Zhenming Liu
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Nanjing University
MEMS Gyroscope Multi-Feature Calibration Using Machine Learning Technique
Oct 10, 2024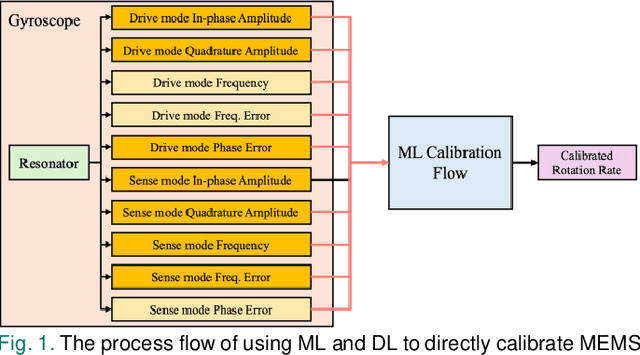
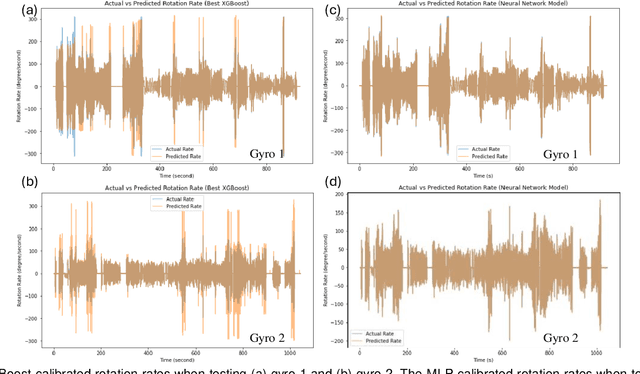
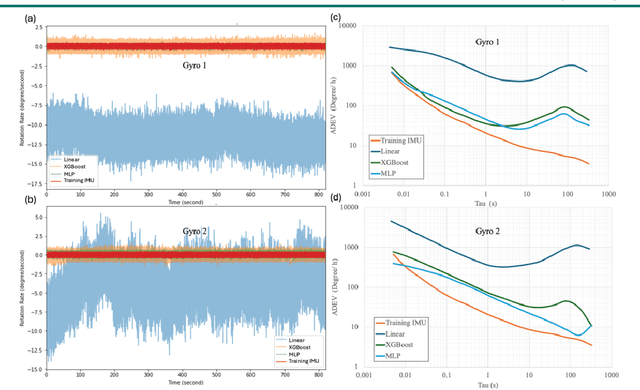
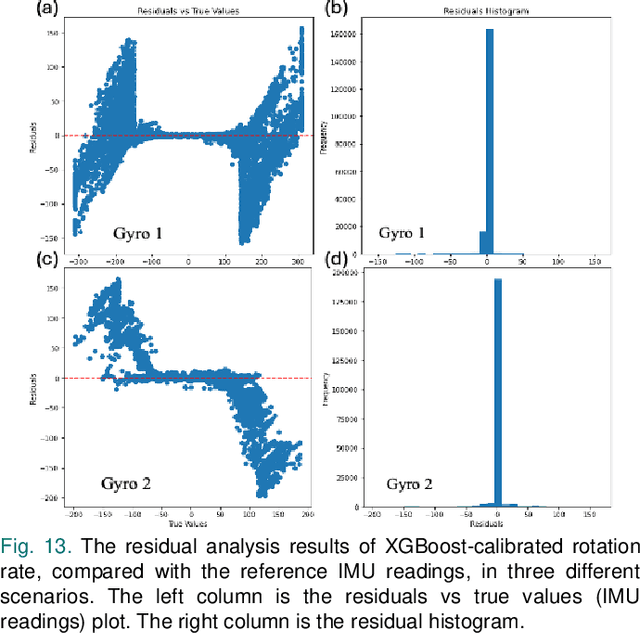
Abstract:Gyroscopes are crucial for accurate angular velocity measurements in navigation, stabilization, and control systems. MEMS gyroscopes offer advantages like compact size and low cost but suffer from errors and inaccuracies that are complex and time varying. This study leverages machine learning (ML) and uses multiple signals of the MEMS resonator gyroscope to improve its calibration. XGBoost, known for its high predictive accuracy and ability to handle complex, non-linear relationships, and MLP, recognized for its capability to model intricate patterns through multiple layers and hidden dimensions, are employed to enhance the calibration process. Our findings show that both XGBoost and MLP models significantly reduce noise and enhance accuracy and stability, outperforming the traditional calibration techniques. Despite higher computational costs, DL models are ideal for high-stakes applications, while ML models are efficient for consumer electronics and environmental monitoring. Both ML and DL models demonstrate the potential of advanced calibration techniques in enhancing MEMS gyroscope performance and calibration efficiency.
Latent Chemical Space Searching for Plug-in Multi-objective Molecule Generation
Apr 10, 2024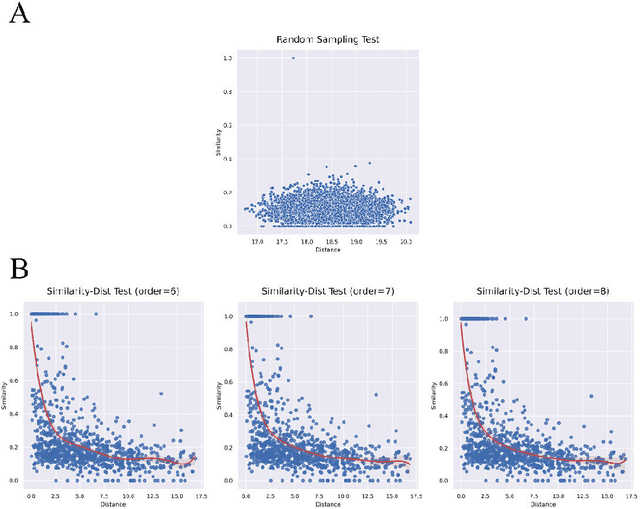
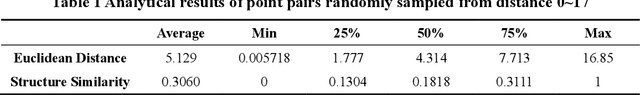
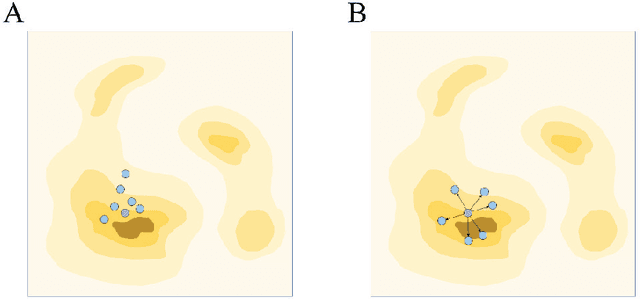
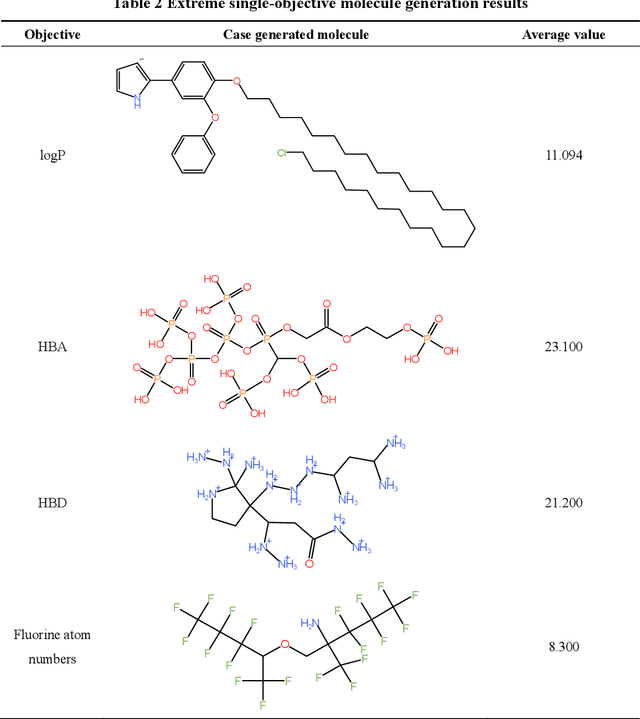
Abstract:Molecular generation, an essential method for identifying new drug structures, has been supported by advancements in machine learning and computational technology. However, challenges remain in multi-objective generation, model adaptability, and practical application in drug discovery. In this study, we developed a versatile 'plug-in' molecular generation model that incorporates multiple objectives related to target affinity, drug-likeness, and synthesizability, facilitating its application in various drug development contexts. We improved the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) in the context of drug discoveries, and identified PSO-ENP as the optimal variant for multi-objective molecular generation and optimization through comparative experiments. The model also incorporates a novel target-ligand affinity predictor, enhancing the model's utility by supporting three-dimensional information and improving synthetic feasibility. Case studies focused on generating and optimizing drug-like big marine natural products were performed, underscoring PSO-ENP's effectiveness and demonstrating its considerable potential for practical drug discovery applications.
Uni-RXN: A Unified Framework Bridging the Gap between Chemical Reaction Pretraining and Conditional Molecule Generation
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:Chemical reactions are the fundamental building blocks of drug design and organic chemistry research. In recent years, there has been a growing need for a large-scale deep-learning framework that can efficiently capture the basic rules of chemical reactions. In this paper, we have proposed a unified framework that addresses both the reaction representation learning and molecule generation tasks, which allows for a more holistic approach. Inspired by the organic chemistry mechanism, we develop a novel pretraining framework that enables us to incorporate inductive biases into the model. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art results on challenging downstream tasks. By possessing chemical knowledge, this framework can be applied to reaction-based generative models, overcoming the limitations of current molecule generation models that rely on a small number of reaction templates. In the extensive experiments, our model generates synthesizable drug-like structures of high quality. Overall, our work presents a significant step toward a large-scale deep-learning framework for a variety of reaction-based applications.
Symphony in the Latent Space: Provably Integrating High-dimensional Techniques with Non-linear Machine Learning Models
Dec 01, 2022



Abstract:This paper revisits building machine learning algorithms that involve interactions between entities, such as those between financial assets in an actively managed portfolio, or interactions between users in a social network. Our goal is to forecast the future evolution of ensembles of multivariate time series in such applications (e.g., the future return of a financial asset or the future popularity of a Twitter account). Designing ML algorithms for such systems requires addressing the challenges of high-dimensional interactions and non-linearity. Existing approaches usually adopt an ad-hoc approach to integrating high-dimensional techniques into non-linear models and recent studies have shown these approaches have questionable efficacy in time-evolving interacting systems. To this end, we propose a novel framework, which we dub as the additive influence model. Under our modeling assumption, we show that it is possible to decouple the learning of high-dimensional interactions from the learning of non-linear feature interactions. To learn the high-dimensional interactions, we leverage kernel-based techniques, with provable guarantees, to embed the entities in a low-dimensional latent space. To learn the non-linear feature-response interactions, we generalize prominent machine learning techniques, including designing a new statistically sound non-parametric method and an ensemble learning algorithm optimized for vector regressions. Extensive experiments on two common applications demonstrate that our new algorithms deliver significantly stronger forecasting power compared to standard and recently proposed methods.
* 24 pages
Towards Reliable Item Sampling for Recommendation Evaluation
Nov 28, 2022



Abstract:Since Rendle and Krichene argued that commonly used sampling-based evaluation metrics are ``inconsistent'' with respect to the global metrics (even in expectation), there have been a few studies on the sampling-based recommender system evaluation. Existing methods try either mapping the sampling-based metrics to their global counterparts or more generally, learning the empirical rank distribution to estimate the top-$K$ metrics. However, despite existing efforts, there is still a lack of rigorous theoretical understanding of the proposed metric estimators, and the basic item sampling also suffers from the ``blind spot'' issue, i.e., estimation accuracy to recover the top-$K$ metrics when $K$ is small can still be rather substantial. In this paper, we provide an in-depth investigation into these problems and make two innovative contributions. First, we propose a new item-sampling estimator that explicitly optimizes the error with respect to the ground truth, and theoretically highlight its subtle difference against prior work. Second, we propose a new adaptive sampling method which aims to deal with the ``blind spot'' problem and also demonstrate the expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm can be generalized for such a setting. Our experimental results confirm our statistical analysis and the superiority of the proposed works. This study helps lay the theoretical foundation for adopting item sampling metrics for recommendation evaluation, and provides strong evidence towards making item sampling a powerful and reliable tool for recommendation evaluation.
On Extending NLP Techniques from the Categorical to the Latent Space: KL Divergence, Zipf's Law, and Similarity Search
Dec 02, 2020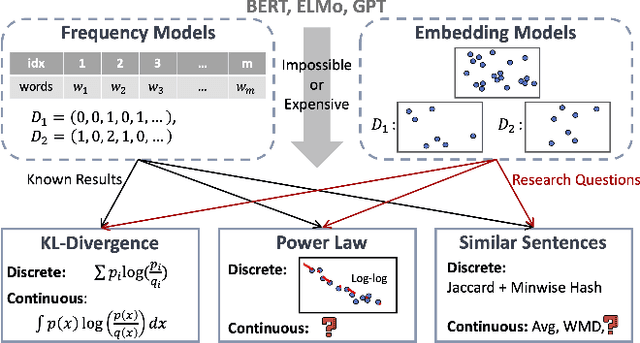
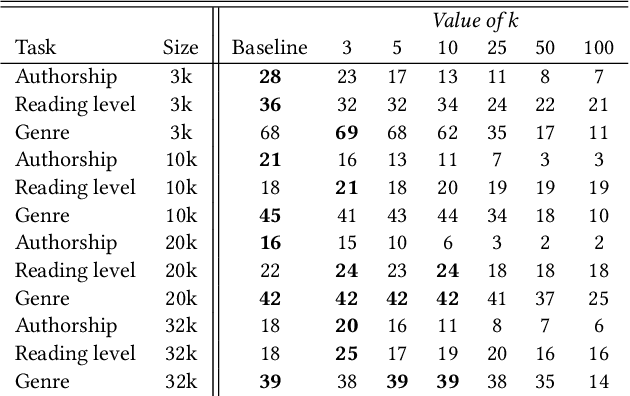
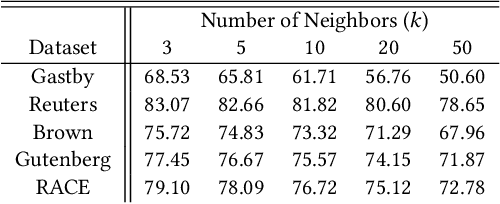
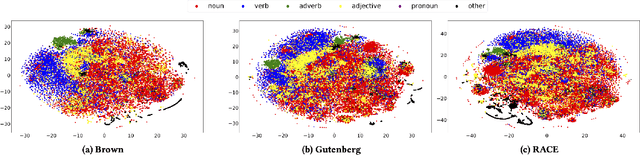
Abstract:Despite the recent successes of deep learning in natural language processing (NLP), there remains widespread usage of and demand for techniques that do not rely on machine learning. The advantage of these techniques is their interpretability and low cost when compared to frequently opaque and expensive machine learning models. Although they may not be be as performant in all cases, they are often sufficient for common and relatively simple problems. In this paper, we aim to modernize these older methods while retaining their advantages by extending approaches from categorical or bag-of-words representations to word embeddings representations in the latent space. First, we show that entropy and Kullback-Leibler divergence can be efficiently estimated using word embeddings and use this estimation to compare text across several categories. Next, we recast the heavy-tailed distribution known as Zipf's law that is frequently observed in the categorical space to the latent space. Finally, we look to improve the Jaccard similarity measure for sentence suggestion by introducing a new method of identifying similar sentences based on the set cover problem. We compare the performance of this algorithm against several baselines including Word Mover's Distance and the Levenshtein distance.
Rosella: A Self-Driving Distributed Scheduler for Heterogeneous Clusters
Nov 10, 2020



Abstract:Large-scale interactive web services and advanced AI applications make sophisticated decisions in real-time, based on executing a massive amount of computation tasks on thousands of servers. Task schedulers, which often operate in heterogeneous and volatile environments, require high throughput, i.e., scheduling millions of tasks per second, and low latency, i.e., incurring minimal scheduling delays for millisecond-level tasks. Scheduling is further complicated by other users' workloads in a shared system, other background activities, and the diverse hardware configurations inside datacenters. We present Rosella, a new self-driving, distributed approach for task scheduling in heterogeneous clusters. Our system automatically learns the compute environment and adjust its scheduling policy in real-time. The solution provides high throughput and low latency simultaneously, because it runs in parallel on multiple machines with minimum coordination and only performs simple operations for each scheduling decision. Our learning module monitors total system load, and uses the information to dynamically determine optimal estimation strategy for the backends' compute-power. Our scheduling policy generalizes power-of-two-choice algorithms to handle heterogeneous workers, reducing the max queue length of $O(\log n)$ obtained by prior algorithms to $O(\log \log n)$. We implement a Rosella prototype and evaluate it with a variety of workloads. Experimental results show that Rosella significantly reduces task response times, and adapts to environment changes quickly.
On Efficient Constructions of Checkpoints
Sep 28, 2020



Abstract:Efficient construction of checkpoints/snapshots is a critical tool for training and diagnosing deep learning models. In this paper, we propose a lossy compression scheme for checkpoint constructions (called LC-Checkpoint). LC-Checkpoint simultaneously maximizes the compression rate and optimizes the recovery speed, under the assumption that SGD is used to train the model. LC-Checkpointuses quantization and priority promotion to store the most crucial information for SGD to recover, and then uses a Huffman coding to leverage the non-uniform distribution of the gradient scales. Our extensive experiments show that LC-Checkpoint achieves a compression rate up to $28\times$ and recovery speedup up to $5.77\times$ over a state-of-the-art algorithm (SCAR).
BATS: A Spectral Biclustering Approach to Single Document Topic Modeling and Segmentation
Aug 05, 2020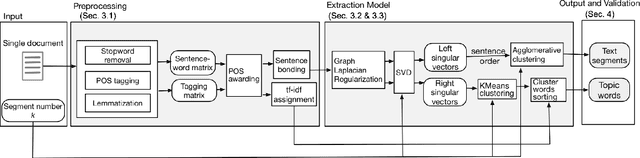
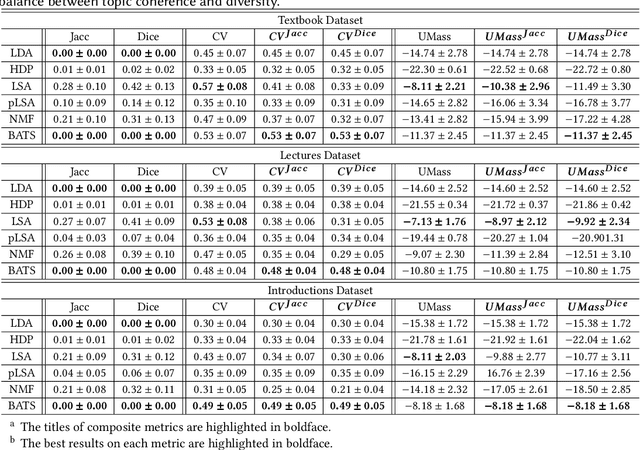
Abstract:Existing topic modeling and text segmentation methodologies generally require large datasets for training, limiting their capabilities when only small collections of text are available. In this work, we reexamine the inter-related problems of "topic identification" and "text segmentation" for sparse document learning, when there is a single new text of interest. In developing a methodology to handle single documents, we face two major challenges. First is sparse information: with access to only one document, we cannot train traditional topic models or deep learning algorithms. Second is significant noise: a considerable portion of words in any single document will produce only noise and not help discern topics or segments. To tackle these issues, we design an unsupervised, computationally efficient methodology called BATS: Biclustering Approach to Topic modeling and Segmentation. BATS leverages three key ideas to simultaneously identify topics and segment text: (i) a new mechanism that uses word order information to reduce sample complexity, (ii) a statistically sound graph-based biclustering technique that identifies latent structures of words and sentences, and (iii) a collection of effective heuristics that remove noise words and award important words to further improve performance. Experiments on four datasets show that our approach outperforms several state-of-the-art baselines when considering topic coherence, topic diversity, segmentation, and runtime comparison metrics.
TF3P: Three-dimensional Force Fields Fingerprint Learned by Deep Capsular Network
Dec 25, 2019



Abstract:Molecular fingerprints are the workhorse in ligand-based drug discovery. In recent years, increasing number of research papers reported fascinating results on using deep neural networks to learn 2D molecular representations as fingerprints. One may anticipate that the integration of deep learning would also contribute to the prosperity of 3D fingerprints. Here, we presented a new 3D small molecule fingerprint, the three-dimensional force fields fingerprint (TF3P), learned by deep capsular network whose training is in no need of labeled dataset for specific predictive tasks. TF3P can encode the 3D force fields information of molecules and demonstrates its stronger ability to capture 3D structural changes, recognize molecules alike in 3D but not in 2D, and recognize similar targets inaccessible by other fingerprints, including the solely existing 3D fingerprint E3FP, based on only ligands similarity. Furthermore, TF3P is compatible with both statistical models (e.g. similarity ensemble approach) and machine learning models. Altogether, we report TF3P as a new 3D small molecule fingerprint with promising future in ligand-based drug discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge