Wenting Duan
RoLID-11K: A Dashcam Dataset for Small-Object Roadside Litter Detection
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Roadside litter poses environmental, safety and economic challenges, yet current monitoring relies on labour-intensive surveys and public reporting, providing limited spatial coverage. Existing vision datasets for litter detection focus on street-level still images, aerial scenes or aquatic environments, and do not reflect the unique characteristics of dashcam footage, where litter appears extremely small, sparse and embedded in cluttered road-verge backgrounds. We introduce RoLID-11K, the first large-scale dataset for roadside litter detection from dashcams, comprising over 11k annotated images spanning diverse UK driving conditions and exhibiting pronounced long-tail and small-object distributions. We benchmark a broad spectrum of modern detectors, from accuracy-oriented transformer architectures to real-time YOLO models, and analyse their strengths and limitations on this challenging task. Our results show that while CO-DETR and related transformers achieve the best localisation accuracy, real-time models remain constrained by coarse feature hierarchies. RoLID-11K establishes a challenging benchmark for extreme small-object detection in dynamic driving scenes and aims to support the development of scalable, low-cost systems for roadside-litter monitoring. The dataset is available at https://github.com/xq141839/RoLID-11K.
FreqDINO: Frequency-Guided Adaptation for Generalized Boundary-Aware Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Dec 12, 2025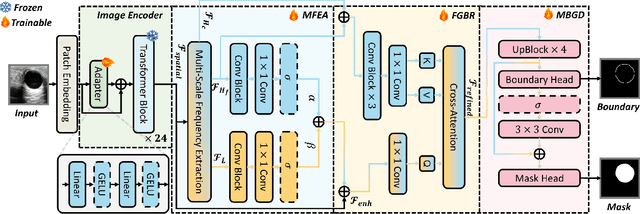
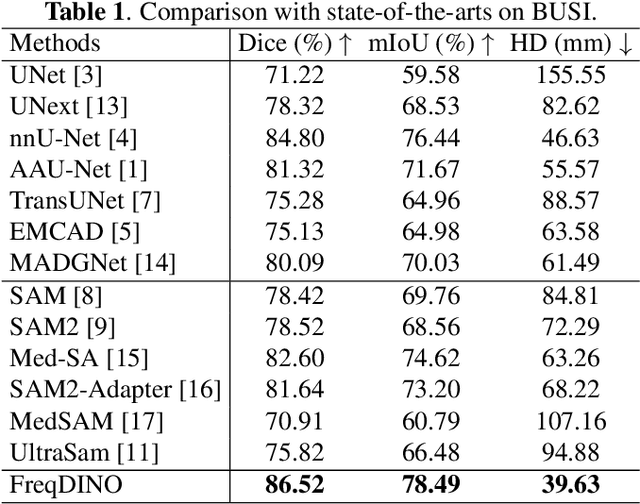
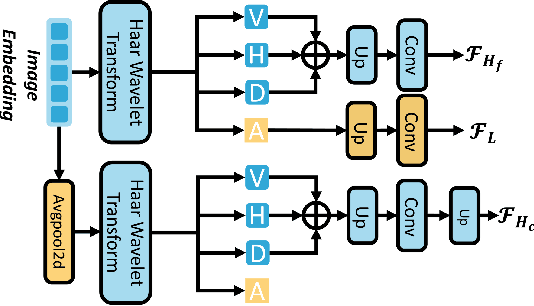
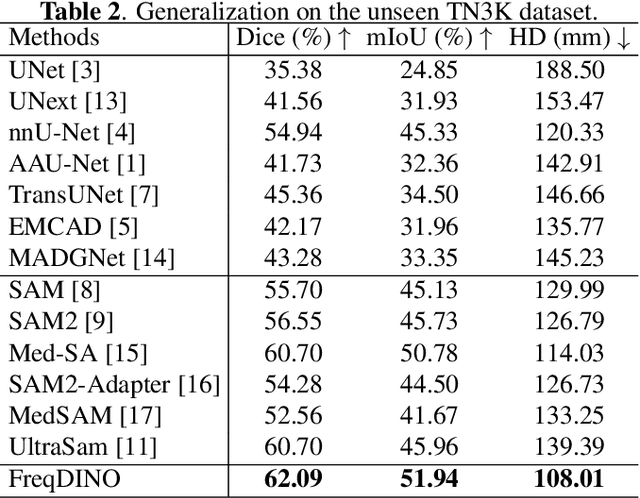
Abstract:Ultrasound image segmentation is pivotal for clinical diagnosis, yet challenged by speckle noise and imaging artifacts. Recently, DINOv3 has shown remarkable promise in medical image segmentation with its powerful representation capabilities. However, DINOv3, pre-trained on natural images, lacks sensitivity to ultrasound-specific boundary degradation. To address this limitation, we propose FreqDINO, a frequency-guided segmentation framework that enhances boundary perception and structural consistency. Specifically, we devise a Multi-scale Frequency Extraction and Alignment (MFEA) strategy to separate low-frequency structures and multi-scale high-frequency boundary details, and align them via learnable attention. We also introduce a Frequency-Guided Boundary Refinement (FGBR) module that extracts boundary prototypes from high-frequency components and refines spatial features. Furthermore, we design a Multi-task Boundary-Guided Decoder (MBGD) to ensure spatial coherence between boundary and semantic predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FreqDINO surpasses state-of-the-art methods with superior achieves remarkable generalization capability. The code is at https://github.com/MingLang-FD/FreqDINO.
LapFM: A Laparoscopic Segmentation Foundation Model via Hierarchical Concept Evolving Pre-training
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Surgical segmentation is pivotal for scene understanding yet remains hindered by annotation scarcity and semantic inconsistency across diverse procedures. Existing approaches typically fine-tune natural foundation models (e.g., SAM) with limited supervision, functioning merely as domain adapters rather than surgical foundation models. Consequently, they struggle to generalize across the vast variability of surgical targets. To bridge this gap, we present LapFM, a foundation model designed to evolve robust segmentation capabilities from massive unlabeled surgical images. Distinct from medical foundation models relying on inefficient self-supervised proxy tasks, LapFM leverages a Hierarchical Concept Evolving Pre-training paradigm. First, we establish a Laparoscopic Concept Hierarchy (LCH) via a hierarchical mask decoder with parent-child query embeddings, unifying diverse entities (i.e., Anatomy, Tissue, and Instrument) into a scalable knowledge structure with cross-granularity semantic consistency. Second, we propose a Confidence-driven Evolving Labeling that iteratively generates and filters pseudo-labels based on hierarchical consistency, progressively incorporating reliable samples from unlabeled images into training. This process yields LapBench-114K, a large-scale benchmark comprising 114K image-mask pairs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LapFM significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, establishing new standards for granularity-adaptive generalization in universal laparoscopic segmentation. The source code is available at https://github.com/xq141839/LapFM.
TM-UNet: Token-Memory Enhanced Sequential Modeling for Efficient Medical Image Segmentation
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Medical image segmentation is essential for clinical diagnosis and treatment planning. Although transformer-based methods have achieved remarkable results, their high computational cost hinders clinical deployment. To address this issue, we propose TM-UNet, a novel lightweight framework that integrates token sequence modeling with an efficient memory mechanism for efficient medical segmentation. Specifically, we introduce a multi-scale token-memory (MSTM) block that transforms 2D spatial features into token sequences through strategic spatial scanning, leveraging matrix memory cells to selectively retain and propagate discriminative contextual information across tokens. This novel token-memory mechanism acts as a dynamic knowledge store that captures long-range dependencies with linear complexity, enabling efficient global reasoning without redundant computation. Our MSTM block further incorporates exponential gating to identify token effectiveness and multi-scale contextual extraction via parallel pooling operations, enabling hierarchical representation learning without computational overhead. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TM-UNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods across diverse medical segmentation tasks with substantially reduced computation cost. The code is available at https://github.com/xq141839/TM-UNet.
HRMedSeg: Unlocking High-resolution Medical Image segmentation via Memory-efficient Attention Modeling
Apr 08, 2025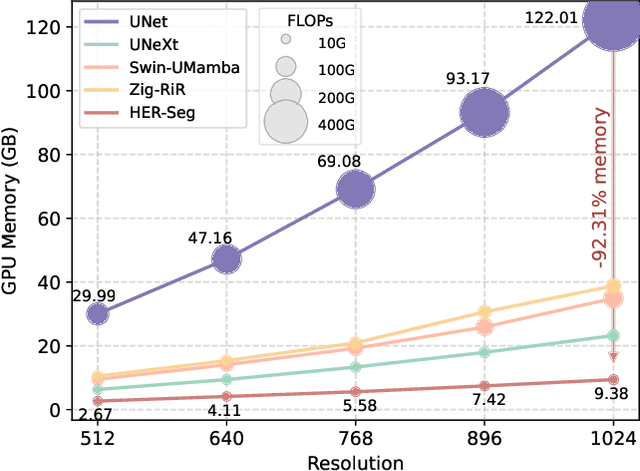
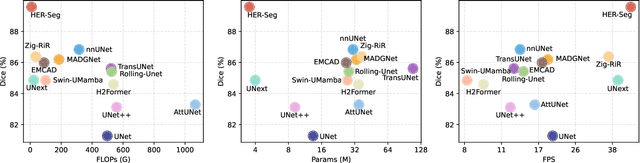
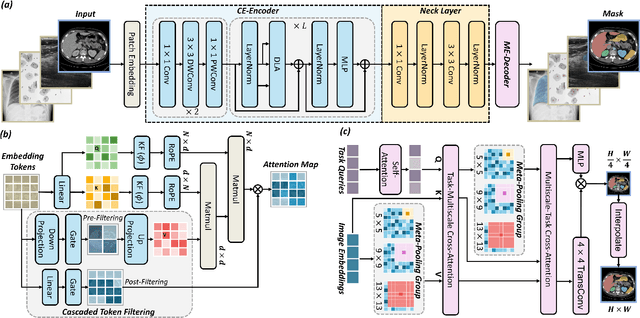
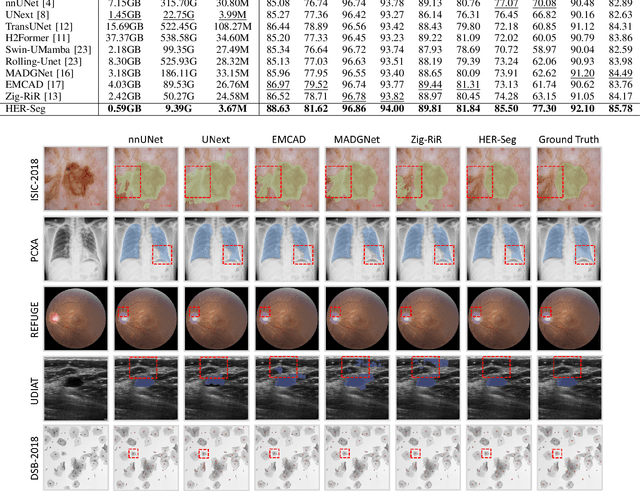
Abstract:High-resolution segmentation is critical for precise disease diagnosis by extracting micro-imaging information from medical images. Existing transformer-based encoder-decoder frameworks have demonstrated remarkable versatility and zero-shot performance in medical segmentation. While beneficial, they usually require huge memory costs when handling large-size segmentation mask predictions, which are expensive to apply to real-world scenarios. To address this limitation, we propose a memory-efficient framework for high-resolution medical image segmentation, called HRMedSeg. Specifically, we first devise a lightweight gated vision transformer (LGViT) as our image encoder to model long-range dependencies with linear complexity. Then, we design an efficient cross-multiscale decoder (ECM-Decoder) to generate high-resolution segmentation masks. Moreover, we utilize feature distillation during pretraining to unleash the potential of our proposed model. Extensive experiments reveal that HRMedSeg outperforms state-of-the-arts in diverse high-resolution medical image segmentation tasks. In particular, HRMedSeg uses only 0.59GB GPU memory per batch during fine-tuning, demonstrating low training costs. Besides, when HRMedSeg meets the Segment Anything Model (SAM), our HRMedSegSAM takes 0.61% parameters of SAM-H. The code is available at https://github.com/xq141839/HRMedSeg.
NuSegDG: Integration of Heterogeneous Space and Gaussian Kernel for Domain-Generalized Nuclei Segmentation
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:Domain-generalized nuclei segmentation refers to the generalizability of models to unseen domains based on knowledge learned from source domains and is challenged by various image conditions, cell types, and stain strategies. Recently, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has made great success in universal image segmentation by interactive prompt modes (e.g., point and box). Despite its strengths, the original SAM presents limited adaptation to medical images. Moreover, SAM requires providing manual bounding box prompts for each object to produce satisfactory segmentation masks, so it is laborious in nuclei segmentation scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose a domain-generalizable framework for nuclei image segmentation, abbreviated to NuSegDG. Specifically, we first devise a Heterogeneous Space Adapter (HS-Adapter) to learn multi-dimensional feature representations of different nuclei domains by injecting a small number of trainable parameters into the image encoder of SAM. To alleviate the labor-intensive requirement of manual prompts, we introduce a Gaussian-Kernel Prompt Encoder (GKP-Encoder) to generate density maps driven by a single point, which guides segmentation predictions by mixing position prompts and semantic prompts. Furthermore, we present a Two-Stage Mask Decoder (TSM-Decoder) to effectively convert semantic masks to instance maps without the manual demand for morphological shape refinement. Based on our experimental evaluations, the proposed NuSegDG demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in nuclei instance segmentation, exhibiting superior domain generalization capabilities. The source code is available at https://github.com/xq141839/NuSegDG.
ESP-MedSAM: Efficient Self-Prompting SAM for Universal Domain-Generalized Medical Image Segmentation
Jul 19, 2024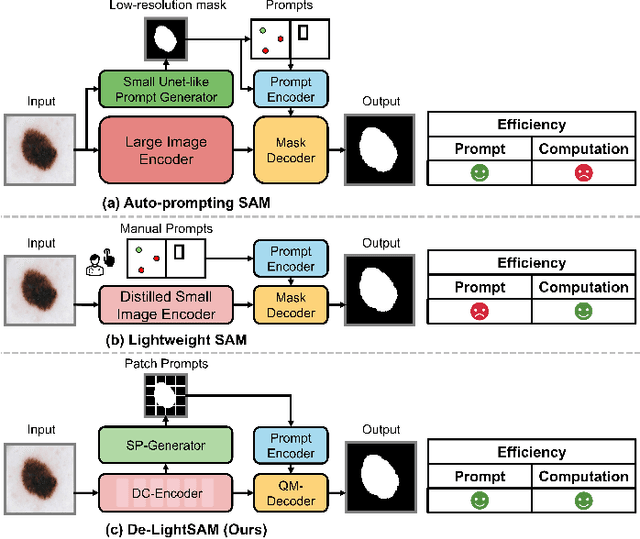
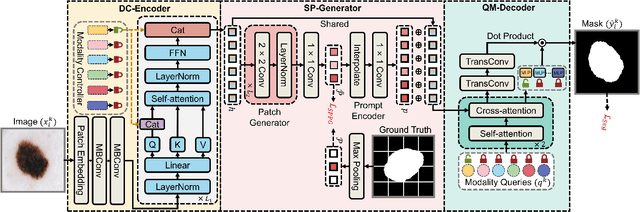
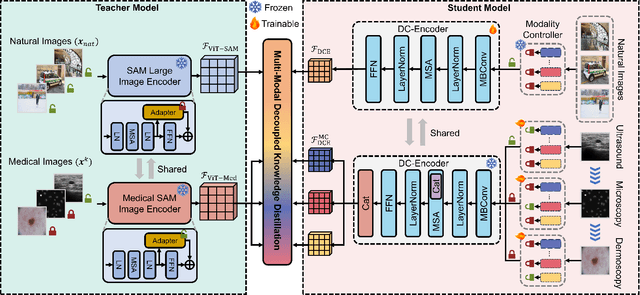
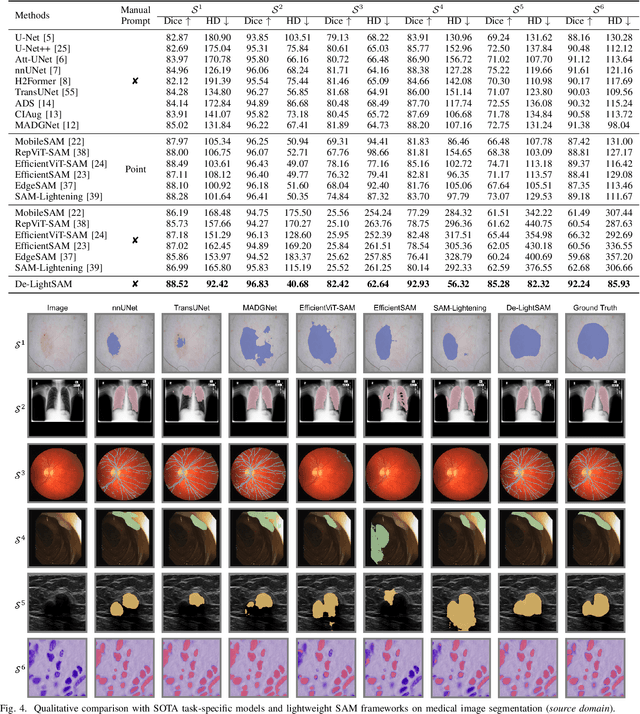
Abstract:The Segment Anything Model (SAM) has demonstrated outstanding adaptation to medical image segmentation but still faces three major challenges. Firstly, the huge computational costs of SAM limit its real-world applicability. Secondly, SAM depends on manual annotations (e.g., points, boxes) as prompts, which are laborious and impractical in clinical scenarios. Thirdly, SAM handles all segmentation targets equally, which is suboptimal for diverse medical modalities with inherent heterogeneity. To address these issues, we propose an Efficient Self-Prompting SAM for universal medical image segmentation, named ESP-MedSAM. We devise a Multi-Modal Decoupled Knowledge Distillation (MMDKD) strategy to distil common image knowledge and domain-specific medical knowledge from the foundation model to train a lightweight image encoder and a modality controller. Further, they combine with the additionally introduced Self-Patch Prompt Generator (SPPG) and Query-Decoupled Modality Decoder (QDMD) to construct ESP-MedSAM. Specifically, SPPG aims to generate a set of patch prompts automatically and QDMD leverages a one-to-one strategy to provide an independent decoding channel for every modality. Extensive experiments indicate that ESP-MedSAM outperforms state-of-the-arts in diverse medical imaging segmentation takes, displaying superior zero-shot learning and modality transfer ability. Especially, our framework uses only 31.4% parameters compared to SAM-Base.
SPPNet: A Single-Point Prompt Network for Nuclei Image Segmentation
Aug 23, 2023Abstract:Image segmentation plays an essential role in nuclei image analysis. Recently, the segment anything model has made a significant breakthrough in such tasks. However, the current model exists two major issues for cell segmentation: (1) the image encoder of the segment anything model involves a large number of parameters. Retraining or even fine-tuning the model still requires expensive computational resources. (2) in point prompt mode, points are sampled from the center of the ground truth and more than one set of points is expected to achieve reliable performance, which is not efficient for practical applications. In this paper, a single-point prompt network is proposed for nuclei image segmentation, called SPPNet. We replace the original image encoder with a lightweight vision transformer. Also, an effective convolutional block is added in parallel to extract the low-level semantic information from the image and compensate for the performance degradation due to the small image encoder. We propose a new point-sampling method based on the Gaussian kernel. The proposed model is evaluated on the MoNuSeg-2018 dataset. The result demonstrated that SPPNet outperforms existing U-shape architectures and shows faster convergence in training. Compared to the segment anything model, SPPNet shows roughly 20 times faster inference, with 1/70 parameters and computational cost. Particularly, only one set of points is required in both the training and inference phases, which is more reasonable for clinical applications. The code for our work and more technical details can be found at https://github.com/xq141839/SPPNet.
DualAttNet: Synergistic Fusion of Image-level and Fine-Grained Disease Attention for Multi-Label Lesion Detection in Chest X-rays
Jun 23, 2023Abstract:Chest radiographs are the most commonly performed radiological examinations for lesion detection. Recent advances in deep learning have led to encouraging results in various thoracic disease detection tasks. Particularly, the architecture with feature pyramid network performs the ability to recognise targets with different sizes. However, such networks are difficult to focus on lesion regions in chest X-rays due to their high resemblance in vision. In this paper, we propose a dual attention supervised module for multi-label lesion detection in chest radiographs, named DualAttNet. It efficiently fuses global and local lesion classification information based on an image-level attention block and a fine-grained disease attention algorithm. A binary cross entropy loss function is used to calculate the difference between the attention map and ground truth at image level. The generated gradient flow is leveraged to refine pyramid representations and highlight lesion-related features. We evaluate the proposed model on VinDr-CXR, ChestX-ray8 and COVID-19 datasets. The experimental results show that DualAttNet surpasses baselines by 0.6% to 2.7% mAP and 1.4% to 4.7% AP50 with different detection architectures. The code for our work and more technical details can be found at https://github.com/xq141839/DualAttNet.
DCSAU-Net: A Deeper and More Compact Split-Attention U-Net for Medical Image Segmentation
Feb 02, 2022



Abstract:Image segmentation is a key step for medical image analysis. Approaches based on deep neural networks have been introduced and performed more reliable results than traditional image processing methods. However, many models focus on one medical image application and still show limited abilities to work with complex images. In this paper, we propose a novel deeper and more compact split-attention u-shape network (DCSAU-Net) that extracts useful features using multi-scale combined split-attention and deeper depthwise convolution. We evaluate the proposed model on CVC-ClinicDB, 2018 Data Science Bowl, ISIC-2018 and SegPC-2021 datasets. As a result, DCSAU-Net displays better performance than other state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods in terms of the mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) and F1-socre. More significantly, the proposed model demonstrate better segmentation performance on challenging images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge