Michael Rebsamen
QU-BraTS: MICCAI BraTS 2020 Challenge on Quantifying Uncertainty in Brain Tumor Segmentation -- Analysis of Ranking Metrics and Benchmarking Results
Dec 19, 2021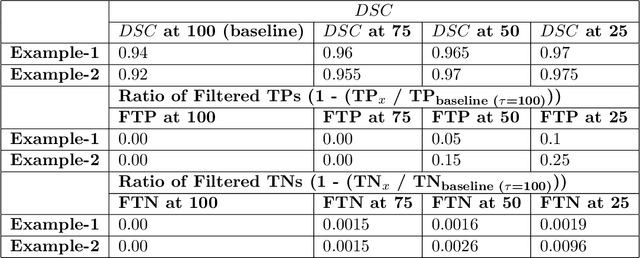
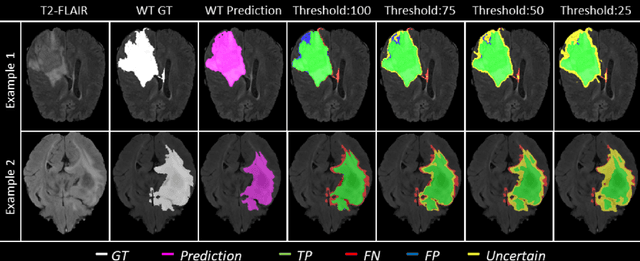
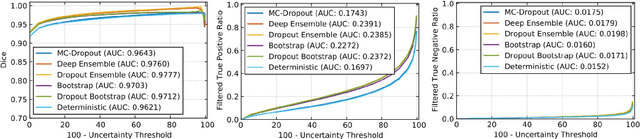
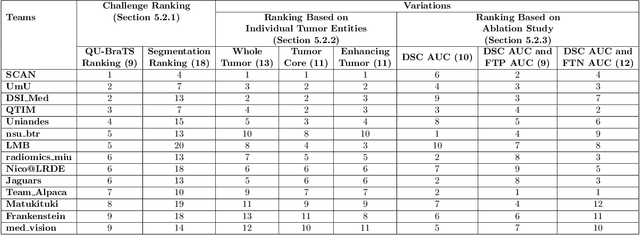
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) models have provided the state-of-the-art performance in a wide variety of medical imaging benchmarking challenges, including the Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) challenges. However, the task of focal pathology multi-compartment segmentation (e.g., tumor and lesion sub-regions) is particularly challenging, and potential errors hinder the translation of DL models into clinical workflows. Quantifying the reliability of DL model predictions in the form of uncertainties, could enable clinical review of the most uncertain regions, thereby building trust and paving the way towards clinical translation. Recently, a number of uncertainty estimation methods have been introduced for DL medical image segmentation tasks. Developing metrics to evaluate and compare the performance of uncertainty measures will assist the end-user in making more informed decisions. In this study, we explore and evaluate a metric developed during the BraTS 2019-2020 task on uncertainty quantification (QU-BraTS), and designed to assess and rank uncertainty estimates for brain tumor multi-compartment segmentation. This metric (1) rewards uncertainty estimates that produce high confidence in correct assertions, and those that assign low confidence levels at incorrect assertions, and (2) penalizes uncertainty measures that lead to a higher percentages of under-confident correct assertions. We further benchmark the segmentation uncertainties generated by 14 independent participating teams of QU-BraTS 2020, all of which also participated in the main BraTS segmentation task. Overall, our findings confirm the importance and complementary value that uncertainty estimates provide to segmentation algorithms, and hence highlight the need for uncertainty quantification in medical image analyses. Our evaluation code is made publicly available at https://github.com/RagMeh11/QU-BraTS.
Few-shot brain segmentation from weakly labeled data with deep heteroscedastic multi-task networks
Apr 04, 2019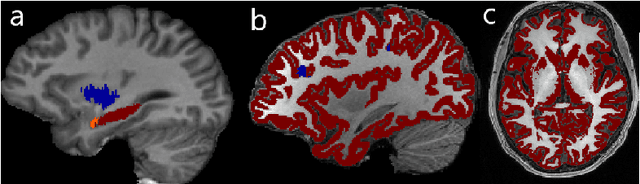
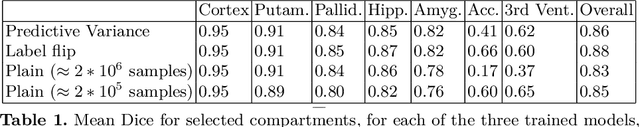
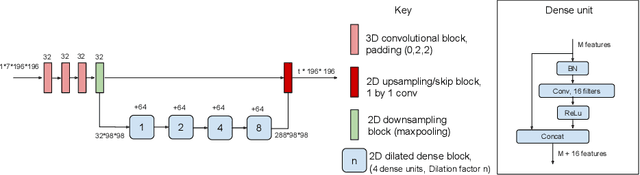
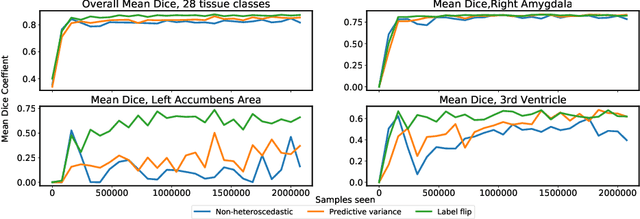
Abstract:In applications of supervised learning applied to medical image segmentation, the need for large amounts of labeled data typically goes unquestioned. In particular, in the case of brain anatomy segmentation, hundreds or thousands of weakly-labeled volumes are often used as training data. In this paper, we first observe that for many brain structures, a small number of training examples, (n=9), weakly labeled using Freesurfer 6.0, plus simple data augmentation, suffice as training data to achieve high performance, achieving an overall mean Dice coefficient of $0.84 \pm 0.12$ compared to Freesurfer over 28 brain structures in T1-weighted images of $\approx 4000$ 9-10 year-olds from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development study. We then examine two varieties of heteroscedastic network as a method for improving classification results. An existing proposal by Kendall and Gal, which uses Monte-Carlo inference to learn to predict the variance of each prediction, yields an overall mean Dice of $0.85 \pm 0.14$ and showed statistically significant improvements over 25 brain structures. Meanwhile a novel heteroscedastic network which directly learns the probability that an example has been mislabeled yielded an overall mean Dice of $0.87 \pm 0.11$ and showed statistically significant improvements over all but one of the brain structures considered. The loss function associated to this network can be interpreted as performing a form of learned label smoothing, where labels are only smoothed where they are judged to be uncertain.
Deep Learning versus Classical Regression for Brain Tumor Patient Survival Prediction
Nov 12, 2018



Abstract:Deep learning for regression tasks on medical imaging data has shown promising results. However, compared to other approaches, their power is strongly linked to the dataset size. In this study, we evaluate 3D-convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and classical regression methods with hand-crafted features for survival time regression of patients with high grade brain tumors. The tested CNNs for regression showed promising but unstable results. The best performing deep learning approach reached an accuracy of 51.5% on held-out samples of the training set. All tested deep learning experiments were outperformed by a Support Vector Classifier (SVC) using 30 radiomic features. The investigated features included intensity, shape, location and deep features. The submitted method to the BraTS 2018 survival prediction challenge is an ensemble of SVCs, which reached a cross-validated accuracy of 72.2% on the BraTS 2018 training set, 57.1% on the validation set, and 42.9% on the testing set. The results suggest that more training data is necessary for a stable performance of a CNN model for direct regression from magnetic resonance images, and that non-imaging clinical patient information is crucial along with imaging information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge