Brandyn White
WOD-E2E: Waymo Open Dataset for End-to-End Driving in Challenging Long-tail Scenarios
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Vision-based end-to-end (E2E) driving has garnered significant interest in the research community due to its scalability and synergy with multimodal large language models (MLLMs). However, current E2E driving benchmarks primarily feature nominal scenarios, failing to adequately test the true potential of these systems. Furthermore, existing open-loop evaluation metrics often fall short in capturing the multi-modal nature of driving or effectively evaluating performance in long-tail scenarios. To address these gaps, we introduce the Waymo Open Dataset for End-to-End Driving (WOD-E2E). WOD-E2E contains 4,021 driving segments (approximately 12 hours), specifically curated for challenging long-tail scenarios that that are rare in daily life with an occurring frequency of less than 0.03%. Concretely, each segment in WOD-E2E includes the high-level routing information, ego states, and 360-degree camera views from 8 surrounding cameras. To evaluate the E2E driving performance on these long-tail situations, we propose a novel open-loop evaluation metric: Rater Feedback Score (RFS). Unlike conventional metrics that measure the distance between predicted way points and the logs, RFS measures how closely the predicted trajectory matches rater-annotated trajectory preference labels. We have released rater preference labels for all WOD-E2E validation set segments, while the held out test set labels have been used for the 2025 WOD-E2E Challenge. Through our work, we aim to foster state of the art research into generalizable, robust, and safe end-to-end autonomous driving agents capable of handling complex real-world situations.
Waymax: An Accelerated, Data-Driven Simulator for Large-Scale Autonomous Driving Research
Oct 12, 2023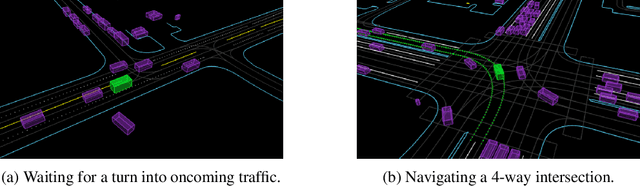
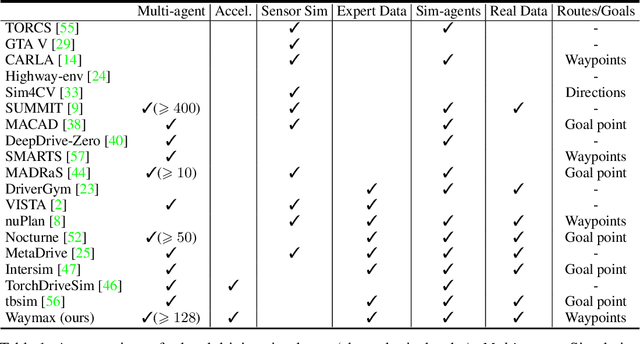
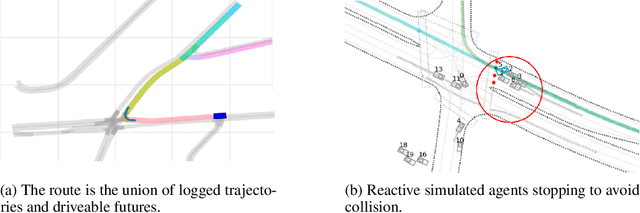
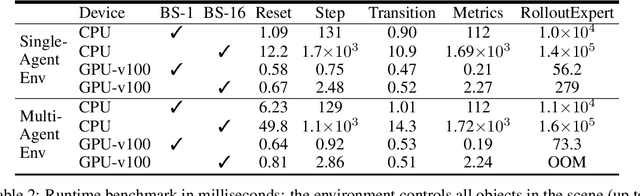
Abstract:Simulation is an essential tool to develop and benchmark autonomous vehicle planning software in a safe and cost-effective manner. However, realistic simulation requires accurate modeling of nuanced and complex multi-agent interactive behaviors. To address these challenges, we introduce Waymax, a new data-driven simulator for autonomous driving in multi-agent scenes, designed for large-scale simulation and testing. Waymax uses publicly-released, real-world driving data (e.g., the Waymo Open Motion Dataset) to initialize or play back a diverse set of multi-agent simulated scenarios. It runs entirely on hardware accelerators such as TPUs/GPUs and supports in-graph simulation for training, making it suitable for modern large-scale, distributed machine learning workflows. To support online training and evaluation, Waymax includes several learned and hard-coded behavior models that allow for realistic interaction within simulation. To supplement Waymax, we benchmark a suite of popular imitation and reinforcement learning algorithms with ablation studies on different design decisions, where we highlight the effectiveness of routes as guidance for planning agents and the ability of RL to overfit against simulated agents.
Hierarchical Imitation Learning for Stochastic Environments
Sep 25, 2023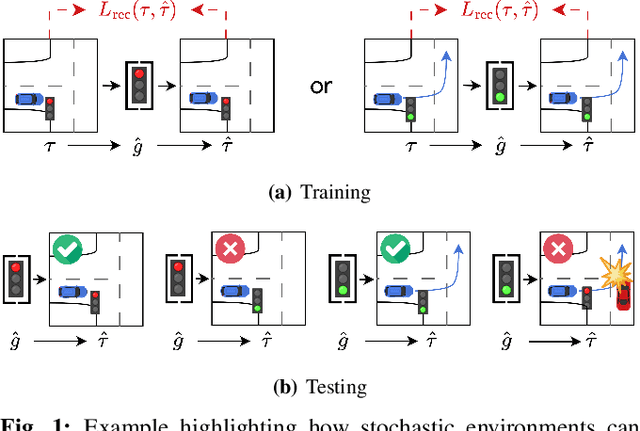
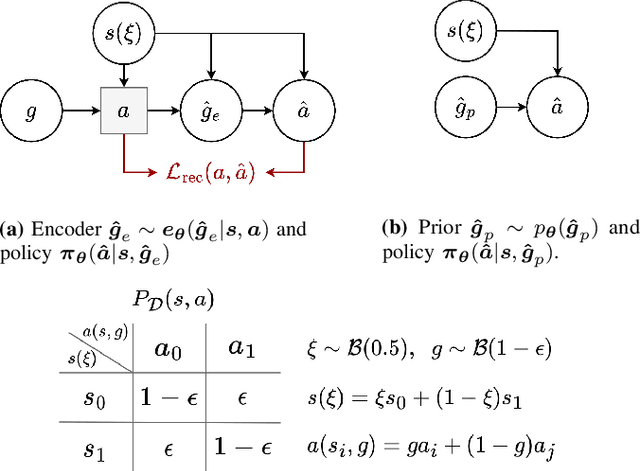
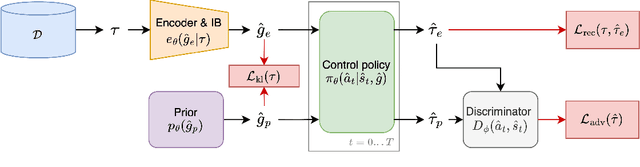
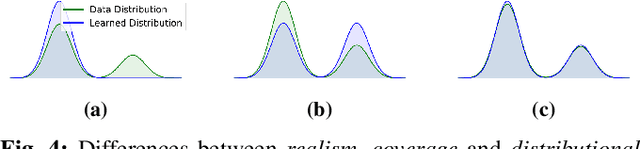
Abstract:Many applications of imitation learning require the agent to generate the full distribution of behaviour observed in the training data. For example, to evaluate the safety of autonomous vehicles in simulation, accurate and diverse behaviour models of other road users are paramount. Existing methods that improve this distributional realism typically rely on hierarchical policies. These condition the policy on types such as goals or personas that give rise to multi-modal behaviour. However, such methods are often inappropriate for stochastic environments where the agent must also react to external factors: because agent types are inferred from the observed future trajectory during training, these environments require that the contributions of internal and external factors to the agent behaviour are disentangled and only internal factors, i.e., those under the agent's control, are encoded in the type. Encoding future information about external factors leads to inappropriate agent reactions during testing, when the future is unknown and types must be drawn independently from the actual future. We formalize this challenge as distribution shift in the conditional distribution of agent types under environmental stochasticity. We propose Robust Type Conditioning (RTC), which eliminates this shift with adversarial training under randomly sampled types. Experiments on two domains, including the large-scale Waymo Open Motion Dataset, show improved distributional realism while maintaining or improving task performance compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
The Waymo Open Sim Agents Challenge
May 19, 2023Abstract:In this work, we define the Waymo Open Sim Agents Challenge (WOSAC). Simulation with realistic, interactive agents represents a key task for autonomous vehicle software development. WOSAC is the first public challenge to tackle this task and propose corresponding metrics. The goal of the challenge is to stimulate the design of realistic simulators that can be used to evaluate and train a behavior model for autonomous driving. We outline our evaluation methodology and present preliminary results for a number of different baseline simulation agent methods.
Imitation Is Not Enough: Robustifying Imitation with Reinforcement Learning for Challenging Driving Scenarios
Dec 21, 2022



Abstract:Imitation learning (IL) is a simple and powerful way to use high-quality human driving data, which can be collected at scale, to identify driving preferences and produce human-like behavior. However, policies based on imitation learning alone often fail to sufficiently account for safety and reliability concerns. In this paper, we show how imitation learning combined with reinforcement learning using simple rewards can substantially improve the safety and reliability of driving policies over those learned from imitation alone. In particular, we use a combination of imitation and reinforcement learning to train a policy on over 100k miles of urban driving data, and measure its effectiveness in test scenarios grouped by different levels of collision risk. To our knowledge, this is the first application of a combined imitation and reinforcement learning approach in autonomous driving that utilizes large amounts of real-world human driving data.
Hierarchical Model-Based Imitation Learning for Planning in Autonomous Driving
Oct 18, 2022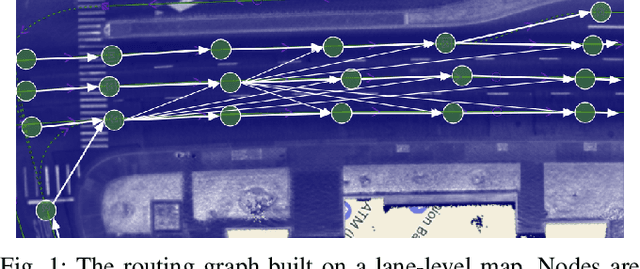
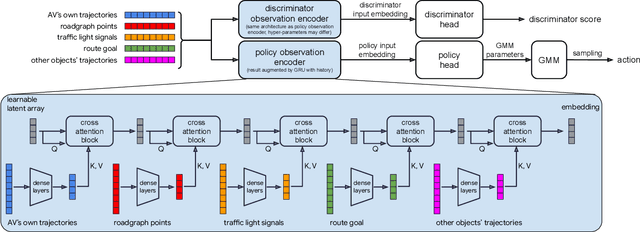
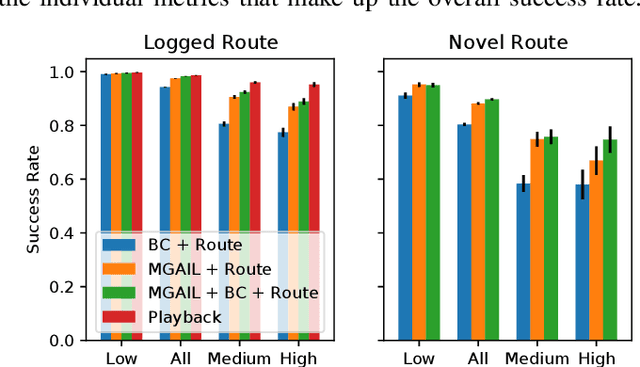
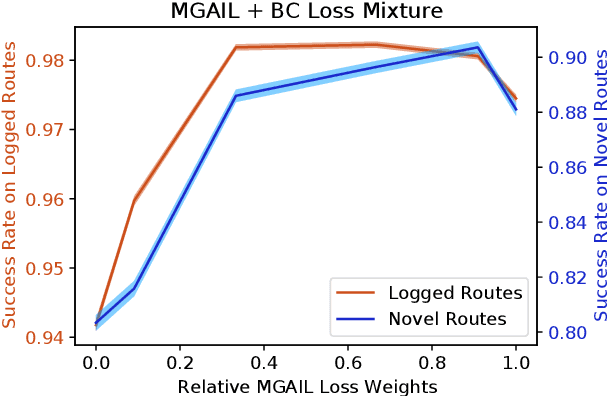
Abstract:We demonstrate the first large-scale application of model-based generative adversarial imitation learning (MGAIL) to the task of dense urban self-driving. We augment standard MGAIL using a hierarchical model to enable generalization to arbitrary goal routes, and measure performance using a closed-loop evaluation framework with simulated interactive agents. We train policies from expert trajectories collected from real vehicles driving over 100,000 miles in San Francisco, and demonstrate a steerable policy that can navigate robustly even in a zero-shot setting, generalizing to synthetic scenarios with novel goals that never occurred in real-world driving. We also demonstrate the importance of mixing closed-loop MGAIL losses with open-loop behavior cloning losses, and show our best policy approaches the performance of the expert. We evaluate our imitative model in both average and challenging scenarios, and show how it can serve as a useful prior to plan successful trajectories.
StopNet: Scalable Trajectory and Occupancy Prediction for Urban Autonomous Driving
Jun 02, 2022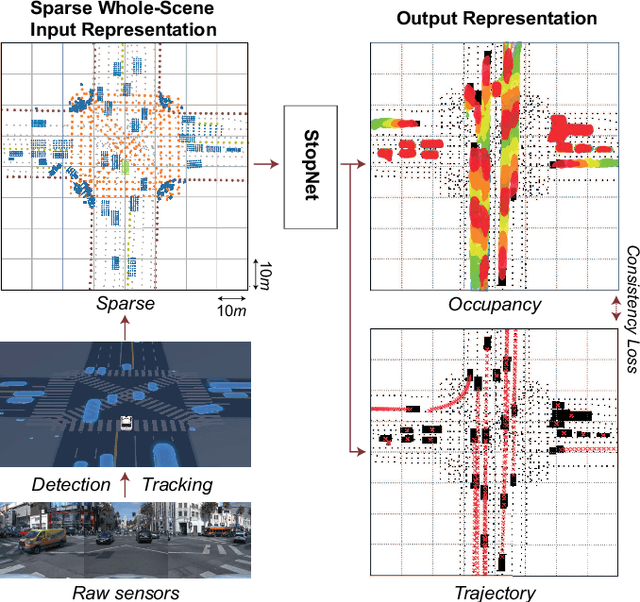
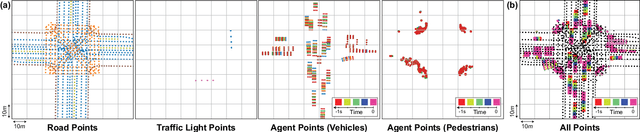
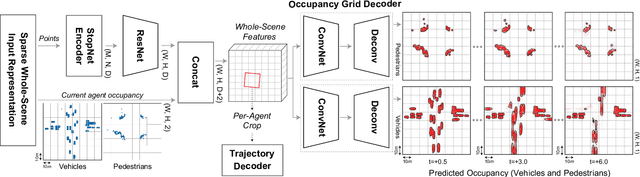
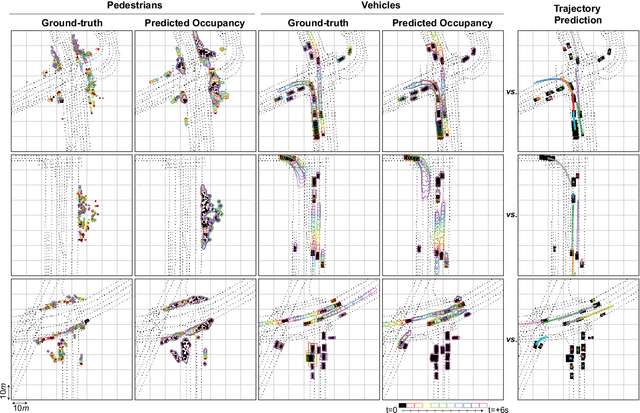
Abstract:We introduce a motion forecasting (behavior prediction) method that meets the latency requirements for autonomous driving in dense urban environments without sacrificing accuracy. A whole-scene sparse input representation allows StopNet to scale to predicting trajectories for hundreds of road agents with reliable latency. In addition to predicting trajectories, our scene encoder lends itself to predicting whole-scene probabilistic occupancy grids, a complementary output representation suitable for busy urban environments. Occupancy grids allow the AV to reason collectively about the behavior of groups of agents without processing their individual trajectories. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our sparse input representation and our model in terms of computation and accuracy over three datasets. We further show that co-training consistent trajectory and occupancy predictions improves upon state-of-the-art performance under standard metrics.
Symphony: Learning Realistic and Diverse Agents for Autonomous Driving Simulation
May 06, 2022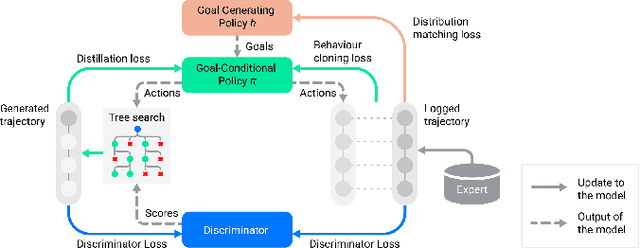
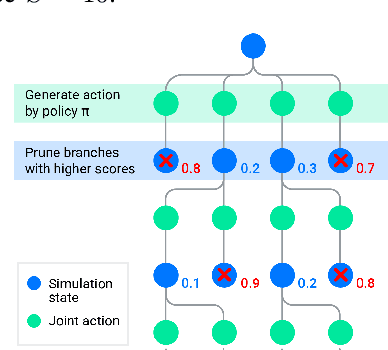
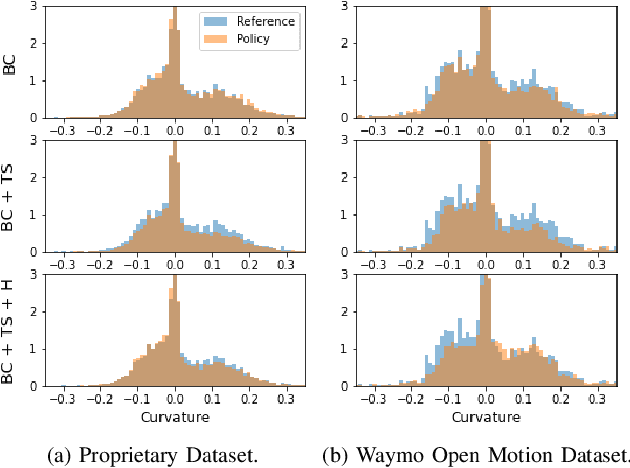
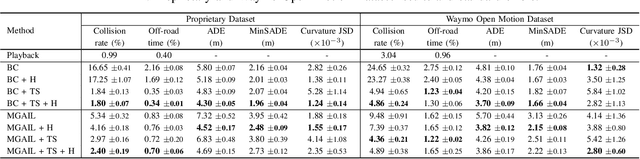
Abstract:Simulation is a crucial tool for accelerating the development of autonomous vehicles. Making simulation realistic requires models of the human road users who interact with such cars. Such models can be obtained by applying learning from demonstration (LfD) to trajectories observed by cars already on the road. However, existing LfD methods are typically insufficient, yielding policies that frequently collide or drive off the road. To address this problem, we propose Symphony, which greatly improves realism by combining conventional policies with a parallel beam search. The beam search refines these policies on the fly by pruning branches that are unfavourably evaluated by a discriminator. However, it can also harm diversity, i.e., how well the agents cover the entire distribution of realistic behaviour, as pruning can encourage mode collapse. Symphony addresses this issue with a hierarchical approach, factoring agent behaviour into goal generation and goal conditioning. The use of such goals ensures that agent diversity neither disappears during adversarial training nor is pruned away by the beam search. Experiments on both proprietary and open Waymo datasets confirm that Symphony agents learn more realistic and diverse behaviour than several baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge