Gustav Markkula
Institute for Transport Studies, University of Leeds, Leeds LS2 9JT, UK
Realistic adversarial scenario generation via human-like pedestrian model for autonomous vehicle control parameter optimisation
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are rapidly advancing and are expected to play a central role in future mobility. Ensuring their safe deployment requires reliable interaction with other road users, not least pedestrians. Direct testing on public roads is costly and unsafe for rare but critical interactions, making simulation a practical alternative. Within simulation-based testing, adversarial scenarios are widely used to probe safety limits, but many prioritise difficulty over realism, producing exaggerated behaviours which may result in AV controllers that are overly conservative. We propose an alternative method, instead using a cognitively inspired pedestrian model featuring both inter-individual and intra-individual variability to generate behaviourally plausible adversarial scenarios. We provide a proof of concept demonstration of this method's potential for AV control optimisation, in closed-loop testing and tuning of an AV controller. Our results show that replacing the rule-based CARLA pedestrian with the human-like model yields more realistic gap acceptance patterns and smoother vehicle decelerations. Unsafe interactions occur only for certain pedestrian individuals and conditions, underscoring the importance of human variability in AV testing. Adversarial scenarios generated by this model can be used to optimise AV control towards safer and more efficient behaviour. Overall, this work illustrates how incorporating human-like road user models into simulation-based adversarial testing can enhance the credibility of AV evaluation and provide a practical basis to behaviourally informed controller optimisation.
Realistic pedestrian-driver interaction modelling using multi-agent RL with human perceptual-motor constraints
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Modelling pedestrian-driver interactions is critical for understanding human road user behaviour and developing safe autonomous vehicle systems. Existing approaches often rely on rule-based logic, game-theoretic models, or 'black-box' machine learning methods. However, these models typically lack flexibility or overlook the underlying mechanisms, such as sensory and motor constraints, which shape how pedestrians and drivers perceive and act in interactive scenarios. In this study, we propose a multi-agent reinforcement learning (RL) framework that integrates both visual and motor constraints of pedestrian and driver agents. Using a real-world dataset from an unsignalised pedestrian crossing, we evaluate four model variants, one without constraints, two with either motor or visual constraints, and one with both, across behavioural metrics of interaction realism. Results show that the combined model with both visual and motor constraints performs best. Motor constraints lead to smoother movements that resemble human speed adjustments during crossing interactions. The addition of visual constraints introduces perceptual uncertainty and field-of-view limitations, leading the agents to exhibit more cautious and variable behaviour, such as less abrupt deceleration. In this data-limited setting, our model outperforms a supervised behavioural cloning model, demonstrating that our approach can be effective without large training datasets. Finally, our framework accounts for individual differences by modelling parameters controlling the human constraints as population-level distributions, a perspective that has not been explored in previous work on pedestrian-vehicle interaction modelling. Overall, our work demonstrates that multi-agent RL with human constraints is a promising modelling approach for simulating realistic road user interactions.
Automated Brake Onset Detection in Naturalistic Driving Data
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Response timing measures play a crucial role in the assessment of automated driving systems (ADS) in collision avoidance scenarios, including but not limited to establishing human benchmarks and comparing ADS to human driver response performance. For example, measuring the response time (of a human driver or ADS) to a conflict requires the determination of a stimulus onset and a response onset. In existing studies, response onset relies on manual annotation or vehicle control signals such as accelerator and brake pedal movements. These methods are not applicable when analyzing large scale data where vehicle control signals are not available. This holds in particular for the rapidly expanding sets of ADS log data where the behavior of surrounding road users is observed via onboard sensors. To advance evaluation techniques for ADS and enable measuring response timing when vehicle control signals are not available, we developed a simple and efficient algorithm, based on a piecewise linear acceleration model, to automatically estimate brake onset that can be applied to any type of driving data that includes vehicle longitudinal time series data. We also proposed a manual annotation method to identify brake onset and used it as ground truth for validation. R2 was used as a confidence metric to measure the accuracy of the algorithm, and its classification performance was analyzed using naturalistic collision avoidance data of both ADS and humans, where our method was validated against human manual annotation. Although our algorithm is subject to certain limitations, it is efficient, generalizable, applicable to any road user and scenario types, and is highly configurable.
WeatherEdit: Controllable Weather Editing with 4D Gaussian Field
May 26, 2025Abstract:In this work, we present WeatherEdit, a novel weather editing pipeline for generating realistic weather effects with controllable types and severity in 3D scenes. Our approach is structured into two key components: weather background editing and weather particle construction. For weather background editing, we introduce an all-in-one adapter that integrates multiple weather styles into a single pretrained diffusion model, enabling the generation of diverse weather effects in 2D image backgrounds. During inference, we design a Temporal-View (TV-) attention mechanism that follows a specific order to aggregate temporal and spatial information, ensuring consistent editing across multi-frame and multi-view images. To construct the weather particles, we first reconstruct a 3D scene using the edited images and then introduce a dynamic 4D Gaussian field to generate snowflakes, raindrops and fog in the scene. The attributes and dynamics of these particles are precisely controlled through physical-based modelling and simulation, ensuring realistic weather representation and flexible severity adjustments. Finally, we integrate the 4D Gaussian field with the 3D scene to render consistent and highly realistic weather effects. Experiments on multiple driving datasets demonstrate that WeatherEdit can generate diverse weather effects with controllable condition severity, highlighting its potential for autonomous driving simulation in adverse weather. See project page: https://jumponthemoon.github.io/w-edit
WeatherGS: 3D Scene Reconstruction in Adverse Weather Conditions via Gaussian Splatting
Dec 25, 2024



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has gained significant attention for 3D scene reconstruction, but still suffers from complex outdoor environments, especially under adverse weather. This is because 3DGS treats the artifacts caused by adverse weather as part of the scene and will directly reconstruct them, largely reducing the clarity of the reconstructed scene. To address this challenge, we propose WeatherGS, a 3DGS-based framework for reconstructing clear scenes from multi-view images under different weather conditions. Specifically, we explicitly categorize the multi-weather artifacts into the dense particles and lens occlusions that have very different characters, in which the former are caused by snowflakes and raindrops in the air, and the latter are raised by the precipitation on the camera lens. In light of this, we propose a dense-to-sparse preprocess strategy, which sequentially removes the dense particles by an Atmospheric Effect Filter (AEF) and then extracts the relatively sparse occlusion masks with a Lens Effect Detector (LED). Finally, we train a set of 3D Gaussians by the processed images and generated masks for excluding occluded areas, and accurately recover the underlying clear scene by Gaussian splatting. We conduct a diverse and challenging benchmark to facilitate the evaluation of 3D reconstruction under complex weather scenarios. Extensive experiments on this benchmark demonstrate that our WeatherGS consistently produces high-quality, clean scenes across various weather scenarios, outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods. See project page:https://jumponthemoon.github.io/weather-gs.
Pedestrian crossing decisions can be explained by bounded optimal decision-making under noisy visual perception
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a model of pedestrian crossing decisions, based on the theory of computational rationality. It is assumed that crossing decisions are boundedly optimal, with bounds on optimality arising from human cognitive limitations. While previous models of pedestrian behaviour have been either 'black-box' machine learning models or mechanistic models with explicit assumptions about cognitive factors, we combine both approaches. Specifically, we model mechanistically noisy human visual perception and assumed rewards in crossing, but we use reinforcement learning to learn bounded optimal behaviour policy. The model reproduces a larger number of known empirical phenomena than previous models, in particular: (1) the effect of the time to arrival of an approaching vehicle on whether the pedestrian accepts the gap, the effect of the vehicle's speed on both (2) gap acceptance and (3) pedestrian timing of crossing in front of yielding vehicles, and (4) the effect on this crossing timing of the stopping distance of the yielding vehicle. Notably, our findings suggest that behaviours previously framed as 'biases' in decision-making, such as speed-dependent gap acceptance, might instead be a product of rational adaptation to the constraints of visual perception. Our approach also permits fitting the parameters of cognitive constraints and rewards per individual, to better account for individual differences. To conclude, by leveraging both RL and mechanistic modelling, our model offers novel insights about pedestrian behaviour, and may provide a useful foundation for more accurate and scalable pedestrian models.
Using Models Based on Cognitive Theory to Predict Human Behavior in Traffic: A Case Study
May 24, 2023Abstract:The development of automated vehicles has the potential to revolutionize transportation, but they are currently unable to ensure a safe and time-efficient driving style. Reliable models predicting human behavior are essential for overcoming this issue. While data-driven models are commonly used to this end, they can be vulnerable in safety-critical edge cases. This has led to an interest in models incorporating cognitive theory, but as such models are commonly developed for explanatory purposes, this approach's effectiveness in behavior prediction has remained largely untested so far. In this article, we investigate the usefulness of the \emph{Commotions} model -- a novel cognitively plausible model incorporating the latest theories of human perception, decision-making, and motor control -- for predicting human behavior in gap acceptance scenarios, which entail many important traffic interactions such as lane changes and intersections. We show that this model can compete with or even outperform well-established data-driven prediction models across several naturalistic datasets. These results demonstrate the promise of incorporating cognitive theory in behavior prediction models for automated vehicles.
Cross or Wait? Predicting Pedestrian Interaction Outcomes at Unsignalized Crossings
Apr 17, 2023



Abstract:Predicting pedestrian behavior when interacting with vehicles is one of the most critical challenges in the field of automated driving. Pedestrian crossing behavior is influenced by various interaction factors, including time to arrival, pedestrian waiting time, the presence of zebra crossing, and the properties and personality traits of both pedestrians and drivers. However, these factors have not been fully explored for use in predicting interaction outcomes. In this paper, we use machine learning to predict pedestrian crossing behavior including pedestrian crossing decision, crossing initiation time (CIT), and crossing duration (CD) when interacting with vehicles at unsignalized crossings. Distributed simulator data are utilized for predicting and analyzing the interaction factors. Compared with the logistic regression baseline model, our proposed neural network model improves the prediction accuracy and F1 score by 4.46% and 3.23%, respectively. Our model also reduces the root mean squared error (RMSE) for CIT and CD by 21.56% and 30.14% compared with the linear regression model. Additionally, we have analyzed the importance of interaction factors, and present the results of models using fewer factors. This provides information for model selection in different scenarios with limited input features.
An active inference model of car following: Advantages and applications
Mar 27, 2023Abstract:Driver process models play a central role in the testing, verification, and development of automated and autonomous vehicle technologies. Prior models developed from control theory and physics-based rules are limited in automated vehicle applications due to their restricted behavioral repertoire. Data-driven machine learning models are more capable than rule-based models but are limited by the need for large training datasets and their lack of interpretability, i.e., an understandable link between input data and output behaviors. We propose a novel car following modeling approach using active inference, which has comparable behavioral flexibility to data-driven models while maintaining interpretability. We assessed the proposed model, the Active Inference Driving Agent (AIDA), through a benchmark analysis against the rule-based Intelligent Driver Model, and two neural network Behavior Cloning models. The models were trained and tested on a real-world driving dataset using a consistent process. The testing results showed that the AIDA predicted driving controls significantly better than the rule-based Intelligent Driver Model and had similar accuracy to the data-driven neural network models in three out of four evaluations. Subsequent interpretability analyses illustrated that the AIDA's learned distributions were consistent with driver behavior theory and that visualizations of the distributions could be used to directly comprehend the model's decision making process and correct model errors attributable to limited training data. The results indicate that the AIDA is a promising alternative to black-box data-driven models and suggest a need for further research focused on modeling driving style and model training with more diverse datasets.
Modeling human road crossing decisions as reward maximization with visual perception limitations
Jan 27, 2023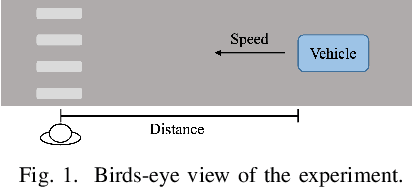
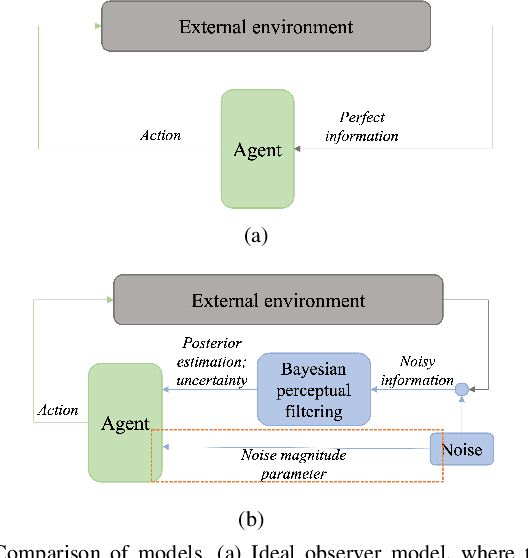
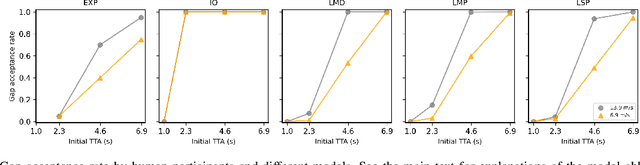
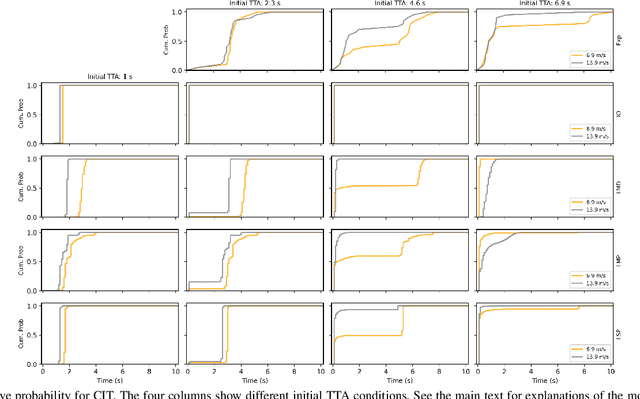
Abstract:Understanding the interaction between different road users is critical for road safety and automated vehicles (AVs). Existing mathematical models on this topic have been proposed based mostly on either cognitive or machine learning (ML) approaches. However, current cognitive models are incapable of simulating road user trajectories in general scenarios, and ML models lack a focus on the mechanisms generating the behavior and take a high-level perspective which can cause failures to capture important human-like behaviors. Here, we develop a model of human pedestrian crossing decisions based on computational rationality, an approach using deep reinforcement learning (RL) to learn boundedly optimal behavior policies given human constraints, in our case a model of the limited human visual system. We show that the proposed combined cognitive-RL model captures human-like patterns of gap acceptance and crossing initiation time. Interestingly, our model's decisions are sensitive to not only the time gap, but also the speed of the approaching vehicle, something which has been described as a "bias" in human gap acceptance behavior. However, our results suggest that this is instead a rational adaption to human perceptual limitations. Moreover, we demonstrate an approach to accounting for individual differences in computational rationality models, by conditioning the RL policy on the parameters of the human constraints. Our results demonstrate the feasibility of generating more human-like road user behavior by combining RL with cognitive models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge