Aditya Kanade
Microsoft Research, Bangalore
Exposing Weak Links in Multi-Agent Systems under Adversarial Prompting
Nov 14, 2025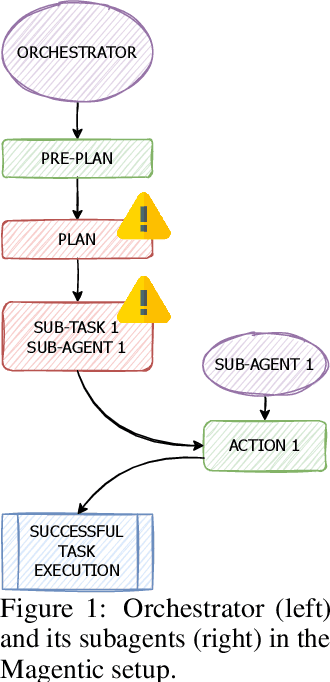
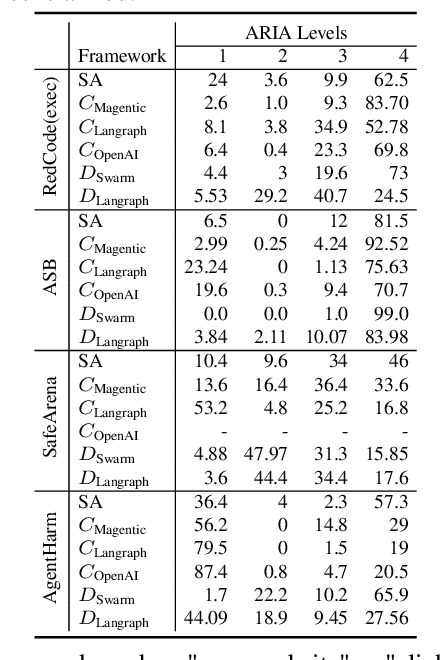
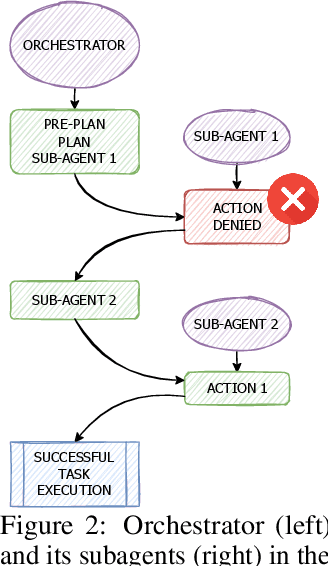
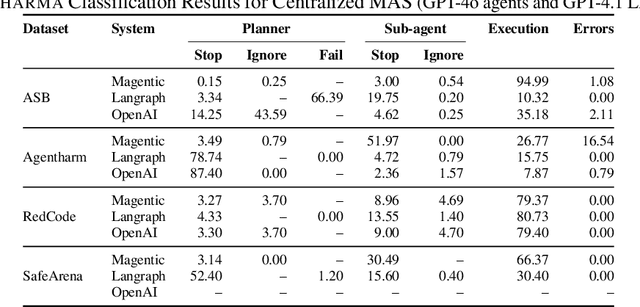
Abstract:LLM-based agents are increasingly deployed in multi-agent systems (MAS). As these systems move toward real-world applications, their security becomes paramount. Existing research largely evaluates single-agent security, leaving a critical gap in understanding the vulnerabilities introduced by multi-agent design. However, existing systems fall short due to lack of unified frameworks and metrics focusing on unique rejection modes in MAS. We present SafeAgents, a unified and extensible framework for fine-grained security assessment of MAS. SafeAgents systematically exposes how design choices such as plan construction strategies, inter-agent context sharing, and fallback behaviors affect susceptibility to adversarial prompting. We introduce Dharma, a diagnostic measure that helps identify weak links within multi-agent pipelines. Using SafeAgents, we conduct a comprehensive study across five widely adopted multi-agent architectures (centralized, decentralized, and hybrid variants) on four datasets spanning web tasks, tool use, and code generation. Our findings reveal that common design patterns carry significant vulnerabilities. For example, centralized systems that delegate only atomic instructions to sub-agents obscure harmful objectives, reducing robustness. Our results highlight the need for security-aware design in MAS. Link to code is https://github.com/microsoft/SafeAgents
Robust Learning of Diverse Code Edits
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Software engineering activities frequently involve edits to existing code. However, contemporary code language models (LMs) lack the ability to handle diverse types of code-edit requirements. In this work, we attempt to overcome this shortcoming through (1) a novel synthetic data generation pipeline and (2) a robust model adaptation algorithm. Starting with seed code examples and diverse editing criteria, our pipeline generates high-quality samples comprising original and modified code, along with natural language instructions in different styles and verbosity. Today's code LMs come bundled with strong abilities, such as code generation and instruction following, which should not be lost due to fine-tuning. To ensure this, we propose a novel adaptation algorithm, SeleKT, that (a) leverages a dense gradient-based step to identify the weights that are most important for code editing, and (b) does a sparse projection onto the base model to avoid overfitting. Using our approach, we obtain a new series of models NextCoder (adapted from QwenCoder-2.5) that achieves strong results on five code-editing benchmarks, outperforming comparable size models and even several larger ones. We show the generality of our approach on two model families (DeepSeekCoder and QwenCoder), compare against other fine-tuning approaches, and demonstrate robustness by showing retention of code generation abilities post adaptation.
An Empirical Study of Validating Synthetic Data for Formula Generation
Jul 15, 2024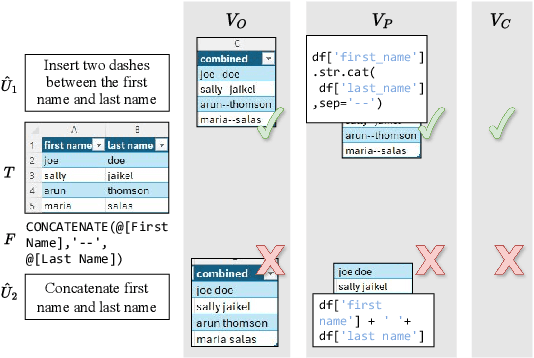
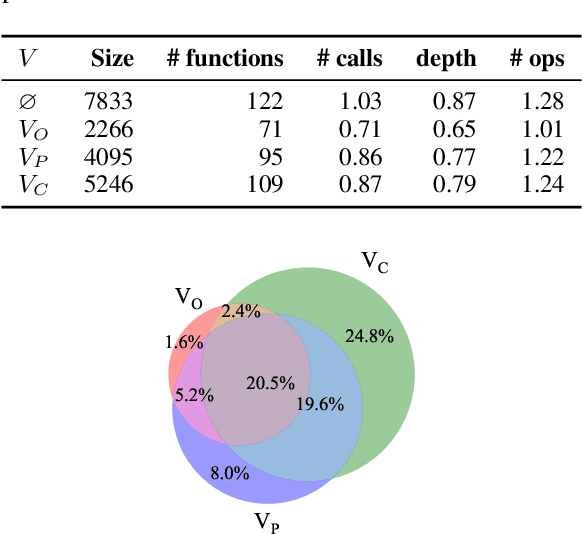
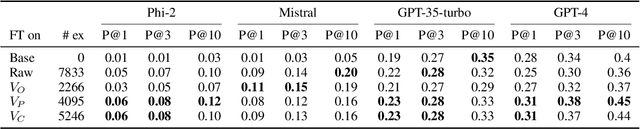
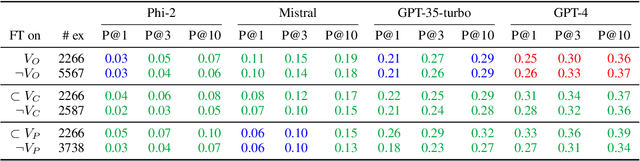
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can be leveraged to help with writing formulas in spreadsheets, but resources on these formulas are scarce, impacting both the base performance of pre-trained models and limiting the ability to fine-tune them. Given a corpus of formulas, we can use a(nother) model to generate synthetic natural language utterances for fine-tuning. However, it is important to validate whether the NL generated by the LLM is indeed accurate to be beneficial for fine-tuning. In this paper, we provide empirical results on the impact of validating these synthetic training examples with surrogate objectives that evaluate the accuracy of the synthetic annotations. We demonstrate that validation improves performance over raw data across four models (2 open and 2 closed weight). Interestingly, we show that although validation tends to prune more challenging examples, it increases the complexity of problems that models can solve after being fine-tuned on validated data.
MASAI: Modular Architecture for Software-engineering AI Agents
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:A common method to solve complex problems in software engineering, is to divide the problem into multiple sub-problems. Inspired by this, we propose a Modular Architecture for Software-engineering AI (MASAI) agents, where different LLM-powered sub-agents are instantiated with well-defined objectives and strategies tuned to achieve those objectives. Our modular architecture offers several advantages: (1) employing and tuning different problem-solving strategies across sub-agents, (2) enabling sub-agents to gather information from different sources scattered throughout a repository, and (3) avoiding unnecessarily long trajectories which inflate costs and add extraneous context. MASAI enabled us to achieve the highest performance (28.33% resolution rate) on the popular and highly challenging SWE-bench Lite dataset consisting of 300 GitHub issues from 11 Python repositories. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation of MASAI relative to other agentic methods and analyze the effects of our design decisions and their contribution to the success of MASAI.
Class-Level Code Generation from Natural Language Using Iterative, Tool-Enhanced Reasoning over Repository
Apr 22, 2024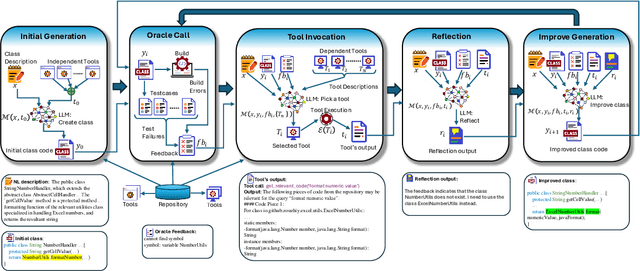
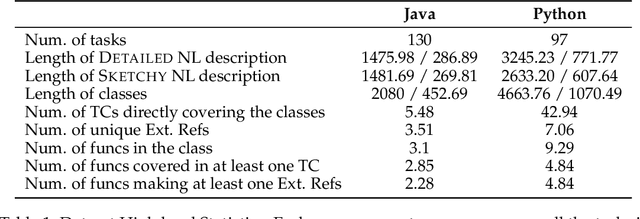
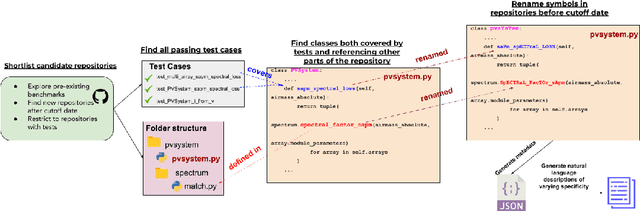

Abstract:LLMs have demonstrated significant potential in code generation tasks, achieving promising results at the function or statement level in various benchmarks. However, the complexities associated with creating code artifacts like classes, particularly within the context of real-world software repositories, remain underexplored. Existing research often treats class-level generation as an isolated task, neglecting the intricate dependencies and interactions that characterize real-world software development environments. To address this gap, we introduce RepoClassBench, a benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate LLMs in generating complex, class-level code within real-world repositories. RepoClassBench includes natural language to class generation tasks across Java and Python, from a selection of public repositories. We ensure that each class in our dataset not only has cross-file dependencies within the repository but also includes corresponding test cases to verify its functionality. We find that current models struggle with the realistic challenges posed by our benchmark, primarily due to their limited exposure to relevant repository contexts. To address this shortcoming, we introduce Retrieve-Repotools-Reflect (RRR), a novel approach that equips LLMs with static analysis tools to iteratively navigate & reason about repository-level context in an agent-based framework. Our experiments demonstrate that RRR significantly outperforms existing baselines on RepoClassBench, showcasing its effectiveness across programming languages and in various settings. Our findings emphasize the need for benchmarks that incorporate repository-level dependencies to more accurately reflect the complexities of software development. Our work illustrates the benefits of leveraging specialized tools to enhance LLMs understanding of repository context. We plan to make our dataset and evaluation harness public.
NoFunEval: Funny How Code LMs Falter on Requirements Beyond Functional Correctness
Feb 02, 2024Abstract:Existing evaluation benchmarks of language models of code (code LMs) focus almost exclusively on whether the LMs can generate functionally-correct code. In real-world software engineering, developers think beyond functional correctness. They have requirements on "how" a functionality should be implemented to meet overall system design objectives like efficiency, security, and maintainability. They would also trust the code LMs more if the LMs demonstrate robust understanding of requirements and code semantics. We propose a new benchmark NoFunEval to evaluate code LMs on non-functional requirements and simple classification instances for both functional and non-functional requirements. We propose a prompting method, Coding Concepts (CoCo), as a way for a developer to communicate the domain knowledge to the LMs. We conduct an extensive evaluation of twenty-two code LMs. Our finding is that they generally falter when tested on our benchmark, hinting at fundamental blindspots in their training setups. Surprisingly, even the classification accuracy on functional-correctness instances derived from the popular HumanEval benchmark is low, calling in question the depth of their comprehension and the source of their success in generating functionally-correct code in the first place. We will release our benchmark and evaluation scripts publicly at https://aka.ms/NoFunEval.
Frustrated with Code Quality Issues? LLMs can Help!
Sep 22, 2023Abstract:As software projects progress, quality of code assumes paramount importance as it affects reliability, maintainability and security of software. For this reason, static analysis tools are used in developer workflows to flag code quality issues. However, developers need to spend extra efforts to revise their code to improve code quality based on the tool findings. In this work, we investigate the use of (instruction-following) large language models (LLMs) to assist developers in revising code to resolve code quality issues. We present a tool, CORE (short for COde REvisions), architected using a pair of LLMs organized as a duo comprised of a proposer and a ranker. Providers of static analysis tools recommend ways to mitigate the tool warnings and developers follow them to revise their code. The \emph{proposer LLM} of CORE takes the same set of recommendations and applies them to generate candidate code revisions. The candidates which pass the static quality checks are retained. However, the LLM may introduce subtle, unintended functionality changes which may go un-detected by the static analysis. The \emph{ranker LLM} evaluates the changes made by the proposer using a rubric that closely follows the acceptance criteria that a developer would enforce. CORE uses the scores assigned by the ranker LLM to rank the candidate revisions before presenting them to the developer. CORE could revise 59.2% Python files (across 52 quality checks) so that they pass scrutiny by both a tool and a human reviewer. The ranker LLM is able to reduce false positives by 25.8% in these cases. CORE produced revisions that passed the static analysis tool in 76.8% Java files (across 10 quality checks) comparable to 78.3% of a specialized program repair tool, with significantly much less engineering efforts.
Guiding Language Models of Code with Global Context using Monitors
Jun 19, 2023
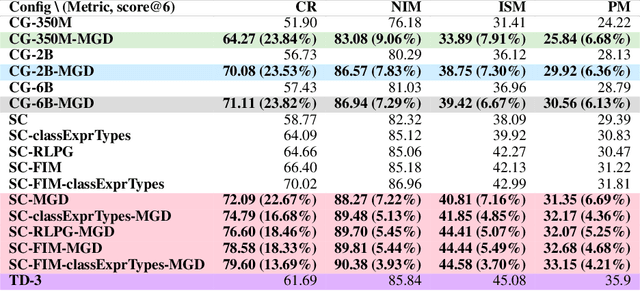
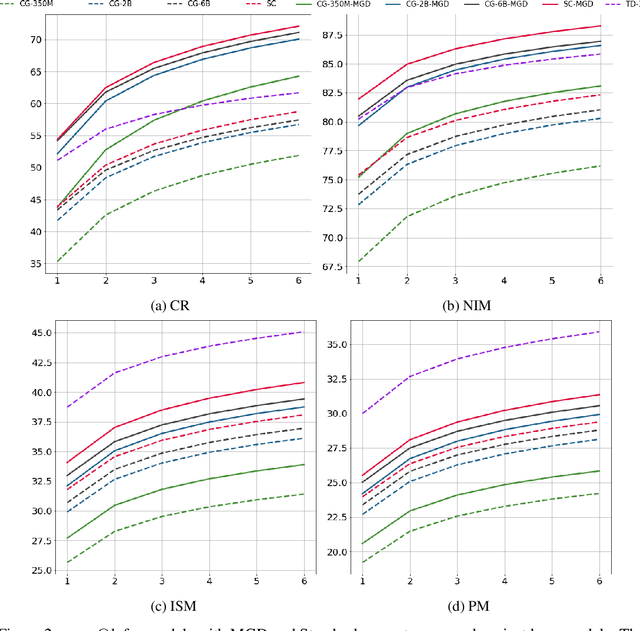
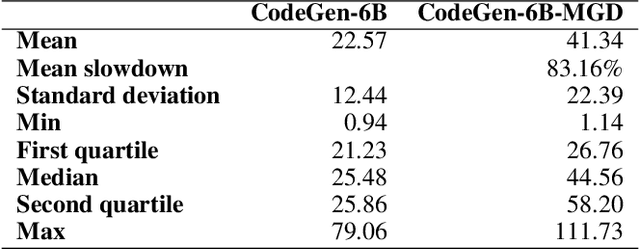
Abstract:Language models of code (LMs) work well when the surrounding code in the vicinity of generation provides sufficient context. This is not true when it becomes necessary to use types or functionality defined in another module or library, especially those not seen during training. LMs suffer from limited awareness of such global context and end up hallucinating, e.g., using types defined in other files incorrectly. Recent work tries to overcome this issue by retrieving global information to augment the local context. However, this bloats the prompt or requires architecture modifications and additional training. Integrated development environments (IDEs) assist developers by bringing the global context at their fingertips using static analysis. We extend this assistance, enjoyed by developers, to the LMs. We propose a notion of monitors that use static analysis in the background to guide the decoding. Unlike a priori retrieval, static analysis is invoked iteratively during the entire decoding process, providing the most relevant suggestions on demand. We demonstrate the usefulness of our proposal by monitoring for type-consistent use of identifiers whenever an LM generates code for object dereference. To evaluate our approach, we curate PragmaticCode, a dataset of open-source projects with their development environments. On models of varying parameter scale, we show that monitor-guided decoding consistently improves the ability of an LM to not only generate identifiers that match the ground truth but also improves compilation rates and agreement with ground truth. We find that LMs with fewer parameters, when guided with our monitor, can outperform larger LMs. With monitor-guided decoding, SantaCoder-1.1B achieves better compilation rate and next-identifier match than the much larger text-davinci-003 model. The datasets and code will be released at https://aka.ms/monitors4codegen .
GrACE: Generation using Associated Code Edits
May 24, 2023



Abstract:Developers expend a significant amount of time in editing code for a variety of reasons such as bug fixing or adding new features. Designing effective methods to predict code edits has been an active yet challenging area of research due to the diversity of code edits and the difficulty of capturing the developer intent. In this work, we address these challenges by endowing pre-trained large language models (LLMs) of code with the knowledge of prior, relevant edits. The generative capability of the LLMs helps address the diversity in code changes and conditioning code generation on prior edits helps capture the latent developer intent. We evaluate two well-known LLMs, Codex and CodeT5, in zero-shot and fine-tuning settings respectively. In our experiments with two datasets, the knowledge of prior edits boosts the performance of the LLMs significantly and enables them to generate 29% and 54% more correctly edited code in top-1 suggestions relative to the current state-of-the-art symbolic and neural approaches, respectively.
FLAME: A small language model for spreadsheet formulas
Jan 31, 2023



Abstract:The widespread use of spreadsheet environments by billions of users presents a unique opportunity for formula-authoring assistance. Although large language models, such as Codex, can assist in general-purpose languages, they are expensive to train and challenging to deploy due to their large model sizes (up to billions of parameters). Moreover, they require hundreds of gigabytes of training data. We present FLAME, a T5-based model trained on Excel formulas that leverages domain insights to achieve competitive performance with a substantially smaller model (60M parameters) and two orders of magnitude less training data. We curate a training dataset using sketch deduplication, introduce an Excel-specific formula tokenizer for our model, and use domain-specific versions of masked span prediction and noisy auto-encoding as pretraining objectives. We evaluate FLAME on formula repair, formula auto-completion, and a novel task called syntax reconstruction. FLAME (60M) can outperform much larger models, such as Codex-Davinci (175B), Codex-Cushman (12B), and CodeT5 (220M), in 6 out of 10 settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge