Bo Qiang
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University
BEnDEM:A Boltzmann Sampler Based on Bootstrapped Denoising Energy Matching
Sep 15, 2024



Abstract:Developing an efficient sampler capable of generating independent and identically distributed (IID) samples from a Boltzmann distribution is a crucial challenge in scientific research, e.g. molecular dynamics. In this work, we intend to learn neural samplers given energy functions instead of data sampled from the Boltzmann distribution. By learning the energies of the noised data, we propose a diffusion-based sampler, ENERGY-BASED DENOISING ENERGY MATCHING, which theoretically has lower variance and more complexity compared to related works. Furthermore, a novel bootstrapping technique is applied to EnDEM to balance between bias and variance. We evaluate EnDEM and BEnDEM on a 2-dimensional 40 Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) and a 4-particle double-welling potential (DW-4). The experimental results demonstrate that BEnDEM can achieve state-of-the-art performance while being more robust.
Latent Chemical Space Searching for Plug-in Multi-objective Molecule Generation
Apr 10, 2024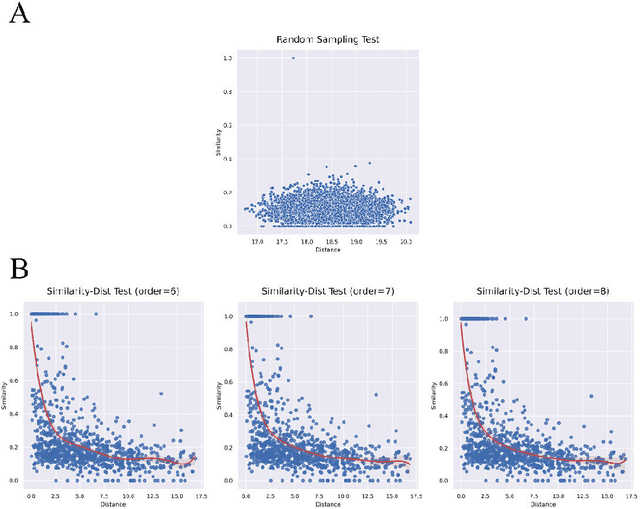
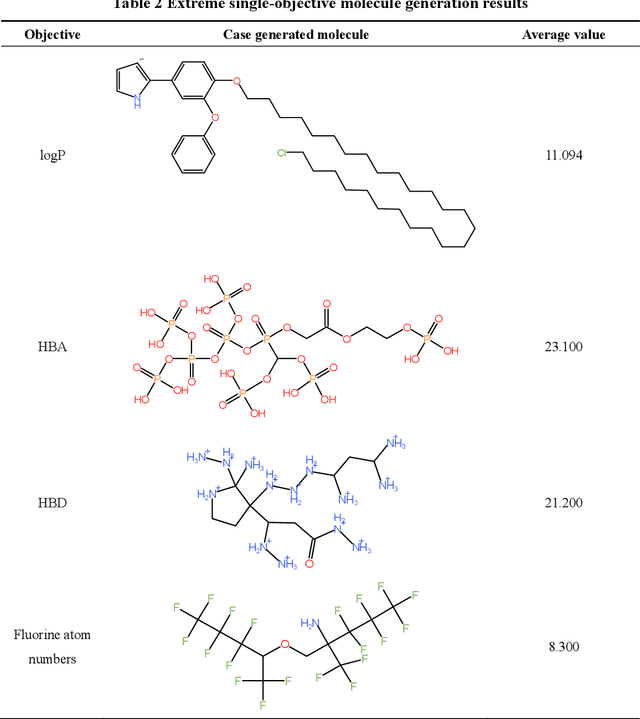
Abstract:Molecular generation, an essential method for identifying new drug structures, has been supported by advancements in machine learning and computational technology. However, challenges remain in multi-objective generation, model adaptability, and practical application in drug discovery. In this study, we developed a versatile 'plug-in' molecular generation model that incorporates multiple objectives related to target affinity, drug-likeness, and synthesizability, facilitating its application in various drug development contexts. We improved the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) in the context of drug discoveries, and identified PSO-ENP as the optimal variant for multi-objective molecular generation and optimization through comparative experiments. The model also incorporates a novel target-ligand affinity predictor, enhancing the model's utility by supporting three-dimensional information and improving synthetic feasibility. Case studies focused on generating and optimizing drug-like big marine natural products were performed, underscoring PSO-ENP's effectiveness and demonstrating its considerable potential for practical drug discovery applications.
Delta Score: Improving the Binding Assessment of Structure-Based Drug Design Methods
Nov 01, 2023Abstract:Structure-based drug design (SBDD) stands at the forefront of drug discovery, emphasizing the creation of molecules that target specific binding pockets. Recent advances in this area have witnessed the adoption of deep generative models and geometric deep learning techniques, modeling SBDD as a conditional generation task where the target structure serves as context. Historically, evaluation of these models centered on docking scores, which quantitatively depict the predicted binding affinity between a molecule and its target pocket. Though state-of-the-art models purport that a majority of their generated ligands exceed the docking score of ground truth ligands in test sets, it begs the question: Do these scores align with real-world biological needs? In this paper, we introduce the delta score, a novel evaluation metric grounded in tangible pharmaceutical requisites. Our experiments reveal that molecules produced by current deep generative models significantly lag behind ground truth reference ligands when assessed with the delta score. This novel metric not only complements existing benchmarks but also provides a pivotal direction for subsequent research in the domain.
DrugCLIP: Contrastive Protein-Molecule Representation Learning for Virtual Screening
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:Virtual screening, which identifies potential drugs from vast compound databases to bind with a particular protein pocket, is a critical step in AI-assisted drug discovery. Traditional docking methods are highly time-consuming, and can only work with a restricted search library in real-life applications. Recent supervised learning approaches using scoring functions for binding-affinity prediction, although promising, have not yet surpassed docking methods due to their strong dependency on limited data with reliable binding-affinity labels. In this paper, we propose a novel contrastive learning framework, DrugCLIP, by reformulating virtual screening as a dense retrieval task and employing contrastive learning to align representations of binding protein pockets and molecules from a large quantity of pairwise data without explicit binding-affinity scores. We also introduce a biological-knowledge inspired data augmentation strategy to learn better protein-molecule representations. Extensive experiments show that DrugCLIP significantly outperforms traditional docking and supervised learning methods on diverse virtual screening benchmarks with highly reduced computation time, especially in zero-shot setting.
Uni-RXN: A Unified Framework Bridging the Gap between Chemical Reaction Pretraining and Conditional Molecule Generation
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:Chemical reactions are the fundamental building blocks of drug design and organic chemistry research. In recent years, there has been a growing need for a large-scale deep-learning framework that can efficiently capture the basic rules of chemical reactions. In this paper, we have proposed a unified framework that addresses both the reaction representation learning and molecule generation tasks, which allows for a more holistic approach. Inspired by the organic chemistry mechanism, we develop a novel pretraining framework that enables us to incorporate inductive biases into the model. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art results on challenging downstream tasks. By possessing chemical knowledge, this framework can be applied to reaction-based generative models, overcoming the limitations of current molecule generation models that rely on a small number of reaction templates. In the extensive experiments, our model generates synthesizable drug-like structures of high quality. Overall, our work presents a significant step toward a large-scale deep-learning framework for a variety of reaction-based applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge