Haozhe Chen
Twin-2K-500: A dataset for building digital twins of over 2,000 people based on their answers to over 500 questions
May 23, 2025Abstract:LLM-based digital twin simulation, where large language models are used to emulate individual human behavior, holds great promise for research in AI, social science, and digital experimentation. However, progress in this area has been hindered by the scarcity of real, individual-level datasets that are both large and publicly available. This lack of high-quality ground truth limits both the development and validation of digital twin methodologies. To address this gap, we introduce a large-scale, public dataset designed to capture a rich and holistic view of individual human behavior. We survey a representative sample of $N = 2,058$ participants (average 2.42 hours per person) in the US across four waves with 500 questions in total, covering a comprehensive battery of demographic, psychological, economic, personality, and cognitive measures, as well as replications of behavioral economics experiments and a pricing survey. The final wave repeats tasks from earlier waves to establish a test-retest accuracy baseline. Initial analyses suggest the data are of high quality and show promise for constructing digital twins that predict human behavior well at the individual and aggregate levels. By making the full dataset publicly available, we aim to establish a valuable testbed for the development and benchmarking of LLM-based persona simulations. Beyond LLM applications, due to its unique breadth and scale the dataset also enables broad social science research, including studies of cross-construct correlations and heterogeneous treatment effects.
RoboVerse: Towards a Unified Platform, Dataset and Benchmark for Scalable and Generalizable Robot Learning
Apr 26, 2025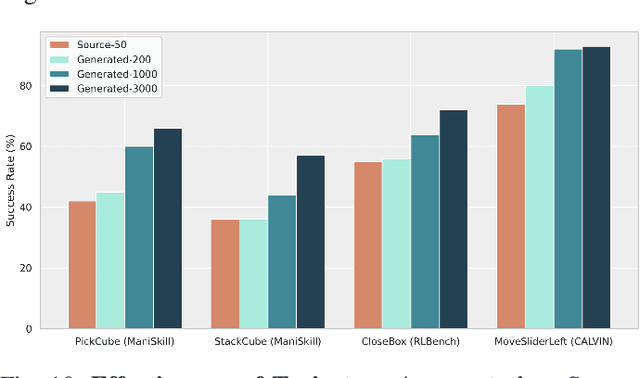
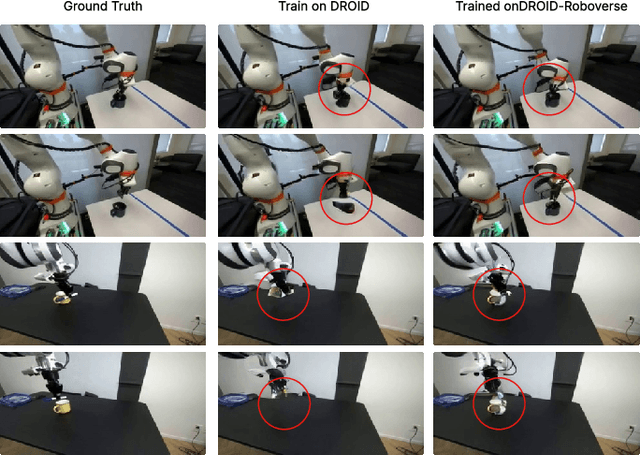

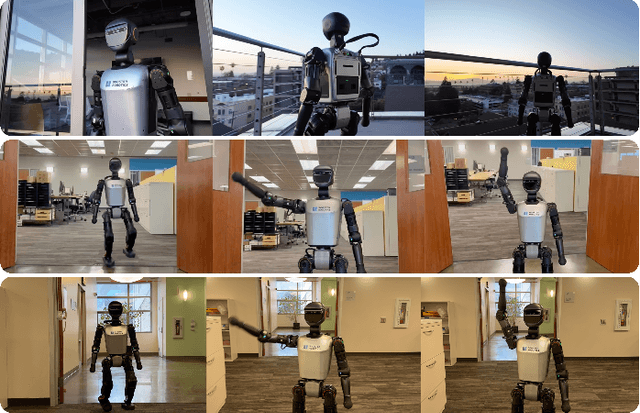
Abstract:Data scaling and standardized evaluation benchmarks have driven significant advances in natural language processing and computer vision. However, robotics faces unique challenges in scaling data and establishing evaluation protocols. Collecting real-world data is resource-intensive and inefficient, while benchmarking in real-world scenarios remains highly complex. Synthetic data and simulation offer promising alternatives, yet existing efforts often fall short in data quality, diversity, and benchmark standardization. To address these challenges, we introduce RoboVerse, a comprehensive framework comprising a simulation platform, a synthetic dataset, and unified benchmarks. Our simulation platform supports multiple simulators and robotic embodiments, enabling seamless transitions between different environments. The synthetic dataset, featuring high-fidelity physics and photorealistic rendering, is constructed through multiple approaches. Additionally, we propose unified benchmarks for imitation learning and reinforcement learning, enabling evaluation across different levels of generalization. At the core of the simulation platform is MetaSim, an infrastructure that abstracts diverse simulation environments into a universal interface. It restructures existing simulation environments into a simulator-agnostic configuration system, as well as an API aligning different simulator functionalities, such as launching simulation environments, loading assets with initial states, stepping the physics engine, etc. This abstraction ensures interoperability and extensibility. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that RoboVerse enhances the performance of imitation learning, reinforcement learning, world model learning, and sim-to-real transfer. These results validate the reliability of our dataset and benchmarks, establishing RoboVerse as a robust solution for advancing robot learning.
Data Mixture Optimization: A Multi-fidelity Multi-scale Bayesian Framework
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Careful curation of data sources can significantly improve the performance of LLM pre-training, but predominant approaches rely heavily on intuition or costly trial-and-error, making them difficult to generalize across different data domains and downstream tasks. Although scaling laws can provide a principled and general approach for data curation, standard deterministic extrapolation from small-scale experiments to larger scales requires strong assumptions on the reliability of such extrapolation, whose brittleness has been highlighted in prior works. In this paper, we introduce a $\textit{probabilistic extrapolation framework}$ for data mixture optimization that avoids rigid assumptions and explicitly models the uncertainty in performance across decision variables. We formulate data curation as a sequential decision-making problem$\unicode{x2013}$multi-fidelity, multi-scale Bayesian optimization$\unicode{x2013}$where $\{$data mixtures, model scale, training steps$\}$ are adaptively selected to balance training cost and potential information gain. Our framework naturally gives rise to algorithm prototypes that leverage noisy information from inexpensive experiments to systematically inform costly training decisions. To accelerate methodological progress, we build a simulator based on 472 language model pre-training runs with varying data compositions from the SlimPajama dataset. We observe that even simple kernels and acquisition functions can enable principled decisions across training models from 20M to 1B parameters and achieve $\textbf{2.6x}$ and $\textbf{3.3x}$ speedups compared to multi-fidelity BO and random search baselines. Taken together, our framework underscores potential efficiency gains achievable by developing principled and transferable data mixture optimization methods.
LLM Generated Persona is a Promise with a Catch
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:The use of large language models (LLMs) to simulate human behavior has gained significant attention, particularly through personas that approximate individual characteristics. Persona-based simulations hold promise for transforming disciplines that rely on population-level feedback, including social science, economic analysis, marketing research, and business operations. Traditional methods to collect realistic persona data face significant challenges. They are prohibitively expensive and logistically challenging due to privacy constraints, and often fail to capture multi-dimensional attributes, particularly subjective qualities. Consequently, synthetic persona generation with LLMs offers a scalable, cost-effective alternative. However, current approaches rely on ad hoc and heuristic generation techniques that do not guarantee methodological rigor or simulation precision, resulting in systematic biases in downstream tasks. Through extensive large-scale experiments including presidential election forecasts and general opinion surveys of the U.S. population, we reveal that these biases can lead to significant deviations from real-world outcomes. Our findings underscore the need to develop a rigorous science of persona generation and outline the methodological innovations, organizational and institutional support, and empirical foundations required to enhance the reliability and scalability of LLM-driven persona simulations. To support further research and development in this area, we have open-sourced approximately one million generated personas, available for public access and analysis at https://huggingface.co/datasets/Tianyi-Lab/Personas.
DiT4Edit: Diffusion Transformer for Image Editing
Nov 05, 2024
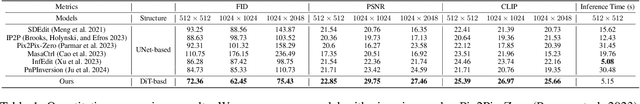
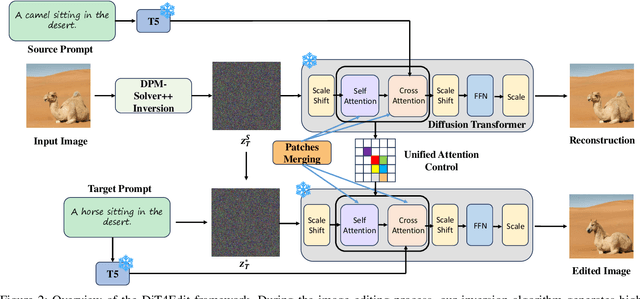
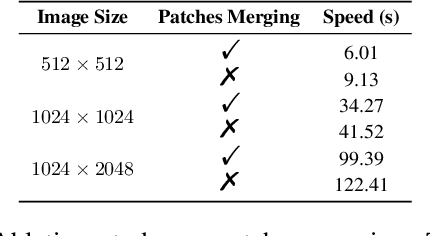
Abstract:Despite recent advances in UNet-based image editing, methods for shape-aware object editing in high-resolution images are still lacking. Compared to UNet, Diffusion Transformers (DiT) demonstrate superior capabilities to effectively capture the long-range dependencies among patches, leading to higher-quality image generation. In this paper, we propose DiT4Edit, the first Diffusion Transformer-based image editing framework. Specifically, DiT4Edit uses the DPM-Solver inversion algorithm to obtain the inverted latents, reducing the number of steps compared to the DDIM inversion algorithm commonly used in UNet-based frameworks. Additionally, we design unified attention control and patches merging, tailored for transformer computation streams. This integration allows our framework to generate higher-quality edited images faster. Our design leverages the advantages of DiT, enabling it to surpass UNet structures in image editing, especially in high-resolution and arbitrary-size images. Extensive experiments demonstrate the strong performance of DiT4Edit across various editing scenarios, highlighting the potential of Diffusion Transformers in supporting image editing.
QGym: Scalable Simulation and Benchmarking of Queuing Network Controllers
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:Queuing network control determines the allocation of scarce resources to manage congestion, a fundamental problem in manufacturing, communications, and healthcare. Compared to standard RL problems, queueing problems are distinguished by unique challenges: i) a system operating in continuous time, ii) high stochasticity, and iii) long horizons over which the system can become unstable (exploding delays). To spur methodological progress tackling these challenges, we present an open-sourced queueing simulation framework, QGym, that benchmark queueing policies across realistic problem instances. Our modular framework allows the researchers to build on our initial instances, which provide a wide range of environments including parallel servers, criss-cross, tandem, and re-entrant networks, as well as a realistically calibrated hospital queuing system. QGym makes it easy to compare multiple policies, including both model-free RL methods and classical queuing policies. Our testbed complements the traditional focus on evaluating algorithms based on mathematical guarantees in idealized settings, and significantly expands the scope of empirical benchmarking in prior work. QGym code is open-sourced at https://github.com/namkoong-lab/QGym.
Noisy Data Visualization using Functional Data Analysis
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:Data visualization via dimensionality reduction is an important tool in exploratory data analysis. However, when the data are noisy, many existing methods fail to capture the underlying structure of the data. The method called Empirical Intrinsic Geometry (EIG) was previously proposed for performing dimensionality reduction on high dimensional dynamical processes while theoretically eliminating all noise. However, implementing EIG in practice requires the construction of high-dimensional histograms, which suffer from the curse of dimensionality. Here we propose a new data visualization method called Functional Information Geometry (FIG) for dynamical processes that adapts the EIG framework while using approaches from functional data analysis to mitigate the curse of dimensionality. We experimentally demonstrate that the resulting method outperforms a variant of EIG designed for visualization in terms of capturing the true structure, hyperparameter robustness, and computational speed. We then use our method to visualize EEG brain measurements of sleep activity.
SelfIE: Self-Interpretation of Large Language Model Embeddings
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:How do large language models (LLMs) obtain their answers? The ability to explain and control an LLM's reasoning process is key for reliability, transparency, and future model developments. We propose SelfIE (Self-Interpretation of Embeddings), a framework that enables LLMs to interpret their own embeddings in natural language by leveraging their ability to respond to inquiries about a given passage. Capable of interpreting open-world concepts in the hidden embeddings, SelfIE reveals LLM internal reasoning in cases such as making ethical decisions, internalizing prompt injection, and recalling harmful knowledge. SelfIE's text descriptions on hidden embeddings also open up new avenues to control LLM reasoning. We propose Supervised Control, which allows editing open-ended concepts while only requiring gradient computation of individual layer. We extend RLHF to hidden embeddings and propose Reinforcement Control that erases harmful knowledge in LLM without supervision targets.
Interpreting and Controlling Vision Foundation Models via Text Explanations
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:Large-scale pre-trained vision foundation models, such as CLIP, have become de facto backbones for various vision tasks. However, due to their black-box nature, understanding the underlying rules behind these models' predictions and controlling model behaviors have remained open challenges. We present a framework for interpreting vision transformer's latent tokens with natural language. Given a latent token, our framework retains its semantic information to the final layer using transformer's local operations and retrieves the closest text for explanation. Our approach enables understanding of model visual reasoning procedure without needing additional model training or data collection. Based on the obtained interpretations, our framework allows for model editing that controls model reasoning behaviors and improves model robustness against biases and spurious correlations.
Speech Pattern based Black-box Model Watermarking for Automatic Speech Recognition
Oct 19, 2021



Abstract:As an effective method for intellectual property (IP) protection, model watermarking technology has been applied on a wide variety of deep neural networks (DNN), including speech classification models. However, how to design a black-box watermarking scheme for automatic speech recognition (ASR) models is still an unsolved problem, which is a significant demand for protecting remote ASR Application Programming Interface (API) deployed in cloud servers. Due to conditional independence assumption and label-detection-based evasion attack risk of ASR models, the black-box model watermarking scheme for speech classification models cannot apply to ASR models. In this paper, we propose the first black-box model watermarking framework for protecting the IP of ASR models. Specifically, we synthesize trigger audios by spreading the speech clips of model owners over the entire input audios and labeling the trigger audios with the stego texts, which hides the authorship information with linguistic steganography. Experiments on the state-of-the-art open-source ASR system DeepSpeech demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed watermarking scheme, which is robust against five kinds of attacks and has little impact on accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge