Chengliang Dai
Understanding Dataset Bias in Medical Imaging: A Case Study on Chest X-rays
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Recent work has revisited the infamous task Name that dataset and established that in non-medical datasets, there is an underlying bias and achieved high Accuracies on the dataset origin task. In this work, we revisit the same task applied to popular open-source chest X-ray datasets. Medical images are naturally more difficult to release for open-source due to their sensitive nature, which has led to certain open-source datasets being extremely popular for research purposes. By performing the same task, we wish to explore whether dataset bias also exists in these datasets. % We deliberately try to increase the difficulty of the task by dataset transformations. We apply simple transformations of the datasets to try to identify bias. Given the importance of AI applications in medical imaging, it's vital to establish whether modern methods are taking shortcuts or are focused on the relevant pathology. We implement a range of different network architectures on the datasets: NIH, CheXpert, MIMIC-CXR and PadChest. We hope this work will encourage more explainable research being performed in medical imaging and the creation of more open-source datasets in the medical domain. The corresponding code will be released upon acceptance.
The Extreme Cardiac MRI Analysis Challenge under Respiratory Motion (CMRxMotion)
Oct 12, 2022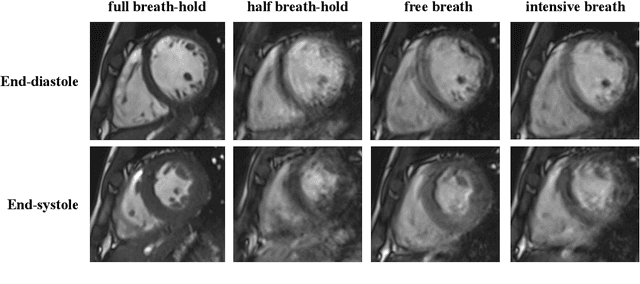
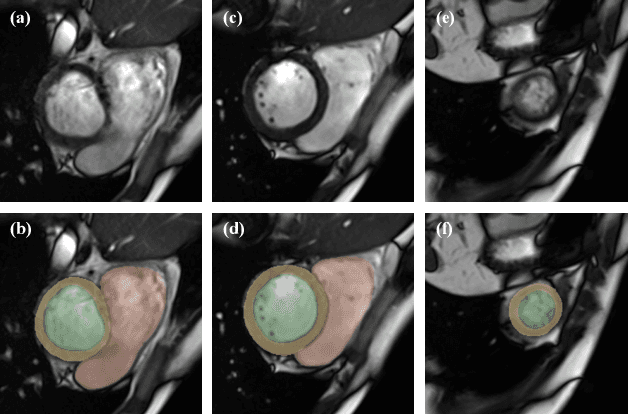

Abstract:The quality of cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging is susceptible to respiratory motion artifacts. The model robustness of automated segmentation techniques in face of real-world respiratory motion artifacts is unclear. This manuscript describes the design of extreme cardiac MRI analysis challenge under respiratory motion (CMRxMotion Challenge). The challenge aims to establish a public benchmark dataset to assess the effects of respiratory motion on image quality and examine the robustness of segmentation models. The challenge recruited 40 healthy volunteers to perform different breath-hold behaviors during one imaging visit, obtaining paired cine imaging with artifacts. Radiologists assessed the image quality and annotated the level of respiratory motion artifacts. For those images with diagnostic quality, radiologists further segmented the left ventricle, left ventricle myocardium and right ventricle. The images of training set (20 volunteers) along with the annotations are released to the challenge participants, to develop an automated image quality assessment model (Task 1) and an automated segmentation model (Task 2). The images of validation set (5 volunteers) are released to the challenge participants but the annotations are withheld for online evaluation of submitted predictions. Both the images and annotations of the test set (15 volunteers) were withheld and only used for offline evaluation of submitted containerized dockers. The image quality assessment task is quantitatively evaluated by the Cohen's kappa statistics and the segmentation task is evaluated by the Dice scores and Hausdorff distances.
Suggestive Annotation of Brain MR Images with Gradient-guided Sampling
Jun 02, 2022



Abstract:Machine learning has been widely adopted for medical image analysis in recent years given its promising performance in image segmentation and classification tasks. The success of machine learning, in particular supervised learning, depends on the availability of manually annotated datasets. For medical imaging applications, such annotated datasets are not easy to acquire, it takes a substantial amount of time and resource to curate an annotated medical image set. In this paper, we propose an efficient annotation framework for brain MR images that can suggest informative sample images for human experts to annotate. We evaluate the framework on two different brain image analysis tasks, namely brain tumour segmentation and whole brain segmentation. Experiments show that for brain tumour segmentation task on the BraTS 2019 dataset, training a segmentation model with only 7% suggestively annotated image samples can achieve a performance comparable to that of training on the full dataset. For whole brain segmentation on the MALC dataset, training with 42% suggestively annotated image samples can achieve a comparable performance to training on the full dataset. The proposed framework demonstrates a promising way to save manual annotation cost and improve data efficiency in medical imaging applications.
QU-BraTS: MICCAI BraTS 2020 Challenge on Quantifying Uncertainty in Brain Tumor Segmentation -- Analysis of Ranking Metrics and Benchmarking Results
Dec 19, 2021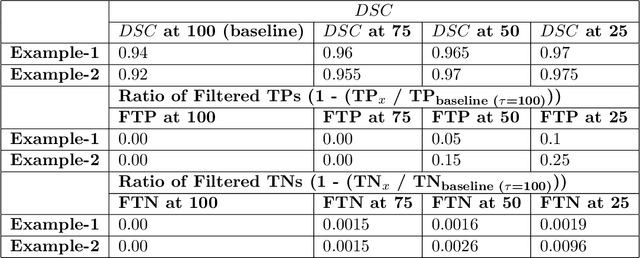
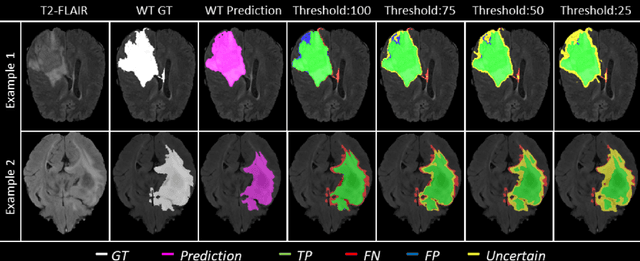
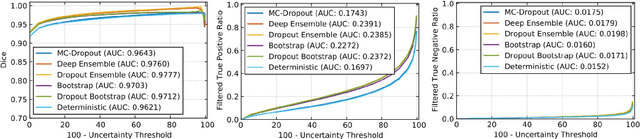
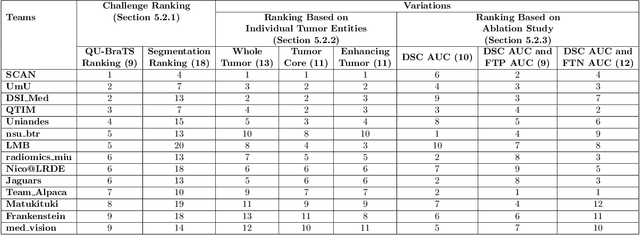
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) models have provided the state-of-the-art performance in a wide variety of medical imaging benchmarking challenges, including the Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) challenges. However, the task of focal pathology multi-compartment segmentation (e.g., tumor and lesion sub-regions) is particularly challenging, and potential errors hinder the translation of DL models into clinical workflows. Quantifying the reliability of DL model predictions in the form of uncertainties, could enable clinical review of the most uncertain regions, thereby building trust and paving the way towards clinical translation. Recently, a number of uncertainty estimation methods have been introduced for DL medical image segmentation tasks. Developing metrics to evaluate and compare the performance of uncertainty measures will assist the end-user in making more informed decisions. In this study, we explore and evaluate a metric developed during the BraTS 2019-2020 task on uncertainty quantification (QU-BraTS), and designed to assess and rank uncertainty estimates for brain tumor multi-compartment segmentation. This metric (1) rewards uncertainty estimates that produce high confidence in correct assertions, and those that assign low confidence levels at incorrect assertions, and (2) penalizes uncertainty measures that lead to a higher percentages of under-confident correct assertions. We further benchmark the segmentation uncertainties generated by 14 independent participating teams of QU-BraTS 2020, all of which also participated in the main BraTS segmentation task. Overall, our findings confirm the importance and complementary value that uncertainty estimates provide to segmentation algorithms, and hence highlight the need for uncertainty quantification in medical image analyses. Our evaluation code is made publicly available at https://github.com/RagMeh11/QU-BraTS.
Suggestive Annotation of Brain Tumour Images with Gradient-guided Sampling
Jul 03, 2020



Abstract:Machine learning has been widely adopted for medical image analysis in recent years given its promising performance in image segmentation and classification tasks. As a data-driven science, the success of machine learning, in particular supervised learning, largely depends on the availability of manually annotated datasets. For medical imaging applications, such annotated datasets are not easy to acquire. It takes a substantial amount of time and resource to curate an annotated medical image set. In this paper, we propose an efficient annotation framework for brain tumour images that is able to suggest informative sample images for human experts to annotate. Our experiments show that training a segmentation model with only 19% suggestively annotated patient scans from BraTS 2019 dataset can achieve a comparable performance to training a model on the full dataset for whole tumour segmentation task. It demonstrates a promising way to save manual annotation cost and improve data efficiency in medical imaging applications.
Deep Generative Model-based Quality Control for Cardiac MRI Segmentation
Jun 23, 2020



Abstract:In recent years, convolutional neural networks have demonstrated promising performance in a variety of medical image segmentation tasks. However, when a trained segmentation model is deployed into the real clinical world, the model may not perform optimally. A major challenge is the potential poor-quality segmentations generated due to degraded image quality or domain shift issues. There is a timely need to develop an automated quality control method that can detect poor segmentations and feedback to clinicians. Here we propose a novel deep generative model-based framework for quality control of cardiac MRI segmentation. It first learns a manifold of good-quality image-segmentation pairs using a generative model. The quality of a given test segmentation is then assessed by evaluating the difference from its projection onto the good-quality manifold. In particular, the projection is refined through iterative search in the latent space. The proposed method achieves high prediction accuracy on two publicly available cardiac MRI datasets. Moreover, it shows better generalisation ability than traditional regression-based methods. Our approach provides a real-time and model-agnostic quality control for cardiac MRI segmentation, which has the potential to be integrated into clinical image analysis workflows.
Efficient Deep Representation Learning by Adaptive Latent Space Sampling
Apr 12, 2020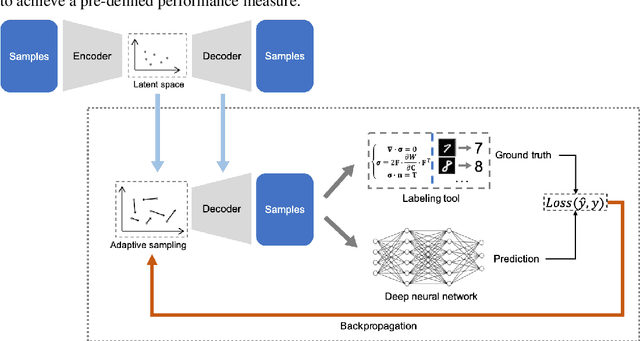
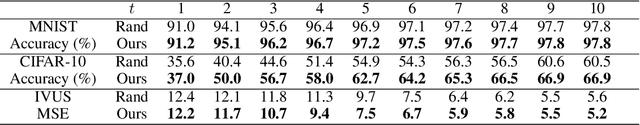
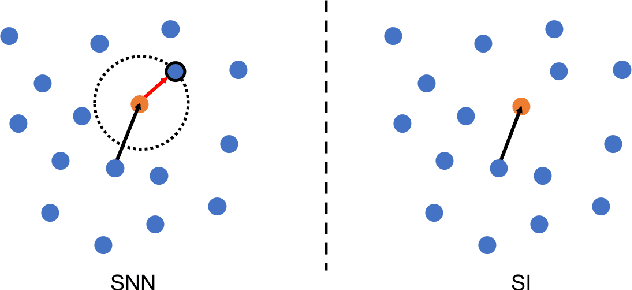
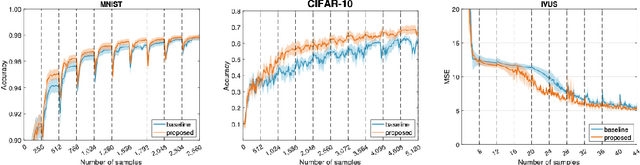
Abstract:Supervised deep learning requires a large amount of training samples with annotations (e.g. label class for classification task, pixel- or voxel-wised label map for segmentation tasks), which are expensive and time-consuming to obtain. During the training of a deep neural network, the annotated samples are fed into the network in a mini-batch way, where they are often regarded of equal importance. However, some of the samples may become less informative during training, as the magnitude of the gradient start to vanish for these samples. In the meantime, other samples of higher utility or hardness may be more demanded for the training process to proceed and require more exploitation. To address the challenges of expensive annotations and loss of sample informativeness, here we propose a novel training framework which adaptively selects informative samples that are fed to the training process. The adaptive selection or sampling is performed based on a hardness-aware strategy in the latent space constructed by a generative model. To evaluate the proposed training framework, we perform experiments on three different datasets, including MNIST and CIFAR-10 for image classification task and a medical image dataset IVUS for biophysical simulation task. On all three datasets, the proposed framework outperforms a random sampling method, which demonstrates the effectiveness of proposed framework.
Automatic Brain Tumour Segmentation and Biophysics-Guided Survival Prediction
Nov 19, 2019



Abstract:Gliomas are the most common malignant brain tumourswith intrinsic heterogeneity. Accurate segmentation of gliomas and theirsub-regions on multi-parametric magnetic resonance images (mpMRI)is of great clinical importance, which defines tumour size, shape andappearance and provides abundant information for preoperative diag-nosis, treatment planning and survival prediction. Recent developmentson deep learning have significantly improved the performance of auto-mated medical image segmentation. In this paper, we compare severalstate-of-the-art convolutional neural network models for brain tumourimage segmentation. Based on the ensembled segmentation, we presenta biophysics-guided prognostic model for patient overall survival predic-tion which outperforms a data-driven radiomics approach. Our methodwon the second place of the MICCAI 2019 BraTS Challenge for theoverall survival prediction.
Unsupervised Annotation of Phenotypic Abnormalities via Semantic Latent Representations on Electronic Health Records
Nov 10, 2019



Abstract:The extraction of phenotype information which is naturally contained in electronic health records (EHRs) has been found to be useful in various clinical informatics applications such as disease diagnosis. However, due to imprecise descriptions, lack of gold standards and the demand for efficiency, annotating phenotypic abnormalities on millions of EHR narratives is still challenging. In this work, we propose a novel unsupervised deep learning framework to annotate the phenotypic abnormalities from EHRs via semantic latent representations. The proposed framework takes the advantage of Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO), which is a knowledge base of phenotypic abnormalities, to standardize the annotation results. Experiments have been conducted on 52,722 EHRs from MIMIC-III dataset. Quantitative and qualitative analysis have shown the proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art annotation performance and computational efficiency compared with other methods.
Transfer Learning from Partial Annotations for Whole Brain Segmentation
Aug 28, 2019



Abstract:Brain MR image segmentation is a key task in neuroimaging studies. It is commonly conducted using standard computational tools, such as FSL, SPM, multi-atlas segmentation etc, which are often registration-based and suffer from expensive computation cost. Recently, there is an increased interest using deep neural networks for brain image segmentation, which have demonstrated advantages in both speed and performance. However, neural networks-based approaches normally require a large amount of manual annotations for optimising the massive amount of network parameters. For 3D networks used in volumetric image segmentation, this has become a particular challenge, as a 3D network consists of many more parameters compared to its 2D counterpart. Manual annotation of 3D brain images is extremely time-consuming and requires extensive involvement of trained experts. To address the challenge with limited manual annotations, here we propose a novel multi-task learning framework for brain image segmentation, which utilises a large amount of automatically generated partial annotations together with a small set of manually created full annotations for network training. Our method yields a high performance comparable to state-of-the-art methods for whole brain segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge