Scott Collins
Abn-BLIP: Abnormality-aligned Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training for Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis and Report Generation from CTPA
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Medical imaging plays a pivotal role in modern healthcare, with computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) being a critical tool for diagnosing pulmonary embolism and other thoracic conditions. However, the complexity of interpreting CTPA scans and generating accurate radiology reports remains a significant challenge. This paper introduces Abn-BLIP (Abnormality-aligned Bootstrapping Language-Image Pretraining), an advanced diagnosis model designed to align abnormal findings to generate the accuracy and comprehensiveness of radiology reports. By leveraging learnable queries and cross-modal attention mechanisms, our model demonstrates superior performance in detecting abnormalities, reducing missed findings, and generating structured reports compared to existing methods. Our experiments show that Abn-BLIP outperforms state-of-the-art medical vision-language models and 3D report generation methods in both accuracy and clinical relevance. These results highlight the potential of integrating multimodal learning strategies for improving radiology reporting. The source code is available at https://github.com/zzs95/abn-blip.
Optimizing Prompt Strategies for SAM: Advancing lesion Segmentation Across Diverse Medical Imaging Modalities
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:Purpose: To evaluate various Segmental Anything Model (SAM) prompt strategies across four lesions datasets and to subsequently develop a reinforcement learning (RL) agent to optimize SAM prompt placement. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study included patients with four independent ovarian, lung, renal, and breast tumor datasets. Manual segmentation and SAM-assisted segmentation were performed for all lesions. A RL model was developed to predict and select SAM points to maximize segmentation performance. Statistical analysis of segmentation was conducted using pairwise t-tests. Results: Results show that increasing the number of prompt points significantly improves segmentation accuracy, with Dice coefficients rising from 0.272 for a single point to 0.806 for five or more points in ovarian tumors. The prompt location also influenced performance, with surface and union-based prompts outperforming center-based prompts, achieving mean Dice coefficients of 0.604 and 0.724 for ovarian and breast tumors, respectively. The RL agent achieved a peak Dice coefficient of 0.595 for ovarian tumors, outperforming random and alternative RL strategies. Additionally, it significantly reduced segmentation time, achieving a nearly 10-fold improvement compared to manual methods using SAM. Conclusion: While increased SAM prompts and non-centered prompts generally improved segmentation accuracy, each pathology and modality has specific optimal thresholds and placement strategies. Our RL agent achieved superior performance compared to other agents while achieving a significant reduction in segmentation time.
Optimizing prompt strategies for the Segment Anything Model are explored, focusing on prompt location, number, and reinforcement learning-based agent for prompt placement across four lesion datasets
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Purpose: To evaluate various Segmental Anything Model (SAM) prompt strategies across four lesions datasets and to subsequently develop a reinforcement learning (RL) agent to optimize SAM prompt placement. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study included patients with four independent ovarian, lung, renal, and breast tumor datasets. Manual segmentation and SAM-assisted segmentation were performed for all lesions. A RL model was developed to predict and select SAM points to maximize segmentation performance. Statistical analysis of segmentation was conducted using pairwise t-tests. Results: Results show that increasing the number of prompt points significantly improves segmentation accuracy, with Dice coefficients rising from 0.272 for a single point to 0.806 for five or more points in ovarian tumors. The prompt location also influenced performance, with surface and union-based prompts outperforming center-based prompts, achieving mean Dice coefficients of 0.604 and 0.724 for ovarian and breast tumors, respectively. The RL agent achieved a peak Dice coefficient of 0.595 for ovarian tumors, outperforming random and alternative RL strategies. Additionally, it significantly reduced segmentation time, achieving a nearly 10-fold improvement compared to manual methods using SAM. Conclusion: While increased SAM prompts and non-centered prompts generally improved segmentation accuracy, each pathology and modality has specific optimal thresholds and placement strategies. Our RL agent achieved superior performance compared to other agents while achieving a significant reduction in segmentation time.
Multi-modality Regional Alignment Network for Covid X-Ray Survival Prediction and Report Generation
May 23, 2024Abstract:In response to the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic, advanced automated technologies have emerged as valuable tools to aid healthcare professionals in managing an increased workload by improving radiology report generation and prognostic analysis. This study proposes Multi-modality Regional Alignment Network (MRANet), an explainable model for radiology report generation and survival prediction that focuses on high-risk regions. By learning spatial correlation in the detector, MRANet visually grounds region-specific descriptions, providing robust anatomical regions with a completion strategy. The visual features of each region are embedded using a novel survival attention mechanism, offering spatially and risk-aware features for sentence encoding while maintaining global coherence across tasks. A cross LLMs alignment is employed to enhance the image-to-text transfer process, resulting in sentences rich with clinical detail and improved explainability for radiologist. Multi-center experiments validate both MRANet's overall performance and each module's composition within the model, encouraging further advancements in radiology report generation research emphasizing clinical interpretation and trustworthiness in AI models applied to medical studies. The code is available at https://github.com/zzs95/MRANet.
Region-specific Risk Quantification for Interpretable Prognosis of COVID-19
May 05, 2024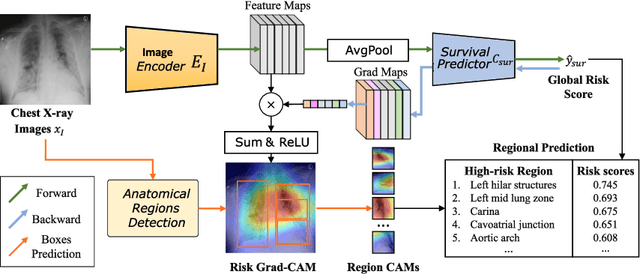
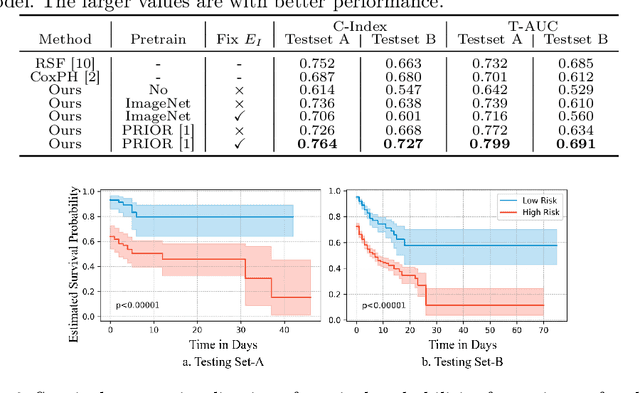
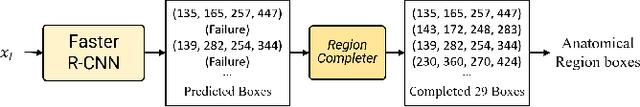
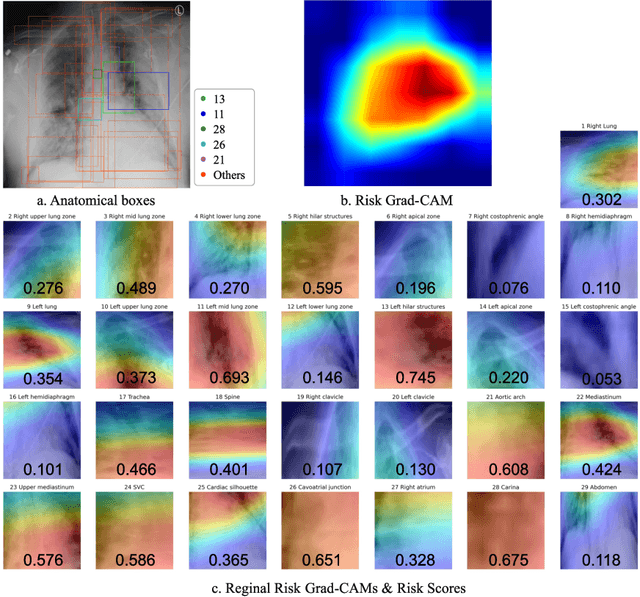
Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has strained global public health, necessitating accurate diagnosis and intervention to control disease spread and reduce mortality rates. This paper introduces an interpretable deep survival prediction model designed specifically for improved understanding and trust in COVID-19 prognosis using chest X-ray (CXR) images. By integrating a large-scale pretrained image encoder, Risk-specific Grad-CAM, and anatomical region detection techniques, our approach produces regional interpretable outcomes that effectively capture essential disease features while focusing on rare but critical abnormal regions. Our model's predictive results provide enhanced clarity and transparency through risk area localization, enabling clinicians to make informed decisions regarding COVID-19 diagnosis with better understanding of prognostic insights. We evaluate the proposed method on a multi-center survival dataset and demonstrate its effectiveness via quantitative and qualitative assessments, achieving superior C-indexes (0.764 and 0.727) and time-dependent AUCs (0.799 and 0.691). These results suggest that our explainable deep survival prediction model surpasses traditional survival analysis methods in risk prediction, improving interpretability for clinical decision making and enhancing AI system trustworthiness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge