Hong Xu
PRISM: Parametrically Refactoring Inference for Speculative Sampling Draft Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs), constrained by their auto-regressive nature, suffer from slow decoding. Speculative decoding methods have emerged as a promising solution to accelerate LLM decoding, attracting attention from both systems and AI research communities. Recently, the pursuit of better draft quality has driven a trend toward parametrically larger draft models, which inevitably introduces substantial computational overhead. While existing work attempts to balance the trade-off between prediction accuracy and compute latency, we address this fundamental dilemma through architectural innovation. We propose PRISM, which disaggregates the computation of each predictive step across different parameter sets, refactoring the computational pathways of draft models to successfully decouple model capacity from inference cost. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that PRISM outperforms all existing draft architectures, achieving exceptional acceptance lengths while maintaining minimal draft latency for superior end-to-end speedup. We also re-examine scaling laws with PRISM, revealing that PRISM scales more effectively with expanding data volumes than other draft architectures. Through rigorous and fair comparison, we show that PRISM boosts the decoding throughput of an already highly optimized inference engine by more than 2.6x.
FOCUS: DLLMs Know How to Tame Their Compute Bound
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (DLLMs) offer a compelling alternative to Auto-Regressive models, but their deployment is constrained by high decoding cost. In this work, we identify a key inefficiency in DLLM decoding: while computation is parallelized over token blocks, only a small subset of tokens is decodable at each diffusion step, causing most compute to be wasted on non-decodable tokens. We further observe a strong correlation between attention-derived token importance and token-wise decoding probability. Based on this insight, we propose FOCUS -- an inference system designed for DLLMs. By dynamically focusing computation on decodable tokens and evicting non-decodable ones on-the-fly, FOCUS increases the effective batch size, alleviating compute limitations and enabling scalable throughput. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that FOCUS achieves up to 3.52$\times$ throughput improvement over the production-grade engine LMDeploy, while preserving or improving generation quality across multiple benchmarks. The FOCUS system is publicly available on GitHub: https://github.com/sands-lab/FOCUS.
SP^2DPO: An LLM-assisted Semantic Per-Pair DPO Generalization
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) controls the trade-off between fitting preference labels and staying close to a reference model using a single global temperature beta, implicitly treating all preference pairs as equally informative. Real-world preference corpora are heterogeneous: they mix high-signal, objective failures (for example, safety, factuality, instruction violations) with low-signal or subjective distinctions (for example, style), and also include label noise. We introduce our method, SP2DPO (Semantic Per-Pair DPO), a generalization that replaces the global temperature with an instance-specific schedule beta_i pre-decided offline from structured semantic-gap annotations (category, magnitude, confidence) produced by teacher language models. We instantiate this procedure on the UltraFeedback preference corpus (59,960 pairs), enabling large-scale construction of an auditable beta_i artifact, and incur zero training-time overhead: the inner-loop optimizer remains standard DPO with beta set per pair. We focus our empirical study on AlpacaEval 2.0, reporting both raw win rate and length-controlled win rate. Across four open-weight, instruction-tuned student backbones (4B-8B), SP2DPO is competitive with a tuned global-beta DPO baseline and improves AlpacaEval 2.0 length-controlled win rate on two of four backbones, while avoiding per-model beta sweeps. All code, annotations, and artifacts will be released.
AGZO: Activation-Guided Zeroth-Order Optimization for LLM Fine-Tuning
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Zeroth-Order (ZO) optimization has emerged as a promising solution for fine-tuning LLMs under strict memory constraints, as it avoids the prohibitive memory cost of storing activations for backpropagation. However, existing ZO methods typically employ isotropic perturbations, neglecting the rich structural information available during the forward pass. In this paper, we identify a crucial link between gradient formation and activation structure: the gradient of a linear layer is confined to the subspace spanned by its input activations. Leveraging this insight, we propose Activation-Guided Zeroth-Order optimization (AGZO). Unlike prior methods, AGZO extracts a compact, activation-informed subspace on the fly during the forward pass and restricts perturbations to this low-rank subspace. We provide a theoretical framework showing that AGZO optimizes a subspace-smoothed objective and provably yields update directions with higher cosine similarity to the true gradient than isotropic baselines. Empirically, we evaluate AGZO on Qwen3 and Pangu models across various benchmarks. AGZO consistently outperforms state-of-the-art ZO baselines and significantly narrows the performance gap with first-order fine-tuning, while maintaining almost the same peak memory footprint as other ZO methods.
The Multi-Query Paradox in Zeroth-Order Optimization
Sep 19, 2025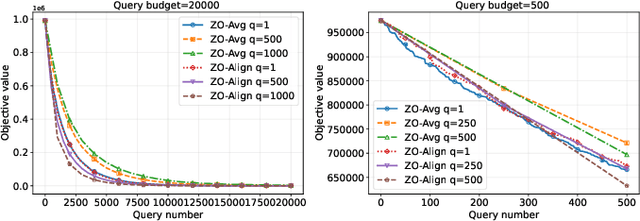
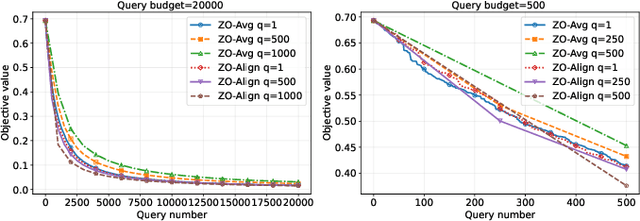
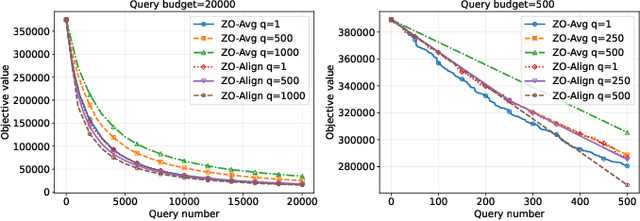
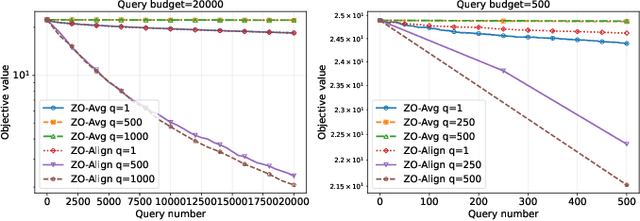
Abstract:Zeroth-order (ZO) optimization provides a powerful framework for problems where explicit gradients are unavailable and have to be approximated using only queries to function value. The prevalent single-query approach is simple, but suffers from high estimation variance, motivating a multi-query paradigm to improves estimation accuracy. This, however, creates a critical trade-off: under a fixed budget of queries (i.e. cost), queries per iteration and the total number of optimization iterations are inversely proportional to one another. How to best allocate this budget is a fundamental, under-explored question. This work systematically resolves this query allocation problem. We analyze two aggregation methods: the de facto simple averaging (ZO-Avg), and a new Projection Alignment method (ZO-Align) we derive from local surrogate minimization. By deriving convergence rates for both methods that make the dependence on the number of queries explicit across strongly convex, convex, non-convex, and stochastic settings, we uncover a stark dichotomy: For ZO-Avg, we prove that using more than one query per iteration is always query-inefficient, rendering the single-query approach optimal. On the contrary, ZO-Align generally performs better with more queries per iteration, resulting in a full-subspace estimation as the optimal approach. Thus, our work clarifies that the multi-query problem boils down to a choice not about an intermediate query size, but between two classic algorithms, a choice dictated entirely by the aggregation method used. These theoretical findings are also consistently validated by extensive experiments.
Multimodal Learning for Fake News Detection in Short Videos Using Linguistically Verified Data and Heterogeneous Modality Fusion
Sep 19, 2025



Abstract:The rapid proliferation of short video platforms has necessitated advanced methods for detecting fake news. This need arises from the widespread influence and ease of sharing misinformation, which can lead to significant societal harm. Current methods often struggle with the dynamic and multimodal nature of short video content. This paper presents HFN, Heterogeneous Fusion Net, a novel multimodal framework that integrates video, audio, and text data to evaluate the authenticity of short video content. HFN introduces a Decision Network that dynamically adjusts modality weights during inference and a Weighted Multi-Modal Feature Fusion module to ensure robust performance even with incomplete data. Additionally, we contribute a comprehensive dataset VESV (VEracity on Short Videos) specifically designed for short video fake news detection. Experiments conducted on the FakeTT and newly collected VESV datasets demonstrate improvements of 2.71% and 4.14% in Marco F1 over state-of-the-art methods. This work establishes a robust solution capable of effectively identifying fake news in the complex landscape of short video platforms, paving the way for more reliable and comprehensive approaches in combating misinformation.
Automating Conflict-Aware ACL Configurations with Natural Language Intents
Aug 25, 2025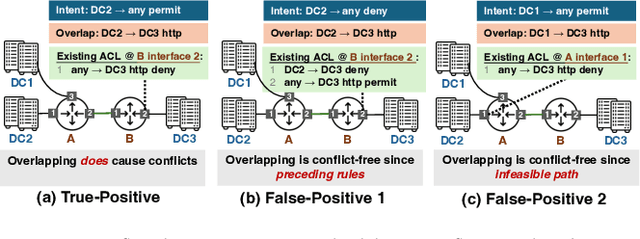
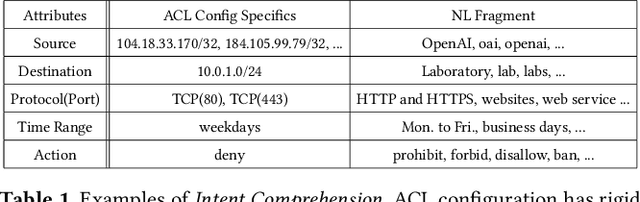
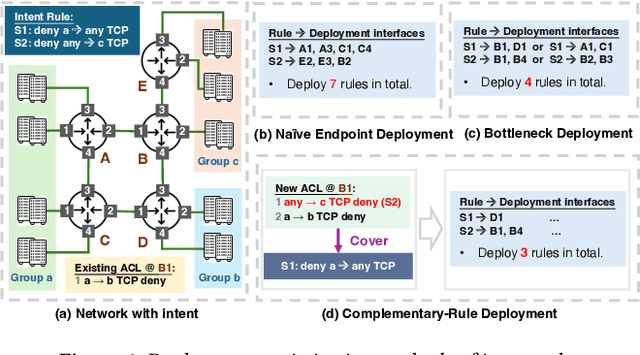
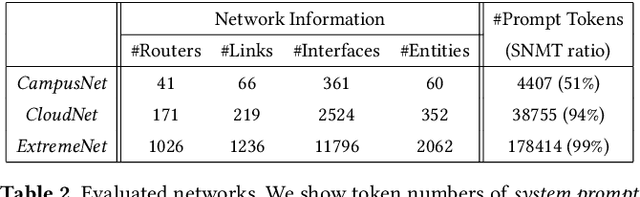
Abstract:ACL configuration is essential for managing network flow reachability, yet its complexity grows significantly with topologies and pre-existing rules. To carry out ACL configuration, the operator needs to (1) understand the new configuration policies or intents and translate them into concrete ACL rules, (2) check and resolve any conflicts between the new and existing rules, and (3) deploy them across the network. Existing systems rely heavily on manual efforts for these tasks, especially for the first two, which are tedious, error-prone, and impractical to scale. We propose Xumi to tackle this problem. Leveraging LLMs with domain knowledge of the target network, Xumi automatically and accurately translates the natural language intents into complete ACL rules to reduce operators' manual efforts. Xumi then detects all potential conflicts between new and existing rules and generates resolved intents for deployment with operators' guidance, and finally identifies the best deployment plan that minimizes the rule additions while satisfying all intents. Evaluation shows that Xumi accelerates the entire configuration pipeline by over 10x compared to current practices, addresses O(100) conflicting ACLs and reduces rule additions by ~40% in modern cloud network.
Adaptive Particle-Based Shape Modeling for Anatomical Surface Correspondence
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Particle-based shape modeling (PSM) is a family of approaches that automatically quantifies shape variability across anatomical cohorts by positioning particles (pseudo landmarks) on shape surfaces in a consistent configuration. Recent advances incorporate implicit radial basis function representations as self-supervised signals to better capture the complex geometric properties of anatomical structures. However, these methods still lack self-adaptivity -- that is, the ability to automatically adjust particle configurations to local geometric features of each surface, which is essential for accurately representing complex anatomical variability. This paper introduces two mechanisms to increase surface adaptivity while maintaining consistent particle configurations: (1) a novel neighborhood correspondence loss to enable high adaptivity and (2) a geodesic correspondence algorithm that regularizes optimization to enforce geodesic neighborhood consistency. We evaluate the efficacy and scalability of our approach on challenging datasets, providing a detailed analysis of the adaptivity-correspondence trade-off and benchmarking against existing methods on surface representation accuracy and correspondence metrics.
DynamicBench: Evaluating Real-Time Report Generation in Large Language Models
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Traditional benchmarks for large language models (LLMs) typically rely on static evaluations through storytelling or opinion expression, which fail to capture the dynamic requirements of real-time information processing in contemporary applications. To address this limitation, we present DynamicBench, a benchmark designed to evaluate the proficiency of LLMs in storing and processing up-to-the-minute data. DynamicBench utilizes a dual-path retrieval pipeline, integrating web searches with local report databases. It necessitates domain-specific knowledge, ensuring accurate responses report generation within specialized fields. By evaluating models in scenarios that either provide or withhold external documents, DynamicBench effectively measures their capability to independently process recent information or leverage contextual enhancements. Additionally, we introduce an advanced report generation system adept at managing dynamic information synthesis. Our experimental results confirm the efficacy of our approach, with our method achieving state-of-the-art performance, surpassing GPT4o in document-free and document-assisted scenarios by 7.0% and 5.8%, respectively. The code and data will be made publicly available.
Towards Robust Learning to Optimize with Theoretical Guarantees
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Learning to optimize (L2O) is an emerging technique to solve mathematical optimization problems with learning-based methods. Although with great success in many real-world scenarios such as wireless communications, computer networks, and electronic design, existing L2O works lack theoretical demonstration of their performance and robustness in out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios. We address this gap by providing comprehensive proofs. First, we prove a sufficient condition for a robust L2O model with homogeneous convergence rates over all In-Distribution (InD) instances. We assume an L2O model achieves robustness for an InD scenario. Based on our proposed methodology of aligning OOD problems to InD problems, we also demonstrate that the L2O model's convergence rate in OOD scenarios will deteriorate by an equation of the L2O model's input features. Moreover, we propose an L2O model with a concise gradient-only feature construction and a novel gradient-based history modeling method. Numerical simulation demonstrates that our proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art baseline in both InD and OOD scenarios and achieves up to 10 $\times$ convergence speedup. The code of our method can be found from https://github.com/NetX-lab/GoMathL2O-Official.
* Published in CVPR 2024, 55 pages, 17 figures, this version fixed some typo
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge