Bei Shi
On the Diversity and Realism of Distilled Dataset: An Efficient Dataset Distillation Paradigm
Dec 06, 2023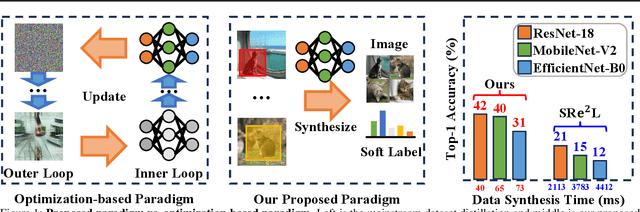
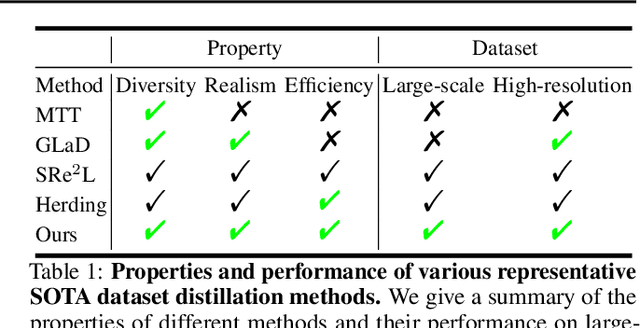
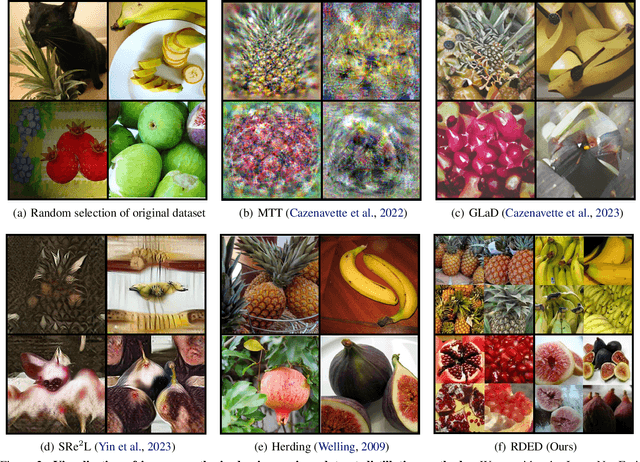
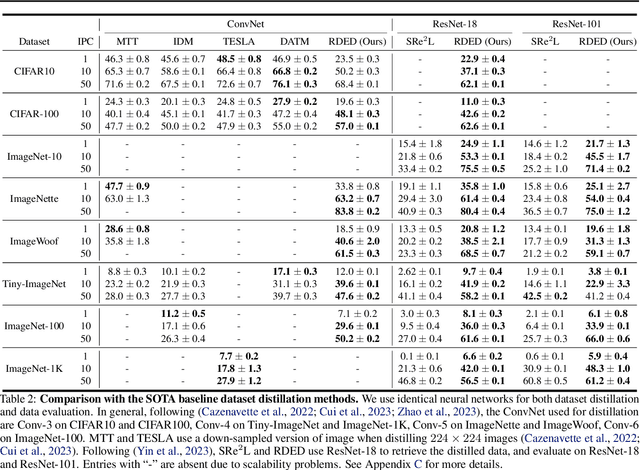
Abstract:Contemporary machine learning requires training large neural networks on massive datasets and thus faces the challenges of high computational demands. Dataset distillation, as a recent emerging strategy, aims to compress real-world datasets for efficient training. However, this line of research currently struggle with large-scale and high-resolution datasets, hindering its practicality and feasibility. To this end, we re-examine the existing dataset distillation methods and identify three properties required for large-scale real-world applications, namely, realism, diversity, and efficiency. As a remedy, we propose RDED, a novel computationally-efficient yet effective data distillation paradigm, to enable both diversity and realism of the distilled data. Extensive empirical results over various neural architectures and datasets demonstrate the advancement of RDED: we can distill the full ImageNet-1K to a small dataset comprising 10 images per class within 7 minutes, achieving a notable 42% top-1 accuracy with ResNet-18 on a single RTX-4090 GPU (while the SOTA only achieves 21% but requires 6 hours).
Learning Diverse Policies in MOBA Games via Macro-Goals
Oct 27, 2021



Abstract:Recently, many researchers have made successful progress in building the AI systems for MOBA-game-playing with deep reinforcement learning, such as on Dota 2 and Honor of Kings. Even though these AI systems have achieved or even exceeded human-level performance, they still suffer from the lack of policy diversity. In this paper, we propose a novel Macro-Goals Guided framework, called MGG, to learn diverse policies in MOBA games. MGG abstracts strategies as macro-goals from human demonstrations and trains a Meta-Controller to predict these macro-goals. To enhance policy diversity, MGG samples macro-goals from the Meta-Controller prediction and guides the training process towards these goals. Experimental results on the typical MOBA game Honor of Kings demonstrate that MGG can execute diverse policies in different matches and lineups, and also outperform the state-of-the-art methods over 102 heroes.
A Theoretical Analysis of the Repetition Problem in Text Generation
Jan 28, 2021



Abstract:Text generation tasks, including translation, summarization, language models, and etc. see rapid growth during recent years. Despite the remarkable achievements, the repetition problem has been observed in nearly all text generation models undermining the generation performance extensively. To solve the repetition problem, many methods have been proposed, but there is no existing theoretical analysis to show why this problem happens and how it is resolved. In this paper, we propose a new framework for theoretical analysis for the repetition problem. We first define the Average Repetition Probability (ARP) to characterize the repetition problem quantitatively. Then, we conduct an extensive analysis of the Markov generation model and derive several upper bounds of the average repetition probability with intuitive understanding. We show that most of the existing methods are essentially minimizing the upper bounds explicitly or implicitly. Grounded on our theory, we show that the repetition problem is, unfortunately, caused by the traits of our language itself. One major reason is attributed to the fact that there exist too many words predicting the same word as the subsequent word with high probability. Consequently, it is easy to go back to that word and form repetitions and we dub it as the high inflow problem. Furthermore, we derive a concentration bound of the average repetition probability for a general generation model. Finally, based on the theoretical upper bounds, we propose a novel rebalanced encoding approach to alleviate the high inflow problem. The experimental results show that our theoretical framework is applicable in general generation models and our proposed rebalanced encoding approach alleviates the repetition problem significantly. The source code of this paper can be obtained from \url{https://github.com/fuzihaofzh/repetition-problem-nlg}.
Towards Playing Full MOBA Games with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Dec 31, 2020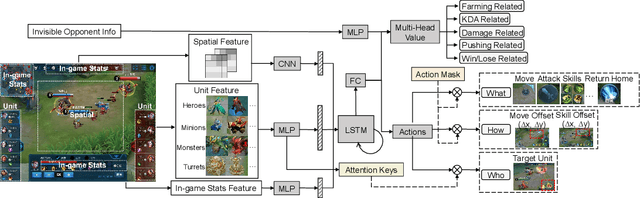
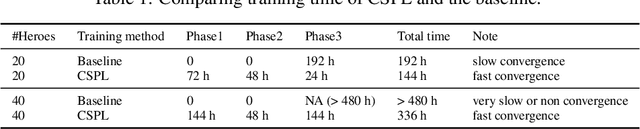
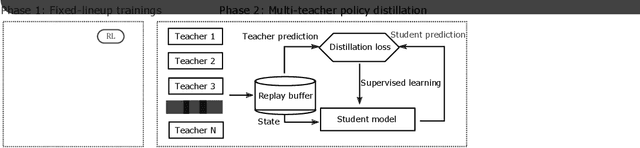

Abstract:MOBA games, e.g., Honor of Kings, League of Legends, and Dota 2, pose grand challenges to AI systems such as multi-agent, enormous state-action space, complex action control, etc. Developing AI for playing MOBA games has raised much attention accordingly. However, existing work falls short in handling the raw game complexity caused by the explosion of agent combinations, i.e., lineups, when expanding the hero pool in case that OpenAI's Dota AI limits the play to a pool of only 17 heroes. As a result, full MOBA games without restrictions are far from being mastered by any existing AI system. In this paper, we propose a MOBA AI learning paradigm that methodologically enables playing full MOBA games with deep reinforcement learning. Specifically, we develop a combination of novel and existing learning techniques, including curriculum self-play learning, policy distillation, off-policy adaption, multi-head value estimation, and Monte-Carlo tree-search, in training and playing a large pool of heroes, meanwhile addressing the scalability issue skillfully. Tested on Honor of Kings, a popular MOBA game, we show how to build superhuman AI agents that can defeat top esports players. The superiority of our AI is demonstrated by the first large-scale performance test of MOBA AI agent in the literature.
Supervised Learning Achieves Human-Level Performance in MOBA Games: A Case Study of Honor of Kings
Nov 25, 2020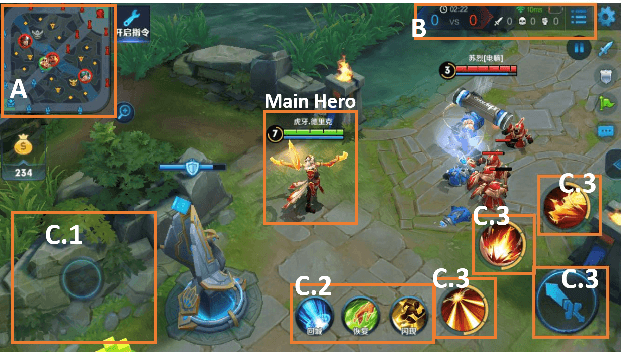
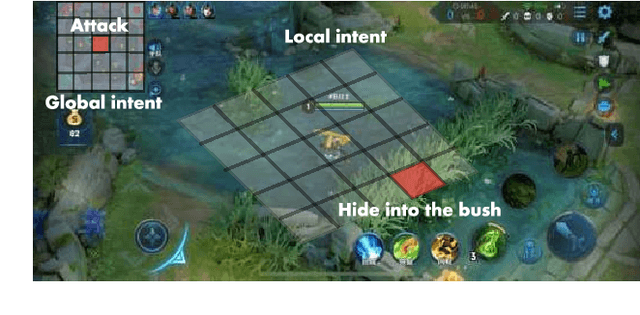
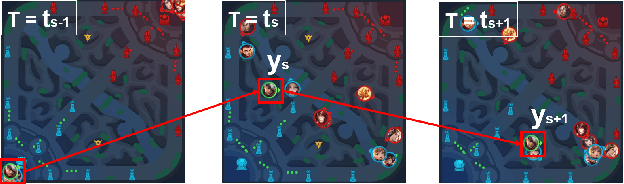
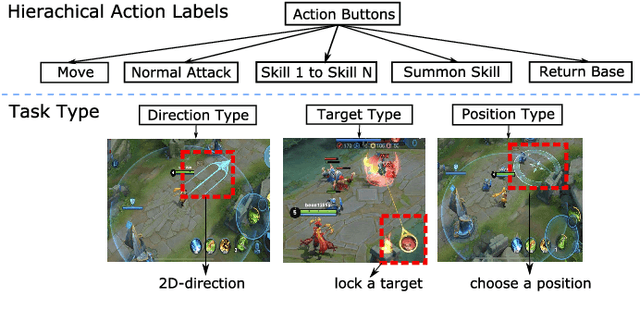
Abstract:We present JueWu-SL, the first supervised-learning-based artificial intelligence (AI) program that achieves human-level performance in playing multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) games. Unlike prior attempts, we integrate the macro-strategy and the micromanagement of MOBA-game-playing into neural networks in a supervised and end-to-end manner. Tested on Honor of Kings, the most popular MOBA at present, our AI performs competitively at the level of High King players in standard 5v5 games.
Partially-Aligned Data-to-Text Generation with Distant Supervision
Oct 03, 2020



Abstract:The Data-to-Text task aims to generate human-readable text for describing some given structured data enabling more interpretability. However, the typical generation task is confined to a few particular domains since it requires well-aligned data which is difficult and expensive to obtain. Using partially-aligned data is an alternative way of solving the dataset scarcity problem. This kind of data is much easier to obtain since it can be produced automatically. However, using this kind of data induces the over-generation problem posing difficulties for existing models, which tends to add unrelated excerpts during the generation procedure. In order to effectively utilize automatically annotated partially-aligned datasets, we extend the traditional generation task to a refined task called Partially-Aligned Data-to-Text Generation (PADTG) which is more practical since it utilizes automatically annotated data for training and thus considerably expands the application domains. To tackle this new task, we propose a novel distant supervision generation framework. It firstly estimates the input data's supportiveness for each target word with an estimator and then applies a supportiveness adaptor and a rebalanced beam search to harness the over-generation problem in the training and generation phases respectively. We also contribute a partially-aligned dataset (The data and source code of this paper can be obtained from https://github.com/fuzihaofzh/distant_supervision_nlg by sampling sentences from Wikipedia and automatically extracting corresponding KB triples for each sentence from Wikidata. The experimental results show that our framework outperforms all baseline models as well as verify the feasibility of utilizing partially-aligned data.
Mastering Complex Control in MOBA Games with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jan 03, 2020
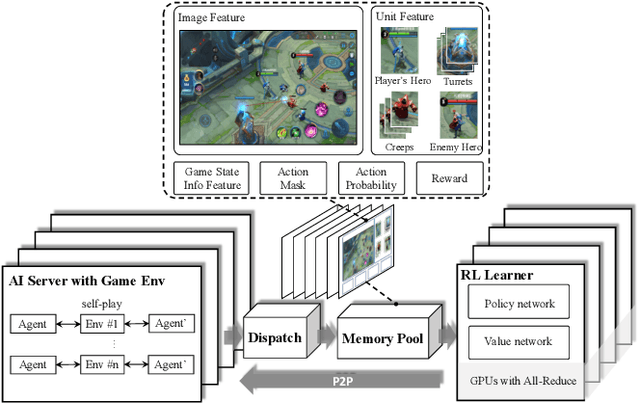
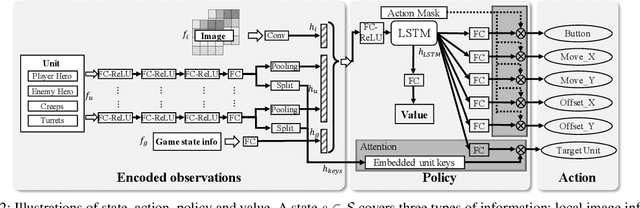

Abstract:We study the reinforcement learning problem of complex action control in the Multi-player Online Battle Arena (MOBA) 1v1 games. This problem involves far more complicated state and action spaces than those of traditional 1v1 games, such as Go and Atari series, which makes it very difficult to search any policies with human-level performance. In this paper, we present a deep reinforcement learning framework to tackle this problem from the perspectives of both system and algorithm. Our system is of low coupling and high scalability, which enables efficient explorations at large scale. Our algorithm includes several novel strategies, including control dependency decoupling, action mask, target attention, and dual-clip PPO, with which our proposed actor-critic network can be effectively trained in our system. Tested on the MOBA game Honor of Kings, the trained AI agents can defeat top professional human players in full 1v1 games.
Learning Domain-Sensitive and Sentiment-Aware Word Embeddings
May 10, 2018



Abstract:Word embeddings have been widely used in sentiment classification because of their efficacy for semantic representations of words. Given reviews from different domains, some existing methods for word embeddings exploit sentiment information, but they cannot produce domain-sensitive embeddings. On the other hand, some other existing methods can generate domain-sensitive word embeddings, but they cannot distinguish words with similar contexts but opposite sentiment polarity. We propose a new method for learning domain-sensitive and sentiment-aware embeddings that simultaneously capture the information of sentiment semantics and domain sensitivity of individual words. Our method can automatically determine and produce domain-common embeddings and domain-specific embeddings. The differentiation of domain-common and domain-specific words enables the advantage of data augmentation of common semantics from multiple domains and capture the varied semantics of specific words from different domains at the same time. Experimental results show that our model provides an effective way to learn domain-sensitive and sentiment-aware word embeddings which benefit sentiment classification at both sentence level and lexicon term level.
* 11 pages, published in ACL2018
Transformation Networks for Target-Oriented Sentiment Classification
May 03, 2018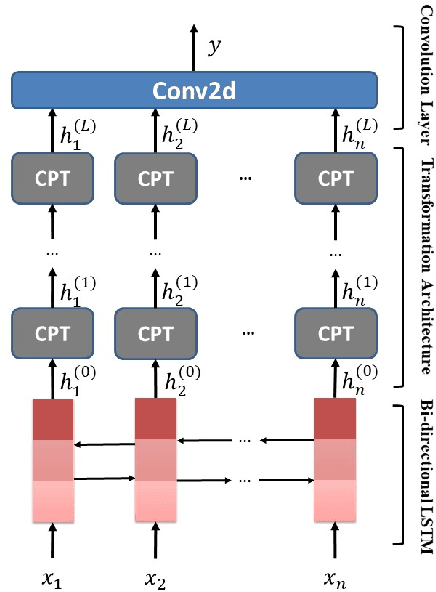

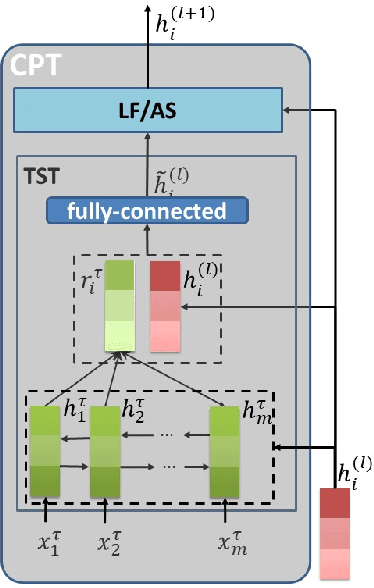

Abstract:Target-oriented sentiment classification aims at classifying sentiment polarities over individual opinion targets in a sentence. RNN with attention seems a good fit for the characteristics of this task, and indeed it achieves the state-of-the-art performance. After re-examining the drawbacks of attention mechanism and the obstacles that block CNN to perform well in this classification task, we propose a new model to overcome these issues. Instead of attention, our model employs a CNN layer to extract salient features from the transformed word representations originated from a bi-directional RNN layer. Between the two layers, we propose a component to generate target-specific representations of words in the sentence, meanwhile incorporate a mechanism for preserving the original contextual information from the RNN layer. Experiments show that our model achieves a new state-of-the-art performance on a few benchmarks.
Jointly Learning Word Embeddings and Latent Topics
Jun 21, 2017



Abstract:Word embedding models such as Skip-gram learn a vector-space representation for each word, based on the local word collocation patterns that are observed in a text corpus. Latent topic models, on the other hand, take a more global view, looking at the word distributions across the corpus to assign a topic to each word occurrence. These two paradigms are complementary in how they represent the meaning of word occurrences. While some previous works have already looked at using word embeddings for improving the quality of latent topics, and conversely, at using latent topics for improving word embeddings, such "two-step" methods cannot capture the mutual interaction between the two paradigms. In this paper, we propose STE, a framework which can learn word embeddings and latent topics in a unified manner. STE naturally obtains topic-specific word embeddings, and thus addresses the issue of polysemy. At the same time, it also learns the term distributions of the topics, and the topic distributions of the documents. Our experimental results demonstrate that the STE model can indeed generate useful topic-specific word embeddings and coherent latent topics in an effective and efficient way.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge