Ali Anaissi
Towards Automated Differential Diagnosis of Skin Diseases Using Deep Learning and Imbalance-Aware Strategies
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:As dermatological conditions become increasingly common and the availability of dermatologists remains limited, there is a growing need for intelligent tools to support both patients and clinicians in the timely and accurate diagnosis of skin diseases. In this project, we developed a deep learning based model for the classification and diagnosis of skin conditions. By leveraging pretraining on publicly available skin disease image datasets, our model effectively extracted visual features and accurately classified various dermatological cases. Throughout the project, we refined the model architecture, optimized data preprocessing workflows, and applied targeted data augmentation techniques to improve overall performance. The final model, based on the Swin Transformer, achieved a prediction accuracy of 87.71 percent across eight skin lesion classes on the ISIC2019 dataset. These results demonstrate the model's potential as a diagnostic support tool for clinicians and a self assessment aid for patients.
Benchmarking Preprocessing and Integration Methods in Single-Cell Genomics
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Single-cell data analysis has the potential to revolutionize personalized medicine by characterizing disease-associated molecular changes at the single-cell level. Advanced single-cell multimodal assays can now simultaneously measure various molecules (e.g., DNA, RNA, Protein) across hundreds of thousands of individual cells, providing a comprehensive molecular readout. A significant analytical challenge is integrating single-cell measurements across different modalities. Various methods have been developed to address this challenge, but there has been no systematic evaluation of these techniques with different preprocessing strategies. This study examines a general pipeline for single-cell data analysis, which includes normalization, data integration, and dimensionality reduction. The performance of different algorithm combinations often depends on the dataset sizes and characteristics. We evaluate six datasets across diverse modalities, tissues, and organisms using three metrics: Silhouette Coefficient Score, Adjusted Rand Index, and Calinski-Harabasz Index. Our experiments involve combinations of seven normalization methods, four dimensional reduction methods, and five integration methods. The results show that Seurat and Harmony excel in data integration, with Harmony being more time-efficient, especially for large datasets. UMAP is the most compatible dimensionality reduction method with the integration techniques, and the choice of normalization method varies depending on the integration method used.
Simplified Swarm Learning Framework for Robust and Scalable Diagnostic Services in Cancer Histopathology
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:The complexities of healthcare data, including privacy concerns, imbalanced datasets, and interoperability issues, necessitate innovative machine learning solutions. Swarm Learning (SL), a decentralized alternative to Federated Learning, offers privacy-preserving distributed training, but its reliance on blockchain technology hinders accessibility and scalability. This paper introduces a \textit{Simplified Peer-to-Peer Swarm Learning (P2P-SL) Framework} tailored for resource-constrained environments. By eliminating blockchain dependencies and adopting lightweight peer-to-peer communication, the proposed framework ensures robust model synchronization while maintaining data privacy. Applied to cancer histopathology, the framework integrates optimized pre-trained models, such as TorchXRayVision, enhanced with DenseNet decoders, to improve diagnostic accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate the framework's efficacy in handling imbalanced and biased datasets, achieving comparable performance to centralized models while preserving privacy. This study paves the way for democratizing advanced machine learning in healthcare, offering a scalable, accessible, and efficient solution for privacy-sensitive diagnostic applications.
Detecting and Understanding Hateful Contents in Memes Through Captioning and Visual Question-Answering
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:Memes are widely used for humor and cultural commentary, but they are increasingly exploited to spread hateful content. Due to their multimodal nature, hateful memes often evade traditional text-only or image-only detection systems, particularly when they employ subtle or coded references. To address these challenges, we propose a multimodal hate detection framework that integrates key components: OCR to extract embedded text, captioning to describe visual content neutrally, sub-label classification for granular categorization of hateful content, RAG for contextually relevant retrieval, and VQA for iterative analysis of symbolic and contextual cues. This enables the framework to uncover latent signals that simpler pipelines fail to detect. Experimental results on the Facebook Hateful Memes dataset reveal that the proposed framework exceeds the performance of unimodal and conventional multimodal models in both accuracy and AUC-ROC.
Vision Transformers with Autoencoders and Explainable AI for Cancer Patient Risk Stratification Using Whole Slide Imaging
Apr 08, 2025



Abstract:Cancer remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, necessitating accurate diagnosis and prognosis. Whole Slide Imaging (WSI) has become an integral part of clinical workflows with advancements in digital pathology. While various studies have utilized WSIs, their extracted features may not fully capture the most relevant pathological information, and their lack of interpretability limits clinical adoption. In this paper, we propose PATH-X, a framework that integrates Vision Transformers (ViT) and Autoencoders with SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations) to enhance model explainability for patient stratification and risk prediction using WSIs from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). A representative image slice is selected from each WSI, and numerical feature embeddings are extracted using Google's pre-trained ViT. These features are then compressed via an autoencoder and used for unsupervised clustering and classification tasks. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis is applied to evaluate stratification into two and three risk groups. SHAP is used to identify key contributing features, which are mapped onto histopathological slices to provide spatial context. PATH-X demonstrates strong performance in breast and glioma cancers, where a sufficient number of WSIs enabled robust stratification. However, performance in lung cancer was limited due to data availability, emphasizing the need for larger datasets to enhance model reliability and clinical applicability.
FedSAF: A Federated Learning Framework for Enhanced Gastric Cancer Detection and Privacy Preservation
Mar 20, 2025
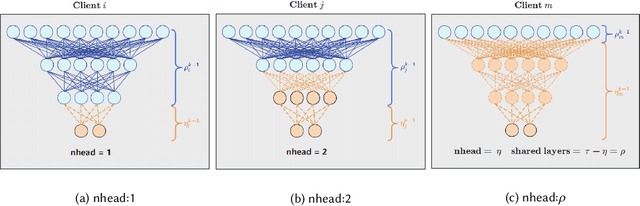
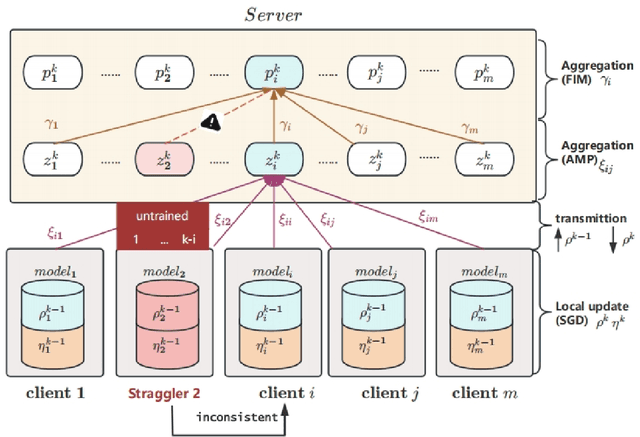
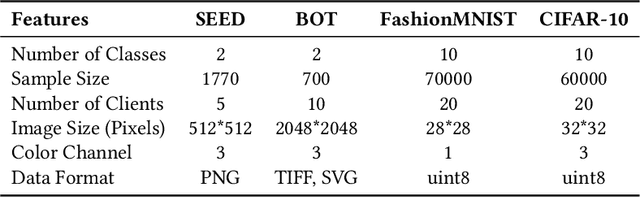
Abstract:Gastric cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers and has a high mortality rate. Due to limited medical resources, developing machine learning models for gastric cancer recognition provides an efficient solution for medical institutions. However, such models typically require large sample sizes for training and testing, which can challenge patient privacy. Federated learning offers an effective alternative by enabling model training across multiple institutions without sharing sensitive patient data. This paper addresses the limited sample size of publicly available gastric cancer data with a modified data processing method. This paper introduces FedSAF, a novel federated learning algorithm designed to improve the performance of existing methods, particularly in non-independent and identically distributed (non-IID) data scenarios. FedSAF incorporates attention-based message passing and the Fisher Information Matrix to enhance model accuracy, while a model splitting function reduces computation and transmission costs. Hyperparameter tuning and ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness of this new algorithm, showing improvements in test accuracy on gastric cancer datasets, with FedSAF outperforming existing federated learning methods like FedAMP, FedAvg, and FedProx. The framework's robustness and generalization ability were further validated across additional datasets (SEED, BOT, FashionMNIST, and CIFAR-10), achieving high performance in diverse environments.
Enhancing Sentiment Analysis through Multimodal Fusion: A BERT-DINOv2 Approach
Mar 11, 2025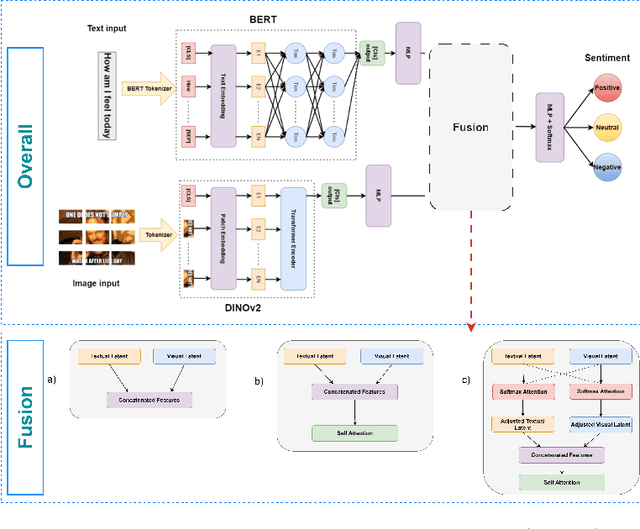
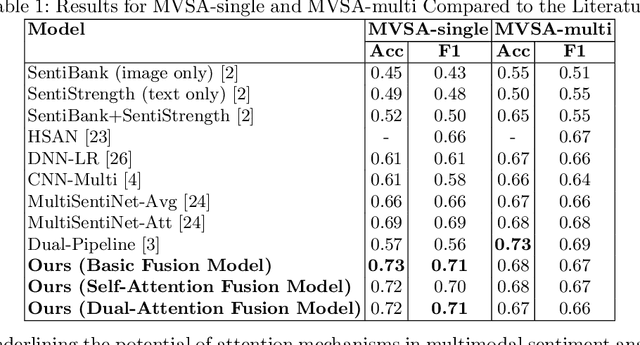
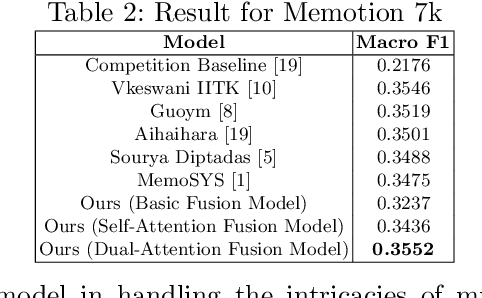
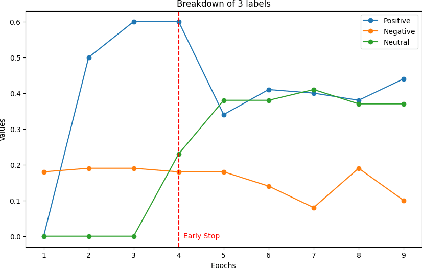
Abstract:Multimodal sentiment analysis enhances conventional sentiment analysis, which traditionally relies solely on text, by incorporating information from different modalities such as images, text, and audio. This paper proposes a novel multimodal sentiment analysis architecture that integrates text and image data to provide a more comprehensive understanding of sentiments. For text feature extraction, we utilize BERT, a natural language processing model. For image feature extraction, we employ DINOv2, a vision-transformer-based model. The textual and visual latent features are integrated using proposed fusion techniques, namely the Basic Fusion Model, Self Attention Fusion Model, and Dual Attention Fusion Model. Experiments on three datasets, Memotion 7k dataset, MVSA single dataset, and MVSA multi dataset, demonstrate the viability and practicality of the proposed multimodal architecture.
Fine-Tuning LLMs for Reliable Medical Question-Answering Services
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:We present an advanced approach to medical question-answering (QA) services, using fine-tuned Large Language Models (LLMs) to improve the accuracy and reliability of healthcare information. Our study focuses on optimizing models like LLaMA-2 and Mistral, which have shown great promise in delivering precise, reliable medical answers. By leveraging comprehensive datasets, we applied fine-tuning techniques such as rsDoRA+ and ReRAG. rsDoRA+ enhances model performance through a combination of decomposed model weights, varied learning rates for low-rank matrices, and rank stabilization, leading to improved efficiency. ReRAG, which integrates retrieval on demand and question rewriting, further refines the accuracy of the responses. This approach enables healthcare providers to access fast, dependable information, aiding in more efficient decision-making and fostering greater patient trust. Our work highlights the potential of fine-tuned LLMs to significantly improve the quality and accessibility of medical information services, ultimately contributing to better healthcare outcomes for all.
Optimized Biomedical Question-Answering Services with LLM and Multi-BERT Integration
Oct 11, 2024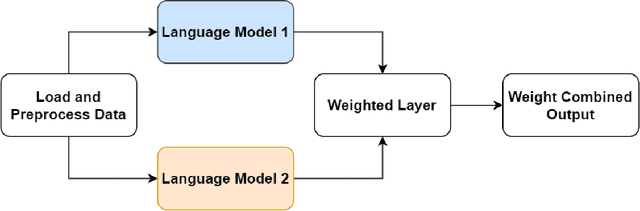
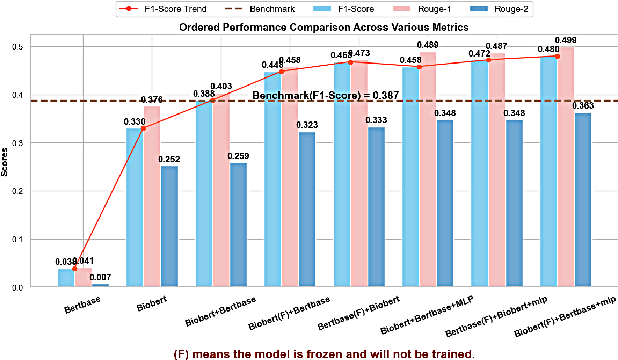
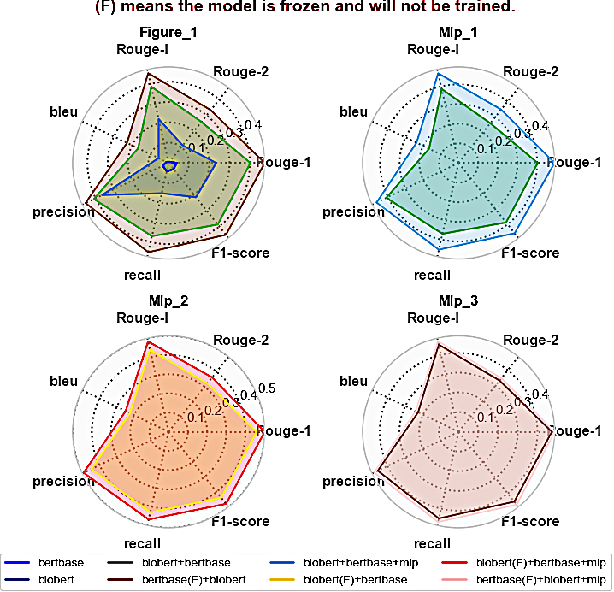
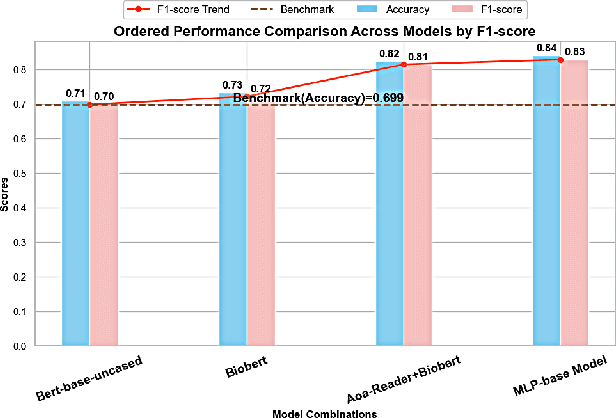
Abstract:We present a refined approach to biomedical question-answering (QA) services by integrating large language models (LLMs) with Multi-BERT configurations. By enhancing the ability to process and prioritize vast amounts of complex biomedical data, this system aims to support healthcare professionals in delivering better patient outcomes and informed decision-making. Through innovative use of BERT and BioBERT models, combined with a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) layer, we enable more specialized and efficient responses to the growing demands of the healthcare sector. Our approach not only addresses the challenge of overfitting by freezing one BERT model while training another but also improves the overall adaptability of QA services. The use of extensive datasets, such as BioASQ and BioMRC, demonstrates the system's ability to synthesize critical information. This work highlights how advanced language models can make a tangible difference in healthcare, providing reliable and responsive tools for professionals to manage complex information, ultimately serving the broader goal of improved care and data-driven insights.
Optimisation of federated learning settings under statistical heterogeneity variations
Jun 10, 2024



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables local devices to collaboratively learn a shared predictive model by only periodically sharing model parameters with a central aggregator. However, FL can be disadvantaged by statistical heterogeneity produced by the diversity in each local devices data distribution, which creates different levels of Independent and Identically Distributed (IID) data. Furthermore, this can be more complex when optimising different combinations of FL parameters and choosing optimal aggregation. In this paper, we present an empirical analysis of different FL training parameters and aggregators over various levels of statistical heterogeneity on three datasets. We propose a systematic data partition strategy to simulate different levels of statistical heterogeneity and a metric to measure the level of IID. Additionally, we empirically identify the best FL model and key parameters for datasets of different characteristics. On the basis of these, we present recommended guidelines for FL parameters and aggregators to optimise model performance under different levels of IID and with different datasets
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge