Zishu Zhang
Optimizing Prompt Strategies for SAM: Advancing lesion Segmentation Across Diverse Medical Imaging Modalities
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:Purpose: To evaluate various Segmental Anything Model (SAM) prompt strategies across four lesions datasets and to subsequently develop a reinforcement learning (RL) agent to optimize SAM prompt placement. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study included patients with four independent ovarian, lung, renal, and breast tumor datasets. Manual segmentation and SAM-assisted segmentation were performed for all lesions. A RL model was developed to predict and select SAM points to maximize segmentation performance. Statistical analysis of segmentation was conducted using pairwise t-tests. Results: Results show that increasing the number of prompt points significantly improves segmentation accuracy, with Dice coefficients rising from 0.272 for a single point to 0.806 for five or more points in ovarian tumors. The prompt location also influenced performance, with surface and union-based prompts outperforming center-based prompts, achieving mean Dice coefficients of 0.604 and 0.724 for ovarian and breast tumors, respectively. The RL agent achieved a peak Dice coefficient of 0.595 for ovarian tumors, outperforming random and alternative RL strategies. Additionally, it significantly reduced segmentation time, achieving a nearly 10-fold improvement compared to manual methods using SAM. Conclusion: While increased SAM prompts and non-centered prompts generally improved segmentation accuracy, each pathology and modality has specific optimal thresholds and placement strategies. Our RL agent achieved superior performance compared to other agents while achieving a significant reduction in segmentation time.
Optimizing prompt strategies for the Segment Anything Model are explored, focusing on prompt location, number, and reinforcement learning-based agent for prompt placement across four lesion datasets
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Purpose: To evaluate various Segmental Anything Model (SAM) prompt strategies across four lesions datasets and to subsequently develop a reinforcement learning (RL) agent to optimize SAM prompt placement. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study included patients with four independent ovarian, lung, renal, and breast tumor datasets. Manual segmentation and SAM-assisted segmentation were performed for all lesions. A RL model was developed to predict and select SAM points to maximize segmentation performance. Statistical analysis of segmentation was conducted using pairwise t-tests. Results: Results show that increasing the number of prompt points significantly improves segmentation accuracy, with Dice coefficients rising from 0.272 for a single point to 0.806 for five or more points in ovarian tumors. The prompt location also influenced performance, with surface and union-based prompts outperforming center-based prompts, achieving mean Dice coefficients of 0.604 and 0.724 for ovarian and breast tumors, respectively. The RL agent achieved a peak Dice coefficient of 0.595 for ovarian tumors, outperforming random and alternative RL strategies. Additionally, it significantly reduced segmentation time, achieving a nearly 10-fold improvement compared to manual methods using SAM. Conclusion: While increased SAM prompts and non-centered prompts generally improved segmentation accuracy, each pathology and modality has specific optimal thresholds and placement strategies. Our RL agent achieved superior performance compared to other agents while achieving a significant reduction in segmentation time.
Optimized Biomedical Question-Answering Services with LLM and Multi-BERT Integration
Oct 11, 2024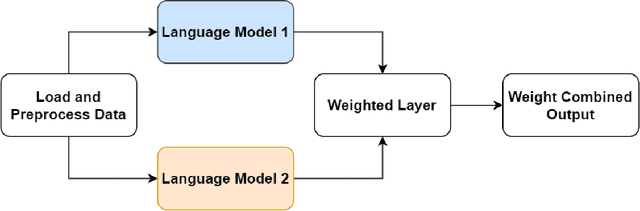
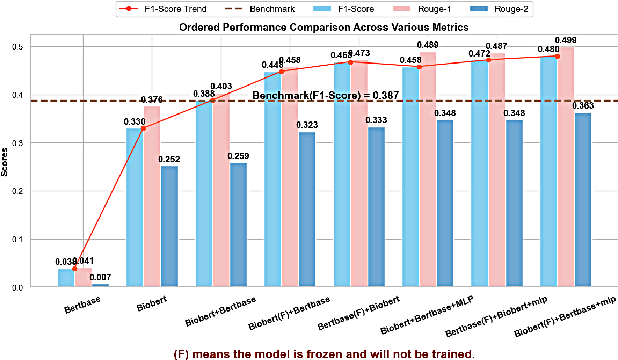
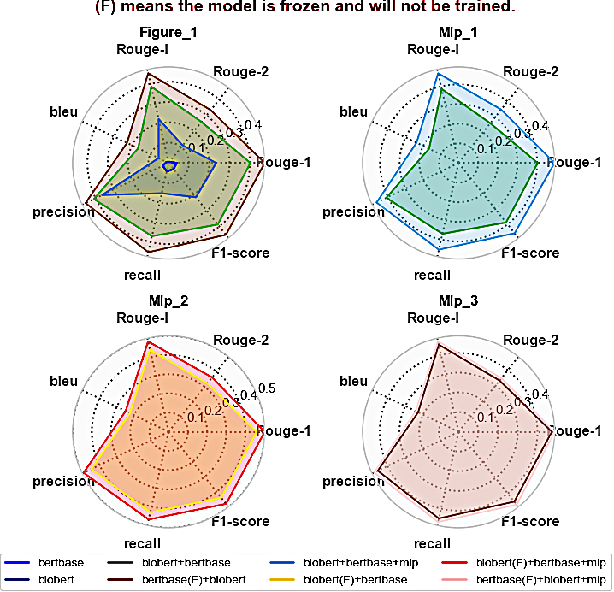
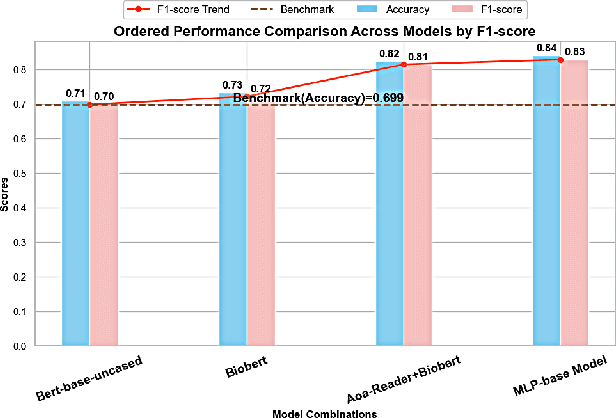
Abstract:We present a refined approach to biomedical question-answering (QA) services by integrating large language models (LLMs) with Multi-BERT configurations. By enhancing the ability to process and prioritize vast amounts of complex biomedical data, this system aims to support healthcare professionals in delivering better patient outcomes and informed decision-making. Through innovative use of BERT and BioBERT models, combined with a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) layer, we enable more specialized and efficient responses to the growing demands of the healthcare sector. Our approach not only addresses the challenge of overfitting by freezing one BERT model while training another but also improves the overall adaptability of QA services. The use of extensive datasets, such as BioASQ and BioMRC, demonstrates the system's ability to synthesize critical information. This work highlights how advanced language models can make a tangible difference in healthcare, providing reliable and responsive tools for professionals to manage complex information, ultimately serving the broader goal of improved care and data-driven insights.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge