Haozhe Zhang
Learning by Imagining: Debiased Feature Augmentation for Compositional Zero-Shot Learning
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Compositional Zero-Shot Learning (CZSL) aims to recognize unseen attribute-object compositions by learning prior knowledge of seen primitives, \textit{i.e.}, attributes and objects. Learning generalizable compositional representations in CZSL remains challenging due to the entangled nature of attributes and objects as well as the prevalence of long-tailed distributions in real-world data. Inspired by neuroscientific findings that imagination and perception share similar neural processes, we propose a novel approach called Debiased Feature Augmentation (DeFA) to address these challenges. The proposed DeFA integrates a disentangle-and-reconstruct framework for feature augmentation with a debiasing strategy. DeFA explicitly leverages the prior knowledge of seen attributes and objects by synthesizing high-fidelity composition features to support compositional generalization. Extensive experiments on three widely used datasets demonstrate that DeFA achieves state-of-the-art performance in both \textit{closed-world} and \textit{open-world} settings.
Reasoning Language Models for Root Cause Analysis in 5G Wireless Networks
Jul 29, 2025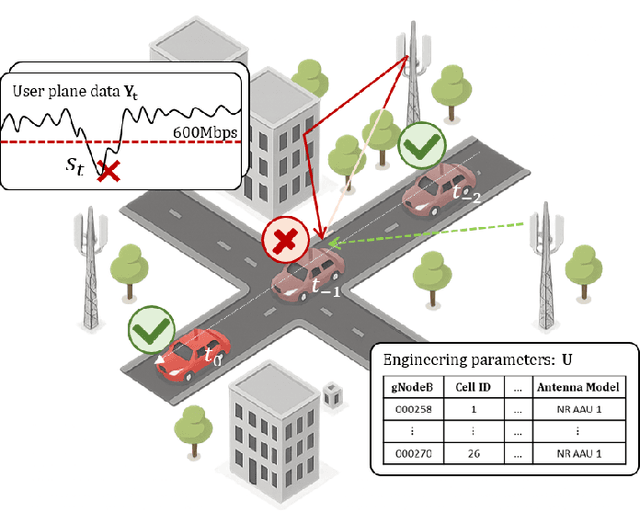
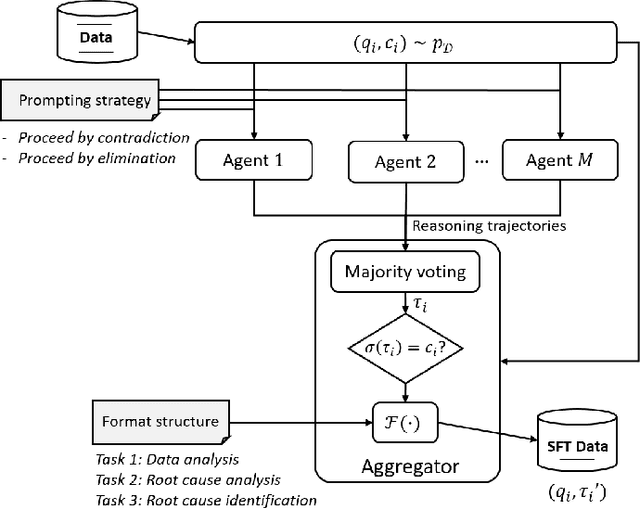
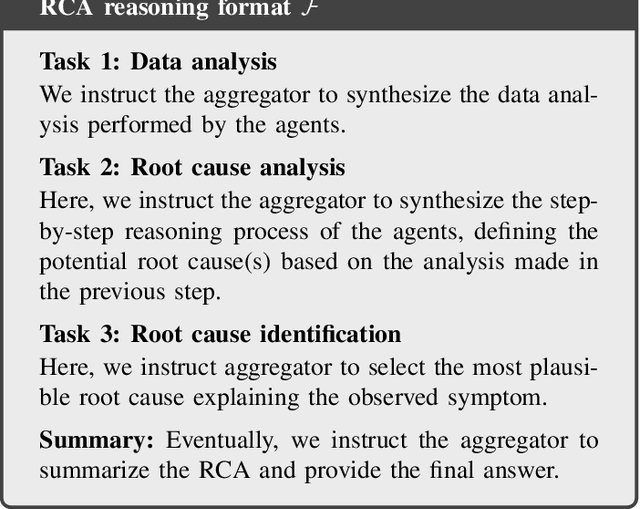
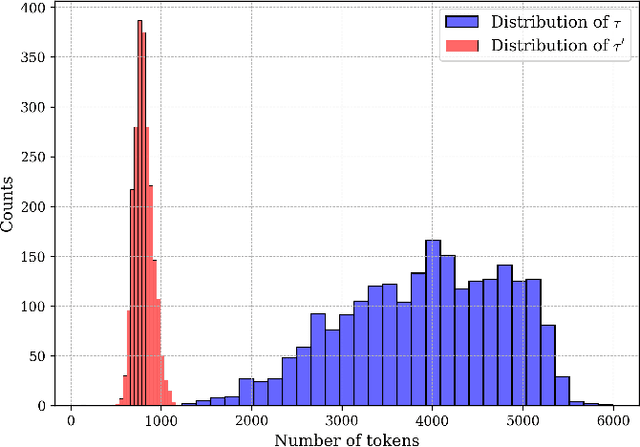
Abstract:Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in mobile networks remains a challenging task due to the need for interpretability, domain expertise, and causal reasoning. In this work, we propose a lightweight framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) for RCA. To do so, we introduce TeleLogs, a curated dataset of annotated troubleshooting problems designed to benchmark RCA capabilities. Our evaluation reveals that existing open-source reasoning LLMs struggle with these problems, underscoring the need for domain-specific adaptation. To address this issue, we propose a two-stage training methodology that combines supervised fine-tuning with reinforcement learning to improve the accuracy and reasoning quality of LLMs. The proposed approach fine-tunes a series of RCA models to integrate domain knowledge and generate structured, multi-step diagnostic explanations, improving both interpretability and effectiveness. Extensive experiments across multiple LLM sizes show significant performance gains over state-of-the-art reasoning and non-reasoning models, including strong generalization to randomized test variants. These results demonstrate the promise of domain-adapted, reasoning-enhanced LLMs for practical and explainable RCA in network operation and management.
MiniMax-Speech: Intrinsic Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech with a Learnable Speaker Encoder
May 12, 2025Abstract:We introduce MiniMax-Speech, an autoregressive Transformer-based Text-to-Speech (TTS) model that generates high-quality speech. A key innovation is our learnable speaker encoder, which extracts timbre features from a reference audio without requiring its transcription. This enables MiniMax-Speech to produce highly expressive speech with timbre consistent with the reference in a zero-shot manner, while also supporting one-shot voice cloning with exceptionally high similarity to the reference voice. In addition, the overall quality of the synthesized audio is enhanced through the proposed Flow-VAE. Our model supports 32 languages and demonstrates excellent performance across multiple objective and subjective evaluations metrics. Notably, it achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on objective voice cloning metrics (Word Error Rate and Speaker Similarity) and has secured the top position on the public TTS Arena leaderboard. Another key strength of MiniMax-Speech, granted by the robust and disentangled representations from the speaker encoder, is its extensibility without modifying the base model, enabling various applications such as: arbitrary voice emotion control via LoRA; text to voice (T2V) by synthesizing timbre features directly from text description; and professional voice cloning (PVC) by fine-tuning timbre features with additional data. We encourage readers to visit https://minimax-ai.github.io/tts_tech_report for more examples.
MMT-Bench: A Comprehensive Multimodal Benchmark for Evaluating Large Vision-Language Models Towards Multitask AGI
Apr 24, 2024



Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) show significant strides in general-purpose multimodal applications such as visual dialogue and embodied navigation. However, existing multimodal evaluation benchmarks cover a limited number of multimodal tasks testing rudimentary capabilities, falling short in tracking LVLM development. In this study, we present MMT-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark designed to assess LVLMs across massive multimodal tasks requiring expert knowledge and deliberate visual recognition, localization, reasoning, and planning. MMT-Bench comprises $31,325$ meticulously curated multi-choice visual questions from various multimodal scenarios such as vehicle driving and embodied navigation, covering $32$ core meta-tasks and $162$ subtasks in multimodal understanding. Due to its extensive task coverage, MMT-Bench enables the evaluation of LVLMs using a task map, facilitating the discovery of in- and out-of-domain tasks. Evaluation results involving $30$ LVLMs such as the proprietary GPT-4V, GeminiProVision, and open-sourced InternVL-Chat, underscore the significant challenges posed by MMT-Bench. We anticipate that MMT-Bench will inspire the community to develop next-generation multimodal foundation models aimed at achieving general-purpose multimodal intelligence.
Building Bilingual and Code-Switched Voice Conversion with Limited Training Data Using Embedding Consistency Loss
Apr 22, 2021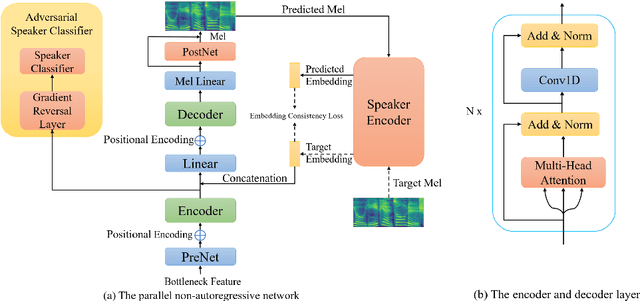
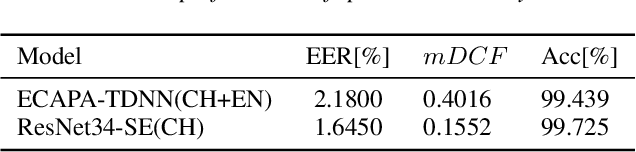
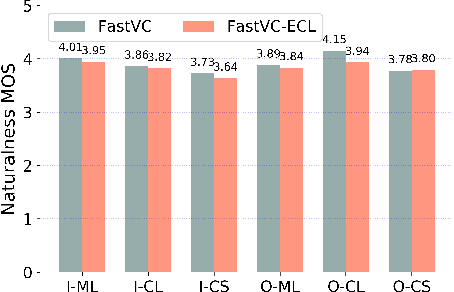
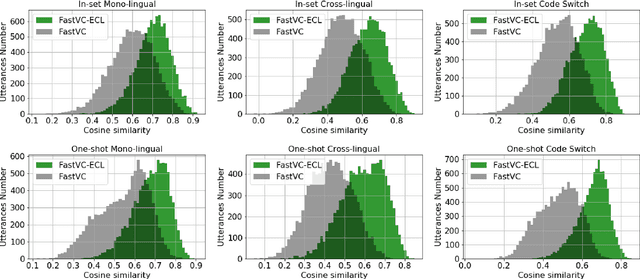
Abstract:Building cross-lingual voice conversion (VC) systems for multiple speakers and multiple languages has been a challenging task for a long time. This paper describes a parallel non-autoregressive network to achieve bilingual and code-switched voice conversion for multiple speakers when there are only mono-lingual corpora for each language. We achieve cross-lingual VC between Mandarin speech with multiple speakers and English speech with multiple speakers by applying bilingual bottleneck features. To boost voice cloning performance, we use an adversarial speaker classifier with a gradient reversal layer to reduce the source speaker's information from the output of encoder. Furthermore, in order to improve speaker similarity between reference speech and converted speech, we adopt an embedding consistency loss between the synthesized speech and its natural reference speech in our network. Experimental results show that our proposed method can achieve high quality converted speech with mean opinion score (MOS) around 4. The conversion system performs well in terms of speaker similarity for both in-set speaker conversion and out-set-of one-shot conversion.
Regression-Enhanced Random Forests
Apr 23, 2019


Abstract:Random forest (RF) methodology is one of the most popular machine learning techniques for prediction problems. In this article, we discuss some cases where random forests may suffer and propose a novel generalized RF method, namely regression-enhanced random forests (RERFs), that can improve on RFs by borrowing the strength of penalized parametric regression. The algorithm for constructing RERFs and selecting its tuning parameters is described. Both simulation study and real data examples show that RERFs have better predictive performance than RFs in important situations often encountered in practice. Moreover, RERFs may incorporate known relationships between the response and the predictors, and may give reliable predictions in extrapolation problems where predictions are required at points out of the domain of the training dataset. Strategies analogous to those described here can be used to improve other machine learning methods via combination with penalized parametric regression techniques.
* 12 pages, 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge