Ajinkya Deshpande
Hybrid deep learning-based strategy for the hepatocellular carcinoma cancer grade classification of H&E stained liver histopathology images
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common type of liver cancer whose early-stage diagnosis is a common challenge, mainly due to the manual assessment of hematoxylin and eosin-stained whole slide images, which is a time-consuming process and may lead to variability in decision-making. For accurate detection of HCC, we propose a hybrid deep learning-based architecture that uses transfer learning to extract the features from pre-trained convolutional neural network (CNN) models and a classifier made up of a sequence of fully connected layers. This study uses a publicly available The Cancer Genome Atlas Hepatocellular Carcinoma (TCGA-LIHC)database (n=491) for model development and database of Kasturba Gandhi Medical College (KMC), India for validation. The pre-processing step involves patch extraction, colour normalization, and augmentation that results in 3920 patches for the TCGA dataset. The developed hybrid deep neural network consisting of a CNN-based pre-trained feature extractor and a customized artificial neural network-based classifier is trained using five-fold cross-validation. For this study, eight different state-of-the-art models are trained and tested as feature extractors for the proposed hybrid model. The proposed hybrid model with ResNet50-based feature extractor provided the sensitivity, specificity, F1-score, accuracy, and AUC of 100.00%, 100.00%, 100.00%, 100.00%, and 1.00, respectively on the TCGA database. On the KMC database, EfficientNetb3 resulted in the optimal choice of the feature extractor giving sensitivity, specificity, F1-score, accuracy, and AUC of 96.97, 98.85, 96.71, 96.71, and 0.99, respectively. The proposed hybrid models showed improvement in accuracy of 2% and 4% over the pre-trained models in TCGA-LIHC and KMC databases.
Class-Level Code Generation from Natural Language Using Iterative, Tool-Enhanced Reasoning over Repository
Apr 22, 2024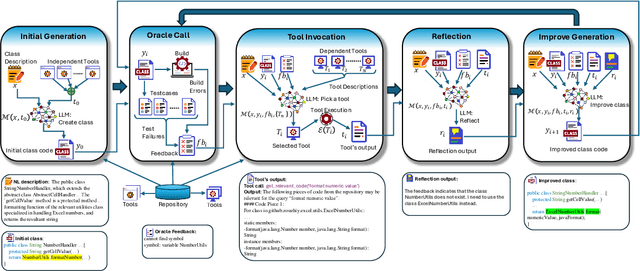
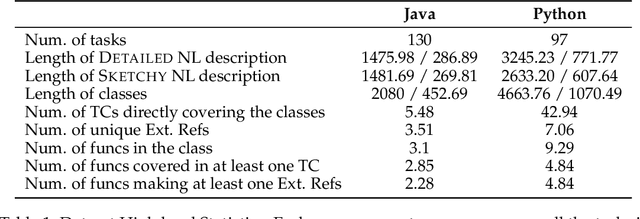
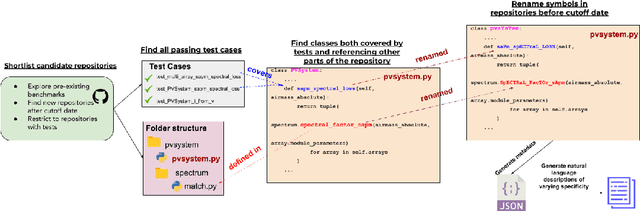

Abstract:LLMs have demonstrated significant potential in code generation tasks, achieving promising results at the function or statement level in various benchmarks. However, the complexities associated with creating code artifacts like classes, particularly within the context of real-world software repositories, remain underexplored. Existing research often treats class-level generation as an isolated task, neglecting the intricate dependencies and interactions that characterize real-world software development environments. To address this gap, we introduce RepoClassBench, a benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate LLMs in generating complex, class-level code within real-world repositories. RepoClassBench includes natural language to class generation tasks across Java and Python, from a selection of public repositories. We ensure that each class in our dataset not only has cross-file dependencies within the repository but also includes corresponding test cases to verify its functionality. We find that current models struggle with the realistic challenges posed by our benchmark, primarily due to their limited exposure to relevant repository contexts. To address this shortcoming, we introduce Retrieve-Repotools-Reflect (RRR), a novel approach that equips LLMs with static analysis tools to iteratively navigate & reason about repository-level context in an agent-based framework. Our experiments demonstrate that RRR significantly outperforms existing baselines on RepoClassBench, showcasing its effectiveness across programming languages and in various settings. Our findings emphasize the need for benchmarks that incorporate repository-level dependencies to more accurately reflect the complexities of software development. Our work illustrates the benefits of leveraging specialized tools to enhance LLMs understanding of repository context. We plan to make our dataset and evaluation harness public.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge