Pulmonary Embolism Detection
Papers and Code
Application of deep learning techniques in non-contrast computed tomography pulmonary angiogram for pulmonary embolism diagnosis
Jan 01, 2026Pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening disease, early detection and treatment can significantly reduce mortality. In recent years, many studies have been using deep learning in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism with contrast medium computed tomography pulmonary angiography, but the contrast medium is likely to cause acute kidney injury in patients with pulmonary embolism and chronic kidney disease, and the contrast medium takes time to work, patients with acute pulmonary embolism may miss the golden treatment time. This study aims to use deep learning techniques to automatically classify pulmonary embolism in CT images without contrast medium by using a 3D convolutional neural network model. The deep learning model used in this study had a significant impact on the pulmonary embolism classification of computed tomography images without contrast with 85\% accuracy and 0.84 AUC, which confirms the feasibility of the model in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism.
Tumor-anchored deep feature random forests for out-of-distribution detection in lung cancer segmentation
Dec 09, 2025Accurate segmentation of cancerous lesions from 3D computed tomography (CT) scans is essential for automated treatment planning and response assessment. However, even state-of-the-art models combining self-supervised learning (SSL) pretrained transformers with convolutional decoders are susceptible to out-of-distribution (OOD) inputs, generating confidently incorrect tumor segmentations, posing risks for safe clinical deployment. Existing logit-based methods suffer from task-specific model biases, while architectural enhancements to explicitly detect OOD increase parameters and computational costs. Hence, we introduce a plug-and-play and lightweight post-hoc random forests-based OOD detection framework called RF-Deep that leverages deep features with limited outlier exposure. RF-Deep enhances generalization to imaging variations by repurposing the hierarchical features from the pretrained-then-finetuned backbone encoder, providing task-relevant OOD detection by extracting the features from multiple regions of interest anchored to the predicted tumor segmentations. Hence, it scales to images of varying fields-of-view. We compared RF-Deep against existing OOD detection methods using 1,916 CT scans across near-OOD (pulmonary embolism, negative COVID-19) and far-OOD (kidney cancer, healthy pancreas) datasets. RF-Deep achieved AUROC > 93.50 for the challenging near-OOD datasets and near-perfect detection (AUROC > 99.00) for the far-OOD datasets, substantially outperforming logit-based and radiomics approaches. RF-Deep maintained similar performance consistency across networks of different depths and pretraining strategies, demonstrating its effectiveness as a lightweight, architecture-agnostic approach to enhance the reliability of tumor segmentation from CT volumes.
Random forest-based out-of-distribution detection for robust lung cancer segmentation
Aug 26, 2025Accurate detection and segmentation of cancerous lesions from computed tomography (CT) scans is essential for automated treatment planning and cancer treatment response assessment. Transformer-based models with self-supervised pretraining can produce reliably accurate segmentation from in-distribution (ID) data but degrade when applied to out-of-distribution (OOD) datasets. We address this challenge with RF-Deep, a random forest classifier that utilizes deep features from a pretrained transformer encoder of the segmentation model to detect OOD scans and enhance segmentation reliability. The segmentation model comprises a Swin Transformer encoder, pretrained with masked image modeling (SimMIM) on 10,432 unlabeled 3D CT scans covering cancerous and non-cancerous conditions, with a convolution decoder, trained to segment lung cancers in 317 3D scans. Independent testing was performed on 603 3D CT public datasets that included one ID dataset and four OOD datasets comprising chest CTs with pulmonary embolism (PE) and COVID-19, and abdominal CTs with kidney cancers and healthy volunteers. RF-Deep detected OOD cases with a FPR95 of 18.26%, 27.66%, and less than 0.1% on PE, COVID-19, and abdominal CTs, consistently outperforming established OOD approaches. The RF-Deep classifier provides a simple and effective approach to enhance reliability of cancer segmentation in ID and OOD scenarios.
Are ECGs enough? Deep learning classification of cardiac anomalies using only electrocardiograms
Mar 11, 2025Electrocardiography (ECG) is an essential tool for diagnosing multiple cardiac anomalies: it provides valuable clinical insights, while being affordable, fast and available in many settings. However, in the current literature, the role of ECG analysis is often unclear: many approaches either rely on additional imaging modalities, such as Computed Tomography Pulmonary Angiography (CTPA), which may not always be available, or do not effectively generalize across different classification problems. Furthermore, the availability of public ECG datasets is limited and, in practice, these datasets tend to be small, making it essential to optimize learning strategies. In this study, we investigate the performance of multiple neural network architectures in order to assess the impact of various approaches. Moreover, we check whether these practices enhance model generalization when transfer learning is used to translate information learned in larger ECG datasets, such as PTB-XL and CPSC18, to a smaller, more challenging dataset for pulmonary embolism (PE) detection. By leveraging transfer learning, we analyze the extent to which we can improve learning efficiency and predictive performance on limited data. Code available at https://github.com/joaodsmarques/Are-ECGs-enough-Deep-Learning-Classifiers .
Abn-BLIP: Abnormality-aligned Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training for Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis and Report Generation from CTPA
Mar 03, 2025Medical imaging plays a pivotal role in modern healthcare, with computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) being a critical tool for diagnosing pulmonary embolism and other thoracic conditions. However, the complexity of interpreting CTPA scans and generating accurate radiology reports remains a significant challenge. This paper introduces Abn-BLIP (Abnormality-aligned Bootstrapping Language-Image Pretraining), an advanced diagnosis model designed to align abnormal findings to generate the accuracy and comprehensiveness of radiology reports. By leveraging learnable queries and cross-modal attention mechanisms, our model demonstrates superior performance in detecting abnormalities, reducing missed findings, and generating structured reports compared to existing methods. Our experiments show that Abn-BLIP outperforms state-of-the-art medical vision-language models and 3D report generation methods in both accuracy and clinical relevance. These results highlight the potential of integrating multimodal learning strategies for improving radiology reporting. The source code is available at https://github.com/zzs95/abn-blip.
Label up: Learning Pulmonary Embolism Segmentation from Image Level Annotation through Model Explainability
Dec 10, 2024



Pulmonary Embolisms (PE) are a leading cause of cardiovascular death. Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography (CTPA) stands as the gold standard for diagnosing pulmonary embolisms (PE) and there has been a lot of interest in developing AI-based models for assisting in PE diagnosis. Performance of these algorithms has been hindered by the scarcity of annotated data, especially those with fine-grained delineation of the thromboembolic burden. In this paper we attempt to address this issue by introducing a weakly supervised learning pipeline, that leverages model explainability to generate fine-grained (pixel level) masks for embolisms starting from more coarse-grained (binary, image level) PE annotations. Furthermore, we show that training models using the automatically generated pixel annotations yields good PE localization performance. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our pipeline on the large-scale, multi-center RSPECT augmented dataset for PE detection and localization.
A Novel Generative Multi-Task Representation Learning Approach for Predicting Postoperative Complications in Cardiac Surgery Patients
Dec 02, 2024


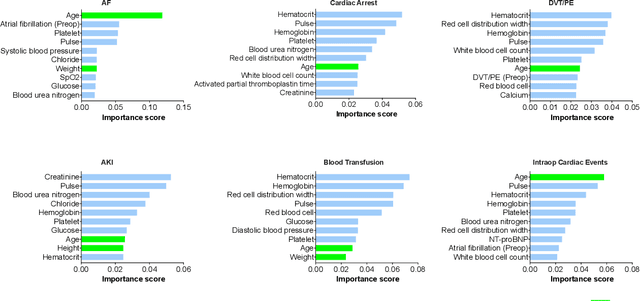
Early detection of surgical complications allows for timely therapy and proactive risk mitigation. Machine learning (ML) can be leveraged to identify and predict patient risks for postoperative complications. We developed and validated the effectiveness of predicting postoperative complications using a novel surgical Variational Autoencoder (surgVAE) that uncovers intrinsic patterns via cross-task and cross-cohort presentation learning. This retrospective cohort study used data from the electronic health records of adult surgical patients over four years (2018 - 2021). Six key postoperative complications for cardiac surgery were assessed: acute kidney injury, atrial fibrillation, cardiac arrest, deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, blood transfusion, and other intraoperative cardiac events. We compared prediction performances of surgVAE against widely-used ML models and advanced representation learning and generative models under 5-fold cross-validation. 89,246 surgeries (49% male, median (IQR) age: 57 (45-69)) were included, with 6,502 in the targeted cardiac surgery cohort (61% male, median (IQR) age: 60 (53-70)). surgVAE demonstrated superior performance over existing ML solutions across all postoperative complications of cardiac surgery patients, achieving macro-averaged AUPRC of 0.409 and macro-averaged AUROC of 0.831, which were 3.4% and 3.7% higher, respectively, than the best alternative method (by AUPRC scores). Model interpretation using Integrated Gradients highlighted key risk factors based on preoperative variable importance. surgVAE showed excellent discriminatory performance for predicting postoperative complications and addressing the challenges of data complexity, small cohort sizes, and low-frequency positive events. surgVAE enables data-driven predictions of patient risks and prognosis while enhancing the interpretability of patient risk profiles.
Improving VTE Identification through Language Models from Radiology Reports: A Comparative Study of Mamba, Phi-3 Mini, and BERT
Aug 16, 2024



Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a critical cardiovascular condition, encompassing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Accurate and timely identification of VTE is essential for effective medical care. This study builds upon our previous work, which addressed VTE detection using deep learning methods for DVT and a hybrid approach combining deep learning and rule-based classification for PE. Our earlier approaches, while effective, had two major limitations: they were complex and required expert involvement for feature engineering of the rule set. To overcome these challenges, we utilize the Mamba architecture-based classifier. This model achieves remarkable results, with a 97\% accuracy and F1 score on the DVT dataset and a 98\% accuracy and F1 score on the PE dataset. In contrast to the previous hybrid method on PE identification, the Mamba classifier eliminates the need for hand-engineered rules, significantly reducing model complexity while maintaining comparable performance. Additionally, we evaluated a lightweight Large Language Model (LLM), Phi-3 Mini, in detecting VTE. While this model delivers competitive results, outperforming the baseline BERT models, it proves to be computationally intensive due to its larger parameter set. Our evaluation shows that the Mamba-based model demonstrates superior performance and efficiency in VTE identification, offering an effective solution to the limitations of previous approaches.
PE-MVCNet: Multi-view and Cross-modal Fusion Network for Pulmonary Embolism Prediction
Feb 29, 2024



The early detection of a pulmonary embolism (PE) is critical for enhancing patient survival rates. Both image-based and non-image-based features are of utmost importance in medical classification tasks. In a clinical setting, physicians tend to rely on the contextual information provided by Electronic Medical Records (EMR) to interpret medical imaging. However, very few models effectively integrate clinical information with imaging data. To address this shortcoming, we suggest a multimodal fusion methodology, termed PE-MVCNet, which capitalizes on Computed Tomography Pulmonary Angiography imaging and EMR data. This method comprises the Image-only module with an integrated multi-view block, the EMR-only module, and the Cross-modal Attention Fusion (CMAF) module. These modules cooperate to extract comprehensive features that subsequently generate predictions for PE. We conducted experiments using the publicly accessible Stanford University Medical Center dataset, achieving an AUROC of 94.1%, an accuracy rate of 90.2%, and an F1 score of 90.6%. Our proposed model outperforms existing methodologies, corroborating that our multimodal fusion model excels compared to models that use a single data modality. Our source code is available at https://github.com/LeavingStarW/PE-MVCNET.
Deep Learning in Computed Tomography Pulmonary Angiography Imaging: A Dual-Pronged Approach for Pulmonary Embolism Detection
Nov 09, 2023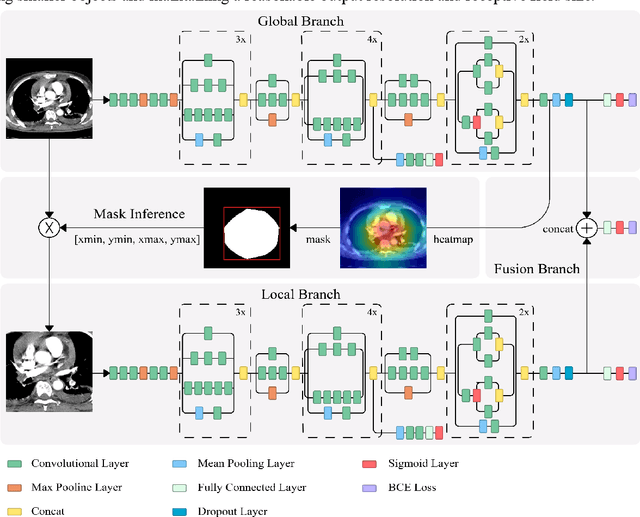
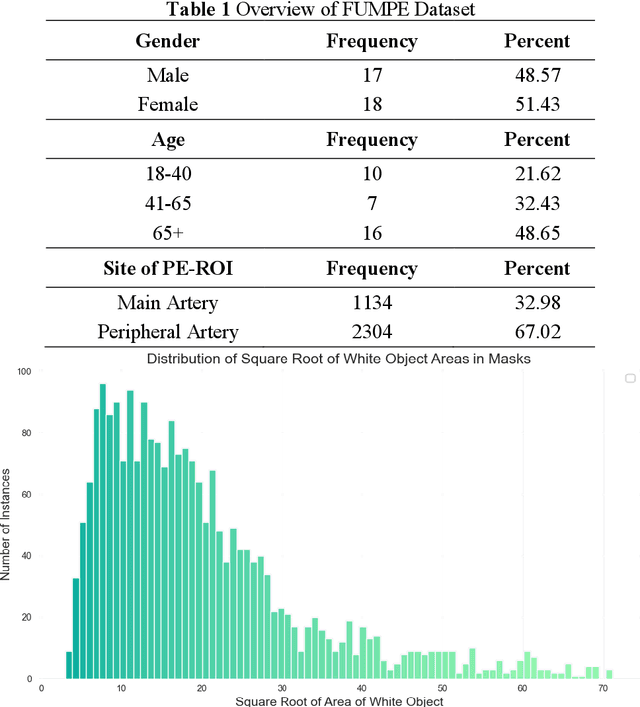
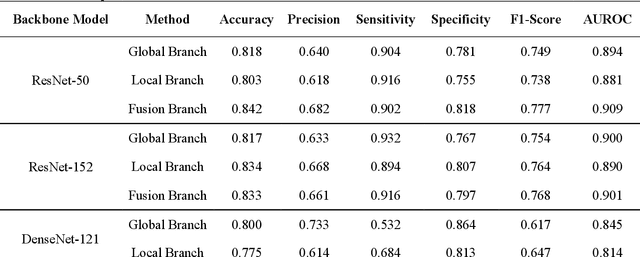
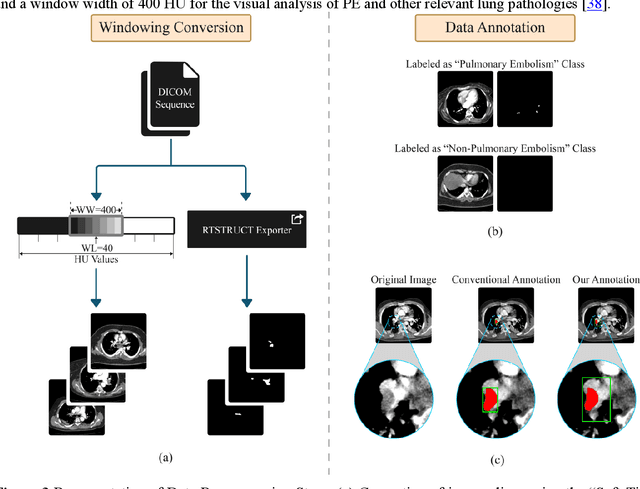
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) is a critical medical condition characterized by obstructions in the pulmonary arteries. Despite being a major health concern, it often goes underdiagnosed leading to detrimental clinical outcomes. The increasing reliance on Computed Tomography Pulmonary Angiography for diagnosis presents challenges and a pressing need for enhanced diagnostic solutions. The primary objective of this study is to leverage deep learning techniques to enhance the Computer Assisted Diagnosis of PE. This study presents a comprehensive dual-pronged approach combining classification and detection for PE diagnosis. We introduce an Attention-Guided Convolutional Neural Network (AG-CNN) for classification, addressing both global and local lesion region. For detection, state-of-the-art models are employed to pinpoint potential PE regions. Different ensembling techniques further improve detection accuracy by combining predictions from different models. Finally, a heuristic strategy integrates classifier outputs with detection results, ensuring robust and accurate PE identification. Our attention-guided classification approach, tested on the Ferdowsi University of Mashhad's Pulmonary Embolism (FUMPE) dataset, outperformed the baseline model DenseNet-121 by achieving an 8.1% increase in the Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic. By employing ensemble techniques with detection models, the mean average precision (mAP) was considerably enhanced by a 4.7% increase. The classifier-guided framework further refined the mAP and F1 scores over the ensemble models. Our research offers a comprehensive approach to PE diagnostics using deep learning, addressing the prevalent issues of underdiagnosis and misdiagnosis. We aim to improve PE patient care by integrating AI solutions into clinical workflows, highlighting the potential of human-AI collaboration in medical diagnostics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge