Color Anomaly Detection
Papers and Code
Privacy Beyond Pixels: Latent Anonymization for Privacy-Preserving Video Understanding
Nov 11, 2025We introduce a novel formulation of visual privacy preservation for video foundation models that operates entirely in the latent space. While spatio-temporal features learned by foundation models have deepened general understanding of video content, sharing or storing these extracted visual features for downstream tasks inadvertently reveals sensitive personal information like skin color, gender, or clothing. Current privacy preservation methods focus on input-pixel-level anonymization, which requires retraining the entire utility video model and results in task-specific anonymization, making them unsuitable for recent video foundational models. To address these challenges, we introduce a lightweight Anonymizing Adapter Module (AAM) that removes private information from video features while retaining general task utility. AAM can be applied in a plug-and-play fashion to frozen video encoders, minimizing the computational burden of finetuning and re-extracting features. Our framework employs three newly designed training objectives: (1) a clip-level self-supervised privacy objective to reduce mutual information between static clips, (2) a co-training objective to retain utility across seen tasks, and (3) a latent consistency loss for generalization on unseen tasks. Our extensive evaluations demonstrate a significant 35% reduction in privacy leakage while maintaining near-baseline utility performance across various downstream tasks: Action Recognition (Kinetics400, UCF101, HMDB51), Temporal Action Detection (THUMOS14), and Anomaly Detection (UCF-Crime). We also provide an analysis on anonymization for sensitive temporal attribute recognition. Additionally, we propose new protocols for assessing gender bias in action recognition models, showing that our method effectively mitigates such biases and promotes more equitable video understanding.
WSCIF: A Weakly-Supervised Color Intelligence Framework for Tactical Anomaly Detection in Surveillance Keyframes
May 14, 2025
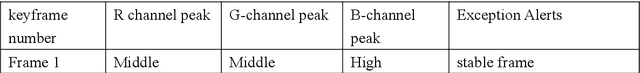
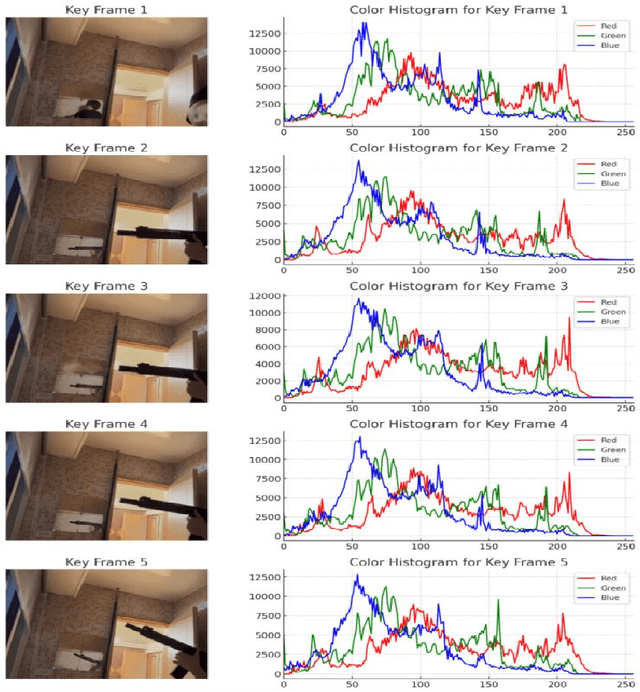
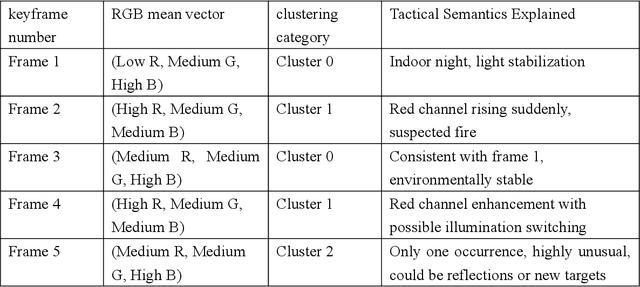
The deployment of traditional deep learning models in high-risk security tasks in an unlabeled, data-non-exploitable video intelligence environment faces significant challenges. In this paper, we propose a lightweight anomaly detection framework based on color features for surveillance video clips in a high sensitivity tactical mission, aiming to quickly identify and interpret potential threat events under resource-constrained and data-sensitive conditions. The method fuses unsupervised KMeans clustering with RGB channel histogram modeling to achieve composite detection of structural anomalies and color mutation signals in key frames. The experiment takes an operation surveillance video occurring in an African country as a research sample, and successfully identifies multiple highly anomalous frames related to high-energy light sources, target presence, and reflective interference under the condition of no access to the original data. The results show that this method can be effectively used for tactical assassination warning, suspicious object screening and environmental drastic change monitoring with strong deployability and tactical interpretation value. The study emphasizes the importance of color features as low semantic battlefield signal carriers, and its battlefield intelligent perception capability will be further extended by combining graph neural networks and temporal modeling in the future.
AnomalyHybrid: A Domain-agnostic Generative Framework for General Anomaly Detection
Apr 06, 2025Anomaly generation is an effective way to mitigate data scarcity for anomaly detection task. Most existing works shine at industrial anomaly generation with multiple specialists or large generative models, rarely generalizing to anomalies in other applications. In this paper, we present AnomalyHybrid, a domain-agnostic framework designed to generate authentic and diverse anomalies simply by combining the reference and target images. AnomalyHybrid is a Generative Adversarial Network(GAN)-based framework having two decoders that integrate the appearance of reference image into the depth and edge structures of target image respectively. With the help of depth decoders, AnomalyHybrid achieves authentic generation especially for the anomalies with depth values changing, such a s protrusion and dent. More, it relaxes the fine granularity structural control of the edge decoder and brings more diversity. Without using annotations, AnomalyHybrid is easily trained with sets of color, depth and edge of same images having different augmentations. Extensive experiments carried on HeliconiusButterfly, MVTecAD and MVTec3D datasets demonstrate that AnomalyHybrid surpasses the GAN-based state-of-the-art on anomaly generation and its downstream anomaly classification, detection and segmentation tasks. On MVTecAD dataset, AnomalyHybrid achieves 2.06/0.32 IS/LPIPS for anomaly generation, 52.6 Acc for anomaly classification with ResNet34, 97.3/72.9 AP for image/pixel-level anomaly detection with a simple UNet.
Anomaly Detection for Hybrid Butterfly Subspecies via Probability Filtering
Apr 02, 2025Detecting butterfly hybrids requires knowledge of the parent subspecies, and the process can be tedious when encountering a new subspecies. This study focuses on a specific scenario where a model trained to recognize hybrid species A can generalize to species B when B biologically mimics A. Since species A and B share similar patterns, we leverage BioCLIP as our feature extractor to capture features based on their taxonomy. Consequently, the algorithm designed for species A can be transferred to B, as their hybrid and non-hybrid patterns exhibit similar relationships. To determine whether a butterfly is a hybrid, we adopt proposed probability filtering and color jittering to augment and simulate the mimicry. With these approaches, we achieve second place in the official development phase. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Justin900429/NSF-HDR-Challenge.
Revisiting DDIM Inversion for Controlling Defect Generation by Disentangling the Background
Nov 25, 2024In anomaly detection, the scarcity of anomalous data compared to normal data poses a challenge in effectively utilizing deep neural network representations to identify anomalous features. From a data-centric perspective, generative models can solve this data imbalance issue by synthesizing anomaly datasets. Although previous research tried to enhance the controllability and quality of generating defects, they do not consider the relation between background and defect. Since the defect depends on the object's background (i.e., the normal part of an object), training only the defect area cannot utilize the background information, and even generation can be biased depending on the mask information. In addition, controlling logical anomalies should consider the dependency between background and defect areas (e.g., orange colored defect on a orange juice bottle). In this paper, our paper proposes modeling a relationship between the background and defect, where background affects denoising defects; however, the reverse is not. We introduce the regularizing term to disentangle denoising background from defects. From the disentanglement loss, we rethink defect generation with DDIM Inversion, where we generate the defect on the target normal image. Additionally, we theoretically prove that our methodology can generate a defect on the target normal image with an invariant background. We demonstrate our synthetic data is realistic and effective in several experiments.
Unveiling Context-Related Anomalies: Knowledge Graph Empowered Decoupling of Scene and Action for Human-Related Video Anomaly Detection
Sep 05, 2024Detecting anomalies in human-related videos is crucial for surveillance applications. Current methods primarily include appearance-based and action-based techniques. Appearance-based methods rely on low-level visual features such as color, texture, and shape. They learn a large number of pixel patterns and features related to known scenes during training, making them effective in detecting anomalies within these familiar contexts. However, when encountering new or significantly changed scenes, i.e., unknown scenes, they often fail because existing SOTA methods do not effectively capture the relationship between actions and their surrounding scenes, resulting in low generalization. In contrast, action-based methods focus on detecting anomalies in human actions but are usually less informative because they tend to overlook the relationship between actions and their scenes, leading to incorrect detection. For instance, the normal event of running on the beach and the abnormal event of running on the street might both be considered normal due to the lack of scene information. In short, current methods struggle to integrate low-level visual and high-level action features, leading to poor anomaly detection in varied and complex scenes. To address this challenge, we propose a novel decoupling-based architecture for human-related video anomaly detection (DecoAD). DecoAD significantly improves the integration of visual and action features through the decoupling and interweaving of scenes and actions, thereby enabling a more intuitive and accurate understanding of complex behaviors and scenes. DecoAD supports fully supervised, weakly supervised, and unsupervised settings.
Texture-AD: An Anomaly Detection Dataset and Benchmark for Real Algorithm Development
Sep 10, 2024



Anomaly detection is a crucial process in industrial manufacturing and has made significant advancements recently. However, there is a large variance between the data used in the development and the data collected by the production environment. Therefore, we present the Texture-AD benchmark based on representative texture-based anomaly detection to evaluate the effectiveness of unsupervised anomaly detection algorithms in real-world applications. This dataset includes images of 15 different cloth, 14 semiconductor wafers and 10 metal plates acquired under different optical schemes. In addition, it includes more than 10 different types of defects produced during real manufacturing processes, such as scratches, wrinkles, color variations and point defects, which are often more difficult to detect than existing datasets. All anomalous areas are provided with pixel-level annotations to facilitate comprehensive evaluation using anomaly detection models. Specifically, to adapt to diverse products in automated pipelines, we present a new evaluation method and results of baseline algorithms. The experimental results show that Texture-AD is a difficult challenge for state-of-the-art algorithms. To our knowledge, Texture-AD is the first dataset to be devoted to evaluating industrial defect detection algorithms in the real world. The dataset is available at https://XXX.
Capsule Endoscopy Multi-classification via Gated Attention and Wavelet Transformations
Oct 25, 2024
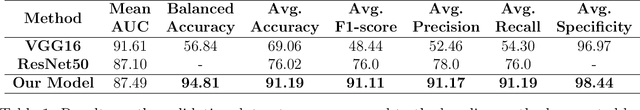
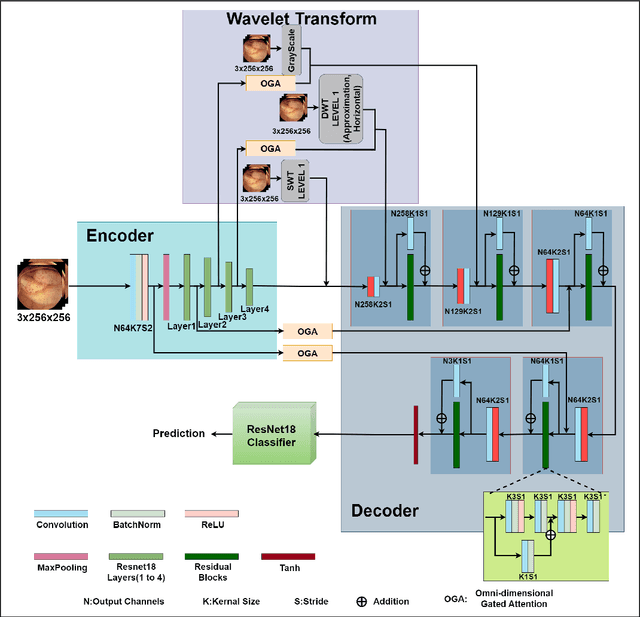
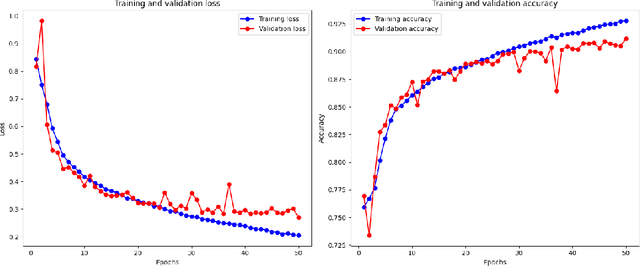
Abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract significantly influence the patient's health and require a timely diagnosis for effective treatment. With such consideration, an effective automatic classification of these abnormalities from a video capsule endoscopy (VCE) frame is crucial for improvement in diagnostic workflows. The work presents the process of developing and evaluating a novel model designed to classify gastrointestinal anomalies from a VCE video frame. Integration of Omni Dimensional Gated Attention (OGA) mechanism and Wavelet transformation techniques into the model's architecture allowed the model to focus on the most critical areas in the endoscopy images, reducing noise and irrelevant features. This is particularly advantageous in capsule endoscopy, where images often contain a high degree of variability in texture and color. Wavelet transformations contributed by efficiently capturing spatial and frequency-domain information, improving feature extraction, especially for detecting subtle features from the VCE frames. Furthermore, the features extracted from the Stationary Wavelet Transform and Discrete Wavelet Transform are concatenated channel-wise to capture multiscale features, which are essential for detecting polyps, ulcerations, and bleeding. This approach improves classification accuracy on imbalanced capsule endoscopy datasets. The proposed model achieved 92.76% and 91.19% as training and validation accuracies respectively. At the same time, Training and Validation losses are 0.2057 and 0.2700. The proposed model achieved a Balanced Accuracy of 94.81%, AUC of 87.49%, F1-score of 91.11%, precision of 91.17%, recall of 91.19% and specificity of 98.44%. Additionally, the model's performance is benchmarked against two base models, VGG16 and ResNet50, demonstrating its enhanced ability to identify and classify a range of gastrointestinal abnormalities accurately.
Fine-grained Abnormality Prompt Learning for Zero-shot Anomaly Detection
Oct 14, 2024



Current zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) methods show remarkable success in prompting large pre-trained vision-language models to detect anomalies in a target dataset without using any dataset-specific training or demonstration. However, these methods are often focused on crafting/learning prompts that capture only coarse-grained semantics of abnormality, e.g., high-level semantics like "damaged", "imperfect", or "defective" on carpet. They therefore have limited capability in recognizing diverse abnormality details with distinctive visual appearance, e.g., specific defect types like color stains, cuts, holes, and threads on carpet. To address this limitation, we propose FAPrompt, a novel framework designed to learn Fine-grained Abnormality Prompts for more accurate ZSAD. To this end, we introduce a novel compound abnormality prompting module in FAPrompt to learn a set of complementary, decomposed abnormality prompts, where each abnormality prompt is formed by a compound of shared normal tokens and a few learnable abnormal tokens. On the other hand, the fine-grained abnormality patterns can be very different from one dataset to another. To enhance their cross-dataset generalization, we further introduce a data-dependent abnormality prior module that learns to derive abnormality features from each query/test image as a sample-wise abnormality prior to ground the abnormality prompts in a given target dataset. Comprehensive experiments conducted across 19 real-world datasets, covering both industrial defects and medical anomalies, demonstrate that FAPrompt substantially outperforms state-of-the-art methods by at least 3%-5% AUC/AP in both image- and pixel-level ZSAD tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/mala-lab/FAPrompt.
DDoS: Diffusion Distribution Similarity for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Sep 16, 2024



Out-of-Distribution (OoD) detection determines whether the given samples are from the training distribution of the classifier-under-protection, i.e., the In-Distribution (InD), or from a different OoD. Latest researches introduce diffusion models pre-trained on InD data to advocate OoD detection by transferring an OoD image into a generated one that is close to InD, so that one could capture the distribution disparities between original and generated images to detect OoD data. Existing diffusion-based detectors adopt perceptual metrics on the two images to measure such disparities, but ignore a fundamental fact: Perceptual metrics are devised essentially for human-perceived similarities of low-level image patterns, e.g., textures and colors, and are not advisable in evaluating distribution disparities, since images with different low-level patterns could possibly come from the same distribution. To address this issue, we formulate a diffusion-based detection framework that considers the distribution similarity between a tested image and its generated counterpart via a novel proper similarity metric in the informative feature space and probability space learned by the classifier-under-protection. An anomaly-removal strategy is further presented to enlarge such distribution disparities by removing abnormal OoD information in the feature space to facilitate the detection. Extensive empirical results unveil the insufficiency of perceptual metrics and the effectiveness of our distribution similarity framework with new state-of-the-art detection performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge