Hebei Li
LLaDA-VLA: Vision Language Diffusion Action Models
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:The rapid progress of auto-regressive vision-language models (VLMs) has inspired growing interest in vision-language-action models (VLA) for robotic manipulation. Recently, masked diffusion models, a paradigm distinct from autoregressive models, have begun to demonstrate competitive performance in text generation and multimodal applications, leading to the development of a series of diffusion-based VLMs (d-VLMs). However, leveraging such models for robot policy learning remains largely unexplored. In this work, we present LLaDA-VLA, the first Vision-Language-Diffusion-Action model built upon pretrained d-VLMs for robotic manipulation. To effectively adapt d-VLMs to robotic domain, we introduce two key designs: (1) a localized special-token classification strategy that replaces full-vocabulary classification with special action token classification, reducing adaptation difficulty; (2) a hierarchical action-structured decoding strategy that decodes action sequences hierarchically considering the dependencies within and across actions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LLaDA-VLA significantly outperforms state-of-the-art VLAs on both simulation and real-world robots.
Create Anything Anywhere: Layout-Controllable Personalized Diffusion Model for Multiple Subjects
May 27, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have significantly advanced text-to-image generation, laying the foundation for the development of personalized generative frameworks. However, existing methods lack precise layout controllability and overlook the potential of dynamic features of reference subjects in improving fidelity. In this work, we propose Layout-Controllable Personalized Diffusion (LCP-Diffusion) model, a novel framework that integrates subject identity preservation with flexible layout guidance in a tuning-free approach. Our model employs a Dynamic-Static Complementary Visual Refining module to comprehensively capture the intricate details of reference subjects, and introduces a Dual Layout Control mechanism to enforce robust spatial control across both training and inference stages. Extensive experiments validate that LCP-Diffusion excels in both identity preservation and layout controllability. To the best of our knowledge, this is a pioneering work enabling users to "create anything anywhere".
Dome-DETR: DETR with Density-Oriented Feature-Query Manipulation for Efficient Tiny Object Detection
May 09, 2025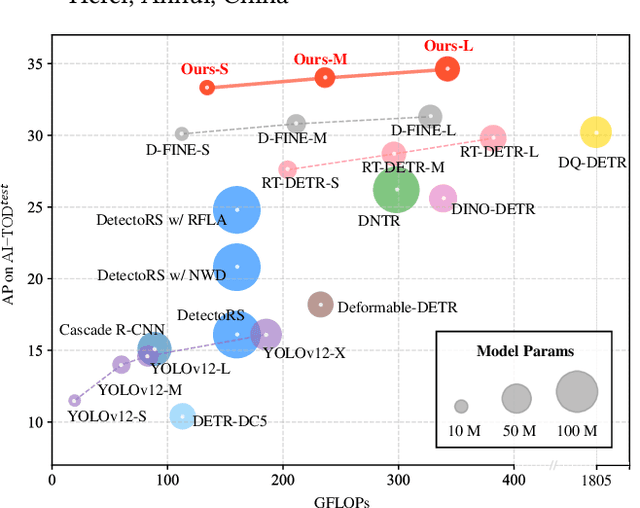
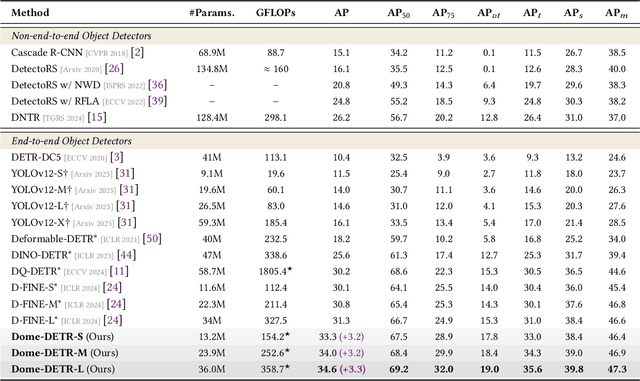
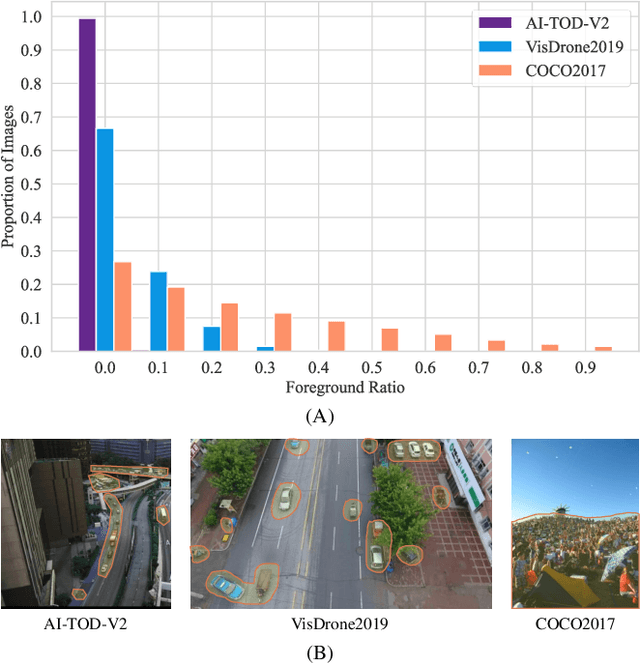
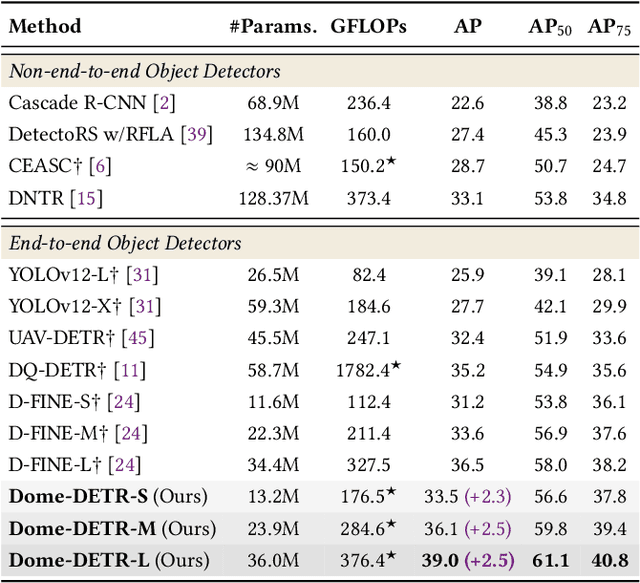
Abstract:Tiny object detection plays a vital role in drone surveillance, remote sensing, and autonomous systems, enabling the identification of small targets across vast landscapes. However, existing methods suffer from inefficient feature leverage and high computational costs due to redundant feature processing and rigid query allocation. To address these challenges, we propose Dome-DETR, a novel framework with Density-Oriented Feature-Query Manipulation for Efficient Tiny Object Detection. To reduce feature redundancies, we introduce a lightweight Density-Focal Extractor (DeFE) to produce clustered compact foreground masks. Leveraging these masks, we incorporate Masked Window Attention Sparsification (MWAS) to focus computational resources on the most informative regions via sparse attention. Besides, we propose Progressive Adaptive Query Initialization (PAQI), which adaptively modulates query density across spatial areas for better query allocation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Dome-DETR achieves state-of-the-art performance (+3.3 AP on AI-TOD-V2 and +2.5 AP on VisDrone) while maintaining low computational complexity and a compact model size. Code will be released upon acceptance.
Efficient Spiking Point Mamba for Point Cloud Analysis
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:Bio-inspired Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) provide an energy-efficient way to extract 3D spatio-temporal features. However, existing 3D SNNs have struggled with long-range dependencies until the recent emergence of Mamba, which offers superior computational efficiency and sequence modeling capability. In this work, we propose Spiking Point Mamba (SPM), the first Mamba-based SNN in the 3D domain. Due to the poor performance of simply transferring Mamba to 3D SNNs, SPM is designed to utilize both the sequence modeling capabilities of Mamba and the temporal feature extraction of SNNs. Specifically, we first introduce Hierarchical Dynamic Encoding (HDE), an improved direct encoding method that effectively introduces dynamic temporal mechanism, thereby facilitating temporal interactions. Then, we propose a Spiking Mamba Block (SMB), which builds upon Mamba while learning inter-time-step features and minimizing information loss caused by spikes. Finally, to further enhance model performance, we adopt an asymmetric SNN-ANN architecture for spike-based pre-training and finetune. Compared with the previous state-of-the-art SNN models, SPM improves OA by +6.2%, +6.1%, and +7.4% on three variants of ScanObjectNN, and boosts instance mIOU by +1.9% on ShapeNetPart. Meanwhile, its energy consumption is at least 3.5x lower than that of its ANN counterpart. The code will be made publicly available.
COSMIC: Clique-Oriented Semantic Multi-space Integration for Robust CLIP Test-Time Adaptation
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:Recent vision-language models (VLMs) face significant challenges in test-time adaptation to novel domains. While cache-based methods show promise by leveraging historical information, they struggle with both caching unreliable feature-label pairs and indiscriminately using single-class information during querying, significantly compromising adaptation accuracy. To address these limitations, we propose COSMIC (Clique-Oriented Semantic Multi-space Integration for CLIP), a robust test-time adaptation framework that enhances adaptability through multi-granular, cross-modal semantic caching and graph-based querying mechanisms. Our framework introduces two key innovations: Dual Semantics Graph (DSG) and Clique Guided Hyper-class (CGH). The Dual Semantics Graph constructs complementary semantic spaces by incorporating textual features, coarse-grained CLIP features, and fine-grained DINOv2 features to capture rich semantic relationships. Building upon these dual graphs, the Clique Guided Hyper-class component leverages structured class relationships to enhance prediction robustness through correlated class selection. Extensive experiments demonstrate COSMIC's superior performance across multiple benchmarks, achieving significant improvements over state-of-the-art methods: 15.81% gain on out-of-distribution tasks and 5.33% on cross-domain generation with CLIP RN-50. Code is available at github.com/hf618/COSMIC.
Spiking Point Transformer for Point Cloud Classification
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) offer an attractive and energy-efficient alternative to conventional Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) due to their sparse binary activation. When SNN meets Transformer, it shows great potential in 2D image processing. However, their application for 3D point cloud remains underexplored. To this end, we present Spiking Point Transformer (SPT), the first transformer-based SNN framework for point cloud classification. Specifically, we first design Queue-Driven Sampling Direct Encoding for point cloud to reduce computational costs while retaining the most effective support points at each time step. We introduce the Hybrid Dynamics Integrate-and-Fire Neuron (HD-IF), designed to simulate selective neuron activation and reduce over-reliance on specific artificial neurons. SPT attains state-of-the-art results on three benchmark datasets that span both real-world and synthetic datasets in the SNN domain. Meanwhile, the theoretical energy consumption of SPT is at least 6.4$\times$ less than its ANN counterpart.
D-FINE: Redefine Regression Task in DETRs as Fine-grained Distribution Refinement
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:We introduce D-FINE, a powerful real-time object detector that achieves outstanding localization precision by redefining the bounding box regression task in DETR models. D-FINE comprises two key components: Fine-grained Distribution Refinement (FDR) and Global Optimal Localization Self-Distillation (GO-LSD). FDR transforms the regression process from predicting fixed coordinates to iteratively refining probability distributions, providing a fine-grained intermediate representation that significantly enhances localization accuracy. GO-LSD is a bidirectional optimization strategy that transfers localization knowledge from refined distributions to shallower layers through self-distillation, while also simplifying the residual prediction tasks for deeper layers. Additionally, D-FINE incorporates lightweight optimizations in computationally intensive modules and operations, achieving a better balance between speed and accuracy. Specifically, D-FINE-L / X achieves 54.0% / 55.8% AP on the COCO dataset at 124 / 78 FPS on an NVIDIA T4 GPU. When pretrained on Objects365, D-FINE-L / X attains 57.1% / 59.3% AP, surpassing all existing real-time detectors. Furthermore, our method significantly enhances the performance of a wide range of DETR models by up to 5.3% AP with negligible extra parameters and training costs. Our code and pretrained models: https://github.com/Peterande/D-FINE.
EE-MLLM: A Data-Efficient and Compute-Efficient Multimodal Large Language Model
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:In the realm of multimodal research, numerous studies leverage substantial image-text pairs to conduct modal alignment learning, transforming Large Language Models (LLMs) into Multimodal LLMs and excelling in a variety of visual-language tasks. The prevailing methodologies primarily fall into two categories: self-attention-based and cross-attention-based methods. While self-attention-based methods offer superior data efficiency due to their simple MLP architecture, they often suffer from lower computational efficiency due to concatenating visual and textual tokens as input for LLM. Conversely, cross-attention-based methods, although less data-efficient due to additional learnable parameters, exhibit higher computational efficiency by avoiding long sequence input for LLM. To address these trade-offs, we introduce the Data-Efficient and Compute-Efficient Multimodal Large Language Model (EE-MLLM). Without introducing additional modules or learnable parameters, EE-MLLM achieves both data and compute efficiency. Specifically, we modify the original self-attention mechanism in MLLM to a composite attention mechanism. This mechanism has two key characteristics: 1) Eliminating the computational overhead of self-attention within visual tokens to achieve compute efficiency, and 2) Reusing the weights on each layer of LLM to facilitate effective modality alignment between vision and language for data efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of EE-MLLM across a range of benchmarks, including general-purpose datasets like MMBench and SeedBench, as well as fine-grained tasks such as TextVQA and DocVQA.
Scene Adaptive Sparse Transformer for Event-based Object Detection
Apr 02, 2024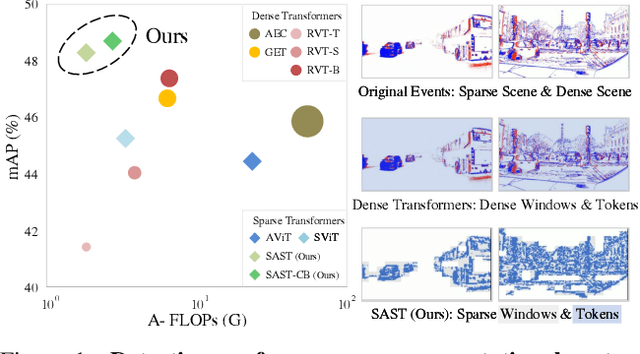
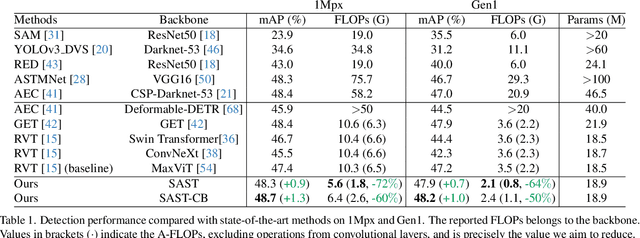
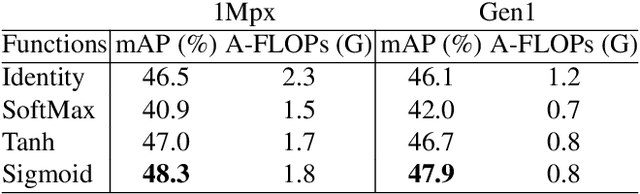
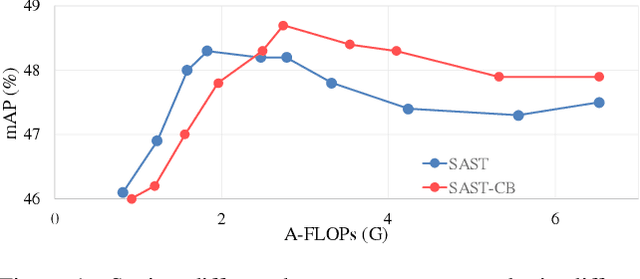
Abstract:While recent Transformer-based approaches have shown impressive performances on event-based object detection tasks, their high computational costs still diminish the low power consumption advantage of event cameras. Image-based works attempt to reduce these costs by introducing sparse Transformers. However, they display inadequate sparsity and adaptability when applied to event-based object detection, since these approaches cannot balance the fine granularity of token-level sparsification and the efficiency of window-based Transformers, leading to reduced performance and efficiency. Furthermore, they lack scene-specific sparsity optimization, resulting in information loss and a lower recall rate. To overcome these limitations, we propose the Scene Adaptive Sparse Transformer (SAST). SAST enables window-token co-sparsification, significantly enhancing fault tolerance and reducing computational overhead. Leveraging the innovative scoring and selection modules, along with the Masked Sparse Window Self-Attention, SAST showcases remarkable scene-aware adaptability: It focuses only on important objects and dynamically optimizes sparsity level according to scene complexity, maintaining a remarkable balance between performance and computational cost. The evaluation results show that SAST outperforms all other dense and sparse networks in both performance and efficiency on two large-scale event-based object detection datasets (1Mpx and Gen1). Code: https://github.com/Peterande/SAST
Event-assisted Low-Light Video Object Segmentation
Apr 02, 2024Abstract:In the realm of video object segmentation (VOS), the challenge of operating under low-light conditions persists, resulting in notably degraded image quality and compromised accuracy when comparing query and memory frames for similarity computation. Event cameras, characterized by their high dynamic range and ability to capture motion information of objects, offer promise in enhancing object visibility and aiding VOS methods under such low-light conditions. This paper introduces a pioneering framework tailored for low-light VOS, leveraging event camera data to elevate segmentation accuracy. Our approach hinges on two pivotal components: the Adaptive Cross-Modal Fusion (ACMF) module, aimed at extracting pertinent features while fusing image and event modalities to mitigate noise interference, and the Event-Guided Memory Matching (EGMM) module, designed to rectify the issue of inaccurate matching prevalent in low-light settings. Additionally, we present the creation of a synthetic LLE-DAVIS dataset and the curation of a real-world LLE-VOS dataset, encompassing frames and events. Experimental evaluations corroborate the efficacy of our method across both datasets, affirming its effectiveness in low-light scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge