Zhenye Lou
HRMedSeg: Unlocking High-resolution Medical Image segmentation via Memory-efficient Attention Modeling
Apr 08, 2025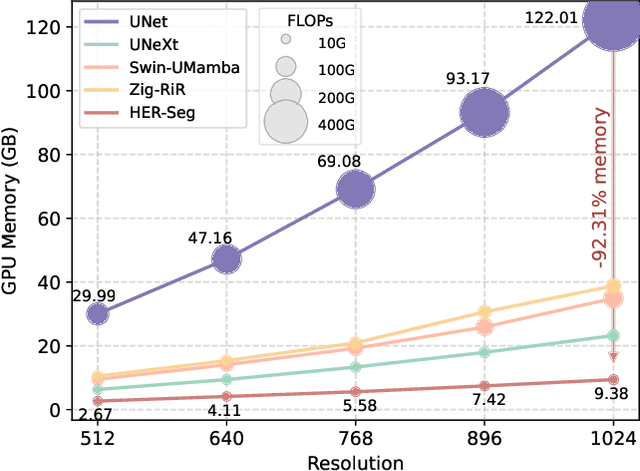
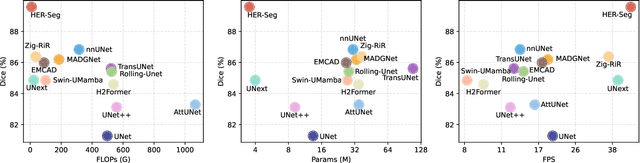
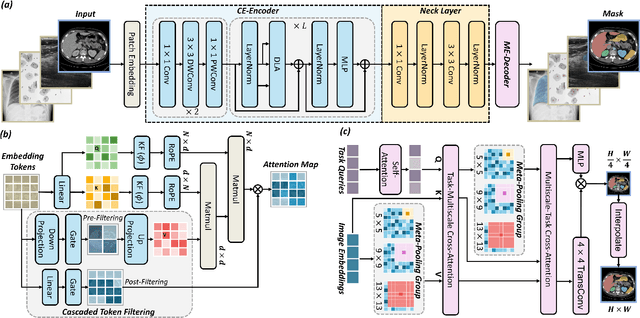
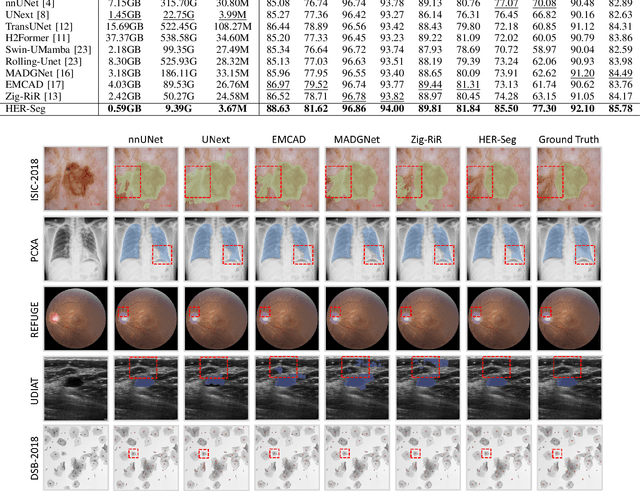
Abstract:High-resolution segmentation is critical for precise disease diagnosis by extracting micro-imaging information from medical images. Existing transformer-based encoder-decoder frameworks have demonstrated remarkable versatility and zero-shot performance in medical segmentation. While beneficial, they usually require huge memory costs when handling large-size segmentation mask predictions, which are expensive to apply to real-world scenarios. To address this limitation, we propose a memory-efficient framework for high-resolution medical image segmentation, called HRMedSeg. Specifically, we first devise a lightweight gated vision transformer (LGViT) as our image encoder to model long-range dependencies with linear complexity. Then, we design an efficient cross-multiscale decoder (ECM-Decoder) to generate high-resolution segmentation masks. Moreover, we utilize feature distillation during pretraining to unleash the potential of our proposed model. Extensive experiments reveal that HRMedSeg outperforms state-of-the-arts in diverse high-resolution medical image segmentation tasks. In particular, HRMedSeg uses only 0.59GB GPU memory per batch during fine-tuning, demonstrating low training costs. Besides, when HRMedSeg meets the Segment Anything Model (SAM), our HRMedSegSAM takes 0.61% parameters of SAM-H. The code is available at https://github.com/xq141839/HRMedSeg.
NuSegDG: Integration of Heterogeneous Space and Gaussian Kernel for Domain-Generalized Nuclei Segmentation
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:Domain-generalized nuclei segmentation refers to the generalizability of models to unseen domains based on knowledge learned from source domains and is challenged by various image conditions, cell types, and stain strategies. Recently, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has made great success in universal image segmentation by interactive prompt modes (e.g., point and box). Despite its strengths, the original SAM presents limited adaptation to medical images. Moreover, SAM requires providing manual bounding box prompts for each object to produce satisfactory segmentation masks, so it is laborious in nuclei segmentation scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose a domain-generalizable framework for nuclei image segmentation, abbreviated to NuSegDG. Specifically, we first devise a Heterogeneous Space Adapter (HS-Adapter) to learn multi-dimensional feature representations of different nuclei domains by injecting a small number of trainable parameters into the image encoder of SAM. To alleviate the labor-intensive requirement of manual prompts, we introduce a Gaussian-Kernel Prompt Encoder (GKP-Encoder) to generate density maps driven by a single point, which guides segmentation predictions by mixing position prompts and semantic prompts. Furthermore, we present a Two-Stage Mask Decoder (TSM-Decoder) to effectively convert semantic masks to instance maps without the manual demand for morphological shape refinement. Based on our experimental evaluations, the proposed NuSegDG demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in nuclei instance segmentation, exhibiting superior domain generalization capabilities. The source code is available at https://github.com/xq141839/NuSegDG.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge