Gyeongrok Oh
ICP-4D: Bridging Iterative Closest Point and LiDAR Panoptic Segmentation
Dec 22, 2025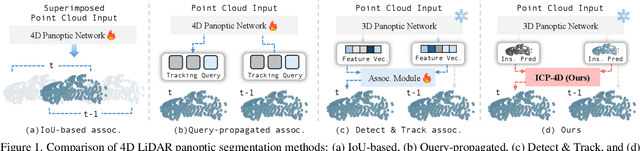
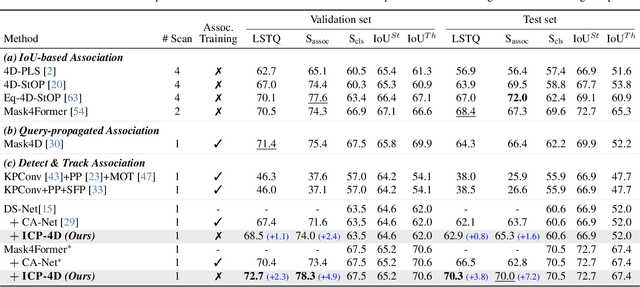
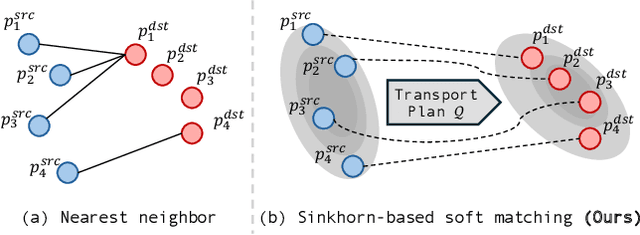
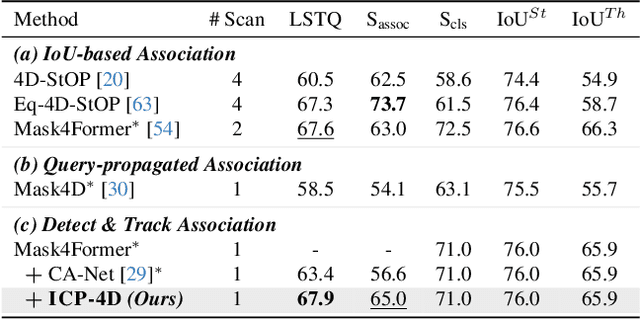
Abstract:Dominant paradigms for 4D LiDAR panoptic segmentation are usually required to train deep neural networks with large superimposed point clouds or design dedicated modules for instance association. However, these approaches perform redundant point processing and consequently become computationally expensive, yet still overlook the rich geometric priors inherently provided by raw point clouds. To this end, we introduce ICP-4D, a simple yet effective training-free framework that unifies spatial and temporal reasoning through geometric relations among instance-level point sets. Specifically, we apply the Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algorithm to directly associate temporally consistent instances by aligning the source and target point sets through the estimated transformation. To stabilize association under noisy instance predictions, we introduce a Sinkhorn-based soft matching. This exploits the underlying instance distribution to obtain accurate point-wise correspondences, resulting in robust geometric alignment. Furthermore, our carefully designed pipeline, which considers three instance types-static, dynamic, and missing-offers computational efficiency and occlusion-aware matching. Our extensive experiments across both SemanticKITTI and panoptic nuScenes demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, even without additional training or extra point cloud inputs.
Active Test-time Vision-Language Navigation
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Navigation (VLN) policies trained on offline datasets often exhibit degraded task performance when deployed in unfamiliar navigation environments at test time, where agents are typically evaluated without access to external interaction or feedback. Entropy minimization has emerged as a practical solution for reducing prediction uncertainty at test time; however, it can suffer from accumulated errors, as agents may become overconfident in incorrect actions without sufficient contextual grounding. To tackle these challenges, we introduce ATENA (Active TEst-time Navigation Agent), a test-time active learning framework that enables a practical human-robot interaction via episodic feedback on uncertain navigation outcomes. In particular, ATENA learns to increase certainty in successful episodes and decrease it in failed ones, improving uncertainty calibration. Here, we propose mixture entropy optimization, where entropy is obtained from a combination of the action and pseudo-expert distributions-a hypothetical action distribution assuming the agent's selected action to be optimal-controlling both prediction confidence and action preference. In addition, we propose a self-active learning strategy that enables an agent to evaluate its navigation outcomes based on confident predictions. As a result, the agent stays actively engaged throughout all iterations, leading to well-grounded and adaptive decision-making. Extensive evaluations on challenging VLN benchmarks-REVERIE, R2R, and R2R-CE-demonstrate that ATENA successfully overcomes distributional shifts at test time, outperforming the compared baseline methods across various settings.
3D Occupancy Prediction with Low-Resolution Queries via Prototype-aware View Transformation
Mar 19, 2025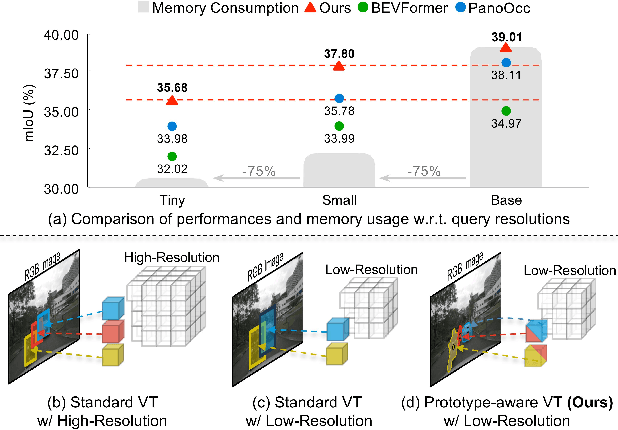
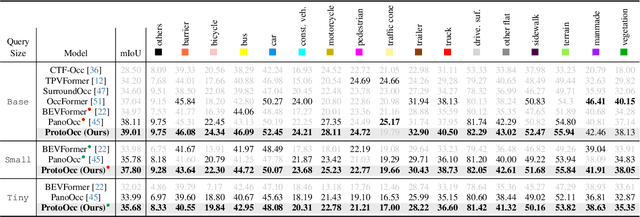
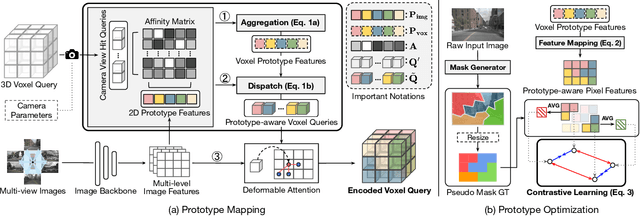
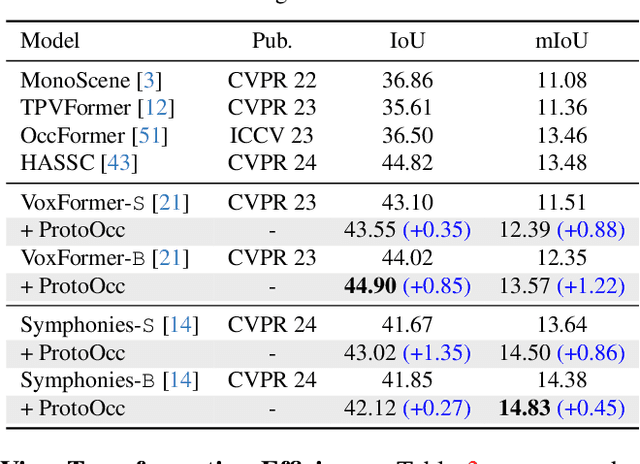
Abstract:The resolution of voxel queries significantly influences the quality of view transformation in camera-based 3D occupancy prediction. However, computational constraints and the practical necessity for real-time deployment require smaller query resolutions, which inevitably leads to an information loss. Therefore, it is essential to encode and preserve rich visual details within limited query sizes while ensuring a comprehensive representation of 3D occupancy. To this end, we introduce ProtoOcc, a novel occupancy network that leverages prototypes of clustered image segments in view transformation to enhance low-resolution context. In particular, the mapping of 2D prototypes onto 3D voxel queries encodes high-level visual geometries and complements the loss of spatial information from reduced query resolutions. Additionally, we design a multi-perspective decoding strategy to efficiently disentangle the densely compressed visual cues into a high-dimensional 3D occupancy scene. Experimental results on both Occ3D and SemanticKITTI benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, showing clear improvements over the baselines. More importantly, ProtoOcc achieves competitive performance against the baselines even with 75\% reduced voxel resolution.
CMDA: Cross-Modal and Domain Adversarial Adaptation for LiDAR-Based 3D Object Detection
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Recent LiDAR-based 3D Object Detection (3DOD) methods show promising results, but they often do not generalize well to target domains outside the source (or training) data distribution. To reduce such domain gaps and thus to make 3DOD models more generalizable, we introduce a novel unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) method, called CMDA, which (i) leverages visual semantic cues from an image modality (i.e., camera images) as an effective semantic bridge to close the domain gap in the cross-modal Bird's Eye View (BEV) representations. Further, (ii) we also introduce a self-training-based learning strategy, wherein a model is adversarially trained to generate domain-invariant features, which disrupt the discrimination of whether a feature instance comes from a source or an unseen target domain. Overall, our CMDA framework guides the 3DOD model to generate highly informative and domain-adaptive features for novel data distributions. In our extensive experiments with large-scale benchmarks, such as nuScenes, Waymo, and KITTI, those mentioned above provide significant performance gains for UDA tasks, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
MTVG : Multi-text Video Generation with Text-to-Video Models
Dec 07, 2023Abstract:Recently, video generation has attracted massive attention and yielded noticeable outcomes. Concerning the characteristics of video, multi-text conditioning incorporating sequential events is necessary for next-step video generation. In this work, we propose a novel multi-text video generation~(MTVG) by directly utilizing a pre-trained diffusion-based text-to-video~(T2V) generation model without additional fine-tuning. To generate consecutive video segments, visual consistency generated by distinct prompts is necessary with diverse variations, such as motion and content-related transitions. Our proposed MTVG includes Dynamic Noise and Last Frame Aware Inversion which reinitialize the noise latent to preserve visual coherence between videos of different prompts and prevent repetitive motion or contents. Furthermore, we present Structure Guiding Sampling to maintain the global appearance across the frames in a single video clip, where we leverage iterative latent updates across the preceding frame. Additionally, our Prompt Generator allows for arbitrary format of text conditions consisting of diverse events. As a result, our extensive experiments, including diverse transitions of descriptions, demonstrate that our proposed methods show superior generated outputs in terms of semantically coherent and temporally seamless video.Video examples are available in our project page: https://kuai-lab.github.io/mtvg-page.
FPANet: Frequency-based Video Demoireing using Frame-level Post Alignment
Jan 18, 2023



Abstract:Interference between overlapping gird patterns creates moire patterns, degrading the visual quality of an image that captures a screen of a digital display device by an ordinary digital camera. Removing such moire patterns is challenging due to their complex patterns of diverse sizes and color distortions. Existing approaches mainly focus on filtering out in the spatial domain, failing to remove a large-scale moire pattern. In this paper, we propose a novel model called FPANet that learns filters in both frequency and spatial domains, improving the restoration quality by removing various sizes of moire patterns. To further enhance, our model takes multiple consecutive frames, learning to extract frame-invariant content features and outputting better quality temporally consistent images. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method with a publicly available large-scale dataset, observing that ours outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches, including ESDNet, VDmoire, MBCNN, WDNet, UNet, and DMCNN, in terms of the image and video quality metrics, such as PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS, FVD, and FSIM.
Robust Sound-Guided Image Manipulation
Aug 31, 2022
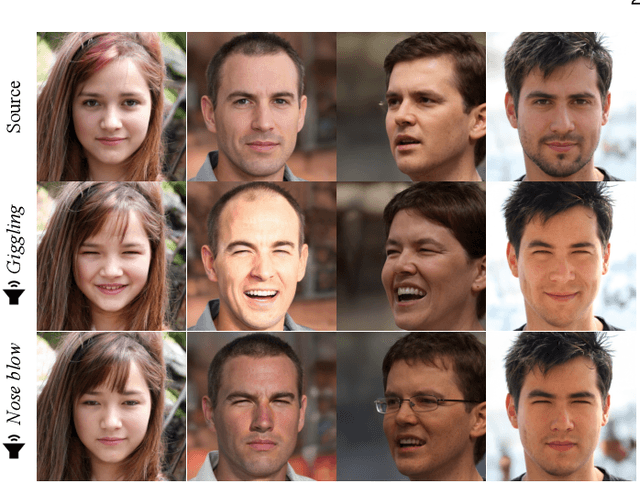
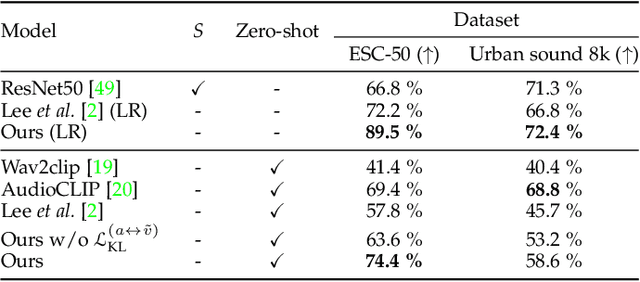


Abstract:Recent successes suggest that an image can be manipulated by a text prompt, e.g., a landscape scene on a sunny day is manipulated into the same scene on a rainy day driven by a text input "raining". These approaches often utilize a StyleCLIP-based image generator, which leverages multi-modal (text and image) embedding space. However, we observe that such text inputs are often bottlenecked in providing and synthesizing rich semantic cues, e.g., differentiating heavy rain from rain with thunderstorms. To address this issue, we advocate leveraging an additional modality, sound, which has notable advantages in image manipulation as it can convey more diverse semantic cues (vivid emotions or dynamic expressions of the natural world) than texts. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that first extends the image-text joint embedding space with sound and applies a direct latent optimization method to manipulate a given image based on audio input, e.g., the sound of rain. Our extensive experiments show that our sound-guided image manipulation approach produces semantically and visually more plausible manipulation results than the state-of-the-art text and sound-guided image manipulation methods, which are further confirmed by our human evaluations. Our downstream task evaluations also show that our learned image-text-sound joint embedding space effectively encodes sound inputs.
Sound-Guided Semantic Video Generation
Apr 21, 2022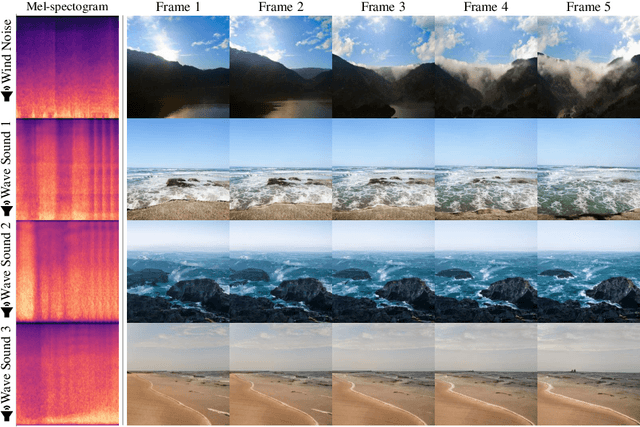
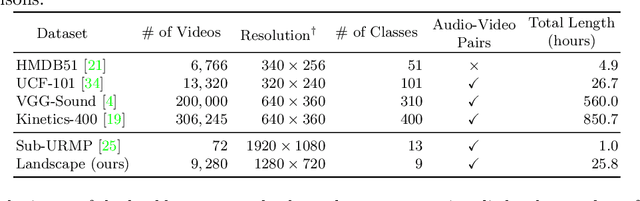
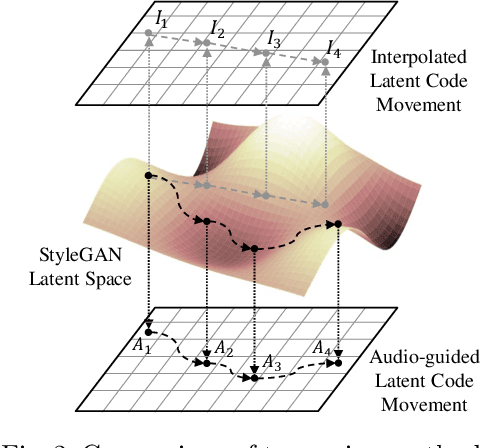

Abstract:The recent success in StyleGAN demonstrates that pre-trained StyleGAN latent space is useful for realistic video generation. However, the generated motion in the video is usually not semantically meaningful due to the difficulty of determining the direction and magnitude in the StyleGAN latent space. In this paper, we propose a framework to generate realistic videos by leveraging multimodal (sound-image-text) embedding space. As sound provides the temporal contexts of the scene, our framework learns to generate a video that is semantically consistent with sound. First, our sound inversion module maps the audio directly into the StyleGAN latent space. We then incorporate the CLIP-based multimodal embedding space to further provide the audio-visual relationships. Finally, the proposed frame generator learns to find the trajectory in the latent space which is coherent with the corresponding sound and generates a video in a hierarchical manner. We provide the new high-resolution landscape video dataset (audio-visual pair) for the sound-guided video generation task. The experiments show that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of video quality. We further show several applications including image and video editing to verify the effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge