in pedestrian trajectory prediction. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/ai-kmu/GUIDE-CoT.
DiffExp: Efficient Exploration in Reward Fine-tuning for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:Fine-tuning text-to-image diffusion models to maximize rewards has proven effective for enhancing model performance. However, reward fine-tuning methods often suffer from slow convergence due to online sample generation. Therefore, obtaining diverse samples with strong reward signals is crucial for improving sample efficiency and overall performance. In this work, we introduce DiffExp, a simple yet effective exploration strategy for reward fine-tuning of text-to-image models. Our approach employs two key strategies: (a) dynamically adjusting the scale of classifier-free guidance to enhance sample diversity, and (b) randomly weighting phrases of the text prompt to exploit high-quality reward signals. We demonstrate that these strategies significantly enhance exploration during online sample generation, improving the sample efficiency of recent reward fine-tuning methods, such as DDPO and AlignProp.
Unified Domain Generalization and Adaptation for Multi-View 3D Object Detection
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in 3D object detection leveraging multi-view cameras have demonstrated their practical and economical value in various challenging vision tasks. However, typical supervised learning approaches face challenges in achieving satisfactory adaptation toward unseen and unlabeled target datasets (\ie, direct transfer) due to the inevitable geometric misalignment between the source and target domains. In practice, we also encounter constraints on resources for training models and collecting annotations for the successful deployment of 3D object detectors. In this paper, we propose Unified Domain Generalization and Adaptation (UDGA), a practical solution to mitigate those drawbacks. We first propose Multi-view Overlap Depth Constraint that leverages the strong association between multi-view, significantly alleviating geometric gaps due to perspective view changes. Then, we present a Label-Efficient Domain Adaptation approach to handle unfamiliar targets with significantly fewer amounts of labels (\ie, 1$\%$ and 5$\%)$, while preserving well-defined source knowledge for training efficiency. Overall, UDGA framework enables stable detection performance in both source and target domains, effectively bridging inevitable domain gaps, while demanding fewer annotations. We demonstrate the robustness of UDGA with large-scale benchmarks: nuScenes, Lyft, and Waymo, where our framework outperforms the current state-of-the-art methods.
ENTP: Encoder-only Next Token Prediction
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:Next-token prediction models have predominantly relied on decoder-only Transformers with causal attention, driven by the common belief that causal attention is essential to prevent "cheating" by masking future tokens. We challenge this widely accepted notion and argue that this design choice is about efficiency rather than necessity. While decoder-only Transformers are still a good choice for practical reasons, they are not the only viable option. In this work, we introduce Encoder-only Next Token Prediction (ENTP). We explore the differences between ENTP and decoder-only Transformers in expressive power and complexity, highlighting potential advantages of ENTP. We introduce the Triplet-Counting task and show, both theoretically and experimentally, that while ENTP can perform this task easily, a decoder-only Transformer cannot. Finally, we empirically demonstrate ENTP's superior performance across various realistic tasks, such as length generalization and in-context learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge