Zekun Jiang
Guiding Medical Vision-Language Models with Explicit Visual Prompts: Framework Design and Comprehensive Exploration of Prompt Variations
Jan 04, 2025Abstract:With the recent advancements in vision-language models (VLMs) driven by large language models (LLMs), many researchers have focused on models that comprised of an image encoder, an image-to-language projection layer, and a text decoder architectures, leading to the emergence of works like LLava-Med. However, these works primarily operate at the whole-image level, aligning general information from 2D medical images without attending to finer details. As a result, these models often provide irrelevant or non-clinically valuable information while missing critical details. Medical vision-language tasks differ significantly from general images, particularly in their focus on fine-grained details, while excluding irrelevant content. General domain VLMs tend to prioritize global information due to their design, which compresses the entire image into a multi-token representation that is passed into the LLM decoder. Therefore, current VLMs all lack the capability to restrict their attention to particular areas. To address this critical issue in the medical domain, we introduce MedVP, an visual prompt generation and fine-tuning framework, which involves extract medical entities, generate visual prompts, and adapt datasets for visual prompt guided fine-tuning. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to explicitly introduce visual prompt into medical VLMs, and we successfully outperform recent state-of-the-art large models across multiple medical VQA datasets. Extensive experiments are conducted to analyze the impact of different visual prompt forms and how they contribute to performance improvement. The results demonstrate both the effectiveness and clinical significance of our approach
EEG-DIF: Early Warning of Epileptic Seizures through Generative Diffusion Model-based Multi-channel EEG Signals Forecasting
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Multi-channel EEG signals are commonly used for the diagnosis and assessment of diseases such as epilepsy. Currently, various EEG diagnostic algorithms based on deep learning have been developed. However, most research efforts focus solely on diagnosing and classifying current signal data but do not consider the prediction of future trends for early warning. Additionally, since multi-channel EEG can be essentially regarded as the spatio-temporal signal data received by detectors at different locations in the brain, how to construct spatio-temporal information representations of EEG signals to facilitate future trend prediction for multi-channel EEG becomes an important problem. This study proposes a multi-signal prediction algorithm based on generative diffusion models (EEG-DIF), which transforms the multi-signal forecasting task into an image completion task, allowing for comprehensive representation and learning of the spatio-temporal correlations and future developmental patterns of multi-channel EEG signals. Here, we employ a publicly available epilepsy EEG dataset to construct and validate the EEG-DIF. The results demonstrate that our method can accurately predict future trends for multi-channel EEG signals simultaneously. Furthermore, the early warning accuracy for epilepsy seizures based on the generated EEG data reaches 0.89. In general, EEG-DIF provides a novel approach for characterizing multi-channel EEG signals and an innovative early warning algorithm for epilepsy seizures, aiding in optimizing and enhancing the clinical diagnosis process. The code is available at https://github.com/JZK00/EEG-DIF.
NuSegDG: Integration of Heterogeneous Space and Gaussian Kernel for Domain-Generalized Nuclei Segmentation
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:Domain-generalized nuclei segmentation refers to the generalizability of models to unseen domains based on knowledge learned from source domains and is challenged by various image conditions, cell types, and stain strategies. Recently, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has made great success in universal image segmentation by interactive prompt modes (e.g., point and box). Despite its strengths, the original SAM presents limited adaptation to medical images. Moreover, SAM requires providing manual bounding box prompts for each object to produce satisfactory segmentation masks, so it is laborious in nuclei segmentation scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose a domain-generalizable framework for nuclei image segmentation, abbreviated to NuSegDG. Specifically, we first devise a Heterogeneous Space Adapter (HS-Adapter) to learn multi-dimensional feature representations of different nuclei domains by injecting a small number of trainable parameters into the image encoder of SAM. To alleviate the labor-intensive requirement of manual prompts, we introduce a Gaussian-Kernel Prompt Encoder (GKP-Encoder) to generate density maps driven by a single point, which guides segmentation predictions by mixing position prompts and semantic prompts. Furthermore, we present a Two-Stage Mask Decoder (TSM-Decoder) to effectively convert semantic masks to instance maps without the manual demand for morphological shape refinement. Based on our experimental evaluations, the proposed NuSegDG demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in nuclei instance segmentation, exhibiting superior domain generalization capabilities. The source code is available at https://github.com/xq141839/NuSegDG.
Increasing SAM Zero-Shot Performance on Multimodal Medical Images Using GPT-4 Generated Descriptive Prompts Without Human Annotation
Feb 24, 2024Abstract:This study develops and evaluates a novel multimodal medical image zero-shot segmentation algorithm named Text-Visual-Prompt SAM (TV-SAM) without any manual annotations. TV-SAM incorporates and integrates large language model GPT-4, Vision Language Model GLIP, and Segment Anything Model (SAM), to autonomously generate descriptive text prompts and visual bounding box prompts from medical images, thereby enhancing SAM for zero-shot segmentation. Comprehensive evaluations are implemented on seven public datasets encompassing eight imaging modalities to demonstrate that TV-SAM can effectively segment unseen targets across various modalities without additional training, significantly outperforming SAM AUTO and GSAM, closely matching the performance of SAM BBOX with gold standard bounding box prompts, and surpassing the state-of-the-art on specific datasets like ISIC and WBC. The study indicates that TV-SAM serves as an effective multimodal medical image zero-shot segmentation algorithm, highlighting the significant contribution of GPT-4 to zero-shot segmentation. By integrating foundational models such as GPT-4, GLIP, and SAM, it could enhance the capability to address complex problems in specialized domains. The code is available at: https://github.com/JZK00/TV-SAM.
Partial Label Learning with a Partner
Dec 18, 2023Abstract:In partial label learning (PLL), each instance is associated with a set of candidate labels among which only one is ground-truth. The majority of the existing works focuses on constructing robust classifiers to estimate the labeling confidence of candidate labels in order to identify the correct one. However, these methods usually struggle to rectify mislabeled samples. To help existing PLL methods identify and rectify mislabeled samples, in this paper, we introduce a novel partner classifier and propose a novel ``mutual supervision'' paradigm. Specifically, we instantiate the partner classifier predicated on the implicit fact that non-candidate labels of a sample should not be assigned to it, which is inherently accurate and has not been fully investigated in PLL. Furthermore, a novel collaborative term is formulated to link the base classifier and the partner one. During each stage of mutual supervision, both classifiers will blur each other's predictions through a blurring mechanism to prevent overconfidence in a specific label. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the performance and disambiguation ability of several well-established stand-alone and deep-learning based PLL approaches can be significantly improved by coupling with this learning paradigm.
SAM on Medical Images: A Comprehensive Study on Three Prompt Modes
Apr 28, 2023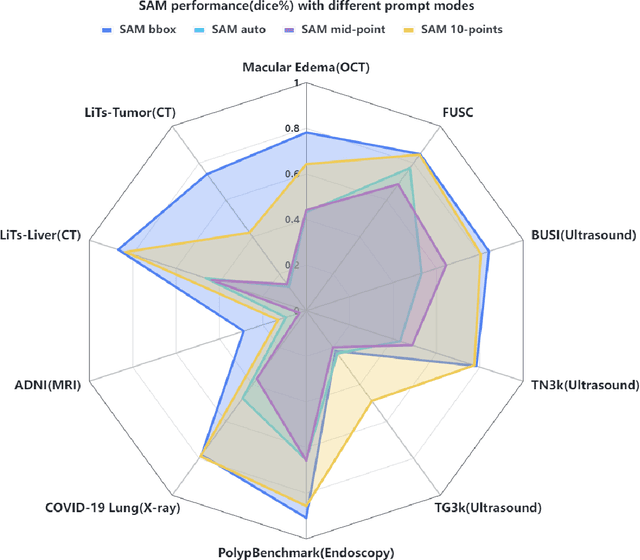
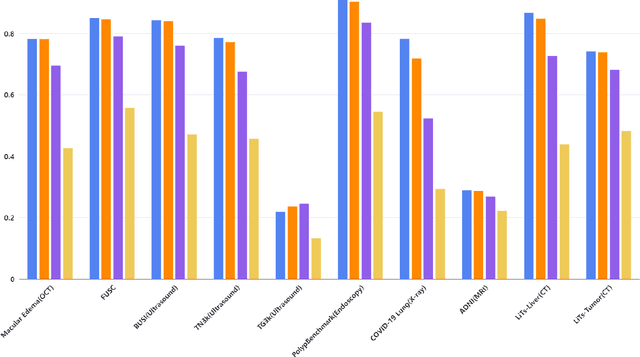
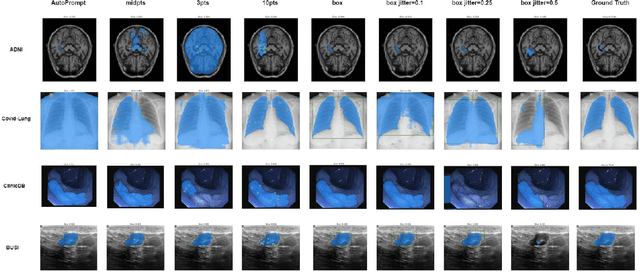
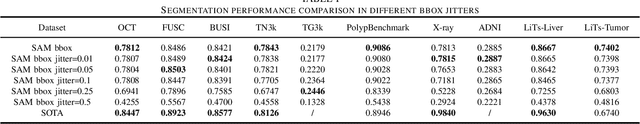
Abstract:The Segment Anything Model (SAM) made an eye-catching debut recently and inspired many researchers to explore its potential and limitation in terms of zero-shot generalization capability. As the first promptable foundation model for segmentation tasks, it was trained on a large dataset with an unprecedented number of images and annotations. This large-scale dataset and its promptable nature endow the model with strong zero-shot generalization. Although the SAM has shown competitive performance on several datasets, we still want to investigate its zero-shot generalization on medical images. As we know, the acquisition of medical image annotation usually requires a lot of effort from professional practitioners. Therefore, if there exists a foundation model that can give high-quality mask prediction simply based on a few point prompts, this model will undoubtedly become the game changer for medical image analysis. To evaluate whether SAM has the potential to become the foundation model for medical image segmentation tasks, we collected more than 12 public medical image datasets that cover various organs and modalities. We also explore what kind of prompt can lead to the best zero-shot performance with different modalities. Furthermore, we find that a pattern shows that the perturbation of the box size will significantly change the prediction accuracy. Finally, Extensive experiments show that the predicted mask quality varied a lot among different datasets. And providing proper prompts, such as bounding boxes, to the SAM will significantly increase its performance.
Towards General Purpose Medical AI: Continual Learning Medical Foundation Model
Mar 12, 2023



Abstract:Inevitable domain and task discrepancies in real-world scenarios can impair the generalization performance of the pre-trained deep models for medical data. Therefore, we audaciously propose that we should build a general-purpose medical AI system that can be seamlessly adapted to downstream domains/tasks. Since the domain/task adaption procedures usually involve additional labeling work for the target data, designing a data-efficient adaption algorithm is desired to save the cost of transferring the learned knowledge. Our recent work found that vision-language models (VLMs) are efficient learners with extraordinary cross-domain ability. Therefore, in this work, we further explore the possibility of leveraging pre-trained VLMs as medical foundation models for building general-purpose medical AI, where we thoroughly investigate three machine-learning paradigms, i.e., domain/task-specialized learning, joint learning, and continual learning, for training the VLMs and evaluate their generalization performance on cross-domain and cross-task test sets. To alleviate the catastrophic forgetting during sequential training, we employ rehearsal learning and receive a sharp boost in terms of generalization capability. In a nutshell, our empirical evidence suggests that continual learning may be a practical and efficient learning paradigm for the medical foundation model. And we hope researchers can use our empirical evidence as basement to further explore the path toward medical foundation model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge