Ze Zhang
Proactive Local-Minima-Free Robot Navigation: Blending Motion Prediction with Safe Control
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This work addresses the challenge of safe and efficient mobile robot navigation in complex dynamic environments with concave moving obstacles. Reactive safe controllers like Control Barrier Functions (CBFs) design obstacle avoidance strategies based only on the current states of the obstacles, risking future collisions. To alleviate this problem, we use Gaussian processes to learn barrier functions online from multimodal motion predictions of obstacles generated by neural networks trained with energy-based learning. The learned barrier functions are then fed into quadratic programs using modulated CBFs (MCBFs), a local-minimum-free version of CBFs, to achieve safe and efficient navigation. The proposed framework makes two key contributions. First, it develops a prediction-to-barrier function online learning pipeline. Second, it introduces an autonomous parameter tuning algorithm that adapts MCBFs to deforming, prediction-based barrier functions. The framework is evaluated in both simulations and real-world experiments, consistently outperforming baselines and demonstrating superior safety and efficiency in crowded dynamic environments.
Infrastructure-based Autonomous Mobile Robots for Internal Logistics -- Challenges and Future Perspectives
Dec 17, 2025



Abstract:The adoption of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) for internal logistics is accelerating, with most solutions emphasizing decentralized, onboard intelligence. While AMRs in indoor environments like factories can be supported by infrastructure, involving external sensors and computational resources, such systems remain underexplored in the literature. This paper presents a comprehensive overview of infrastructure-based AMR systems, outlining key opportunities and challenges. To support this, we introduce a reference architecture combining infrastructure-based sensing, on-premise cloud computing, and onboard autonomy. Based on the architecture, we review core technologies for localization, perception, and planning. We demonstrate the approach in a real-world deployment in a heavy-vehicle manufacturing environment and summarize findings from a user experience (UX) evaluation. Our aim is to provide a holistic foundation for future development of scalable, robust, and human-compatible AMR systems in complex industrial environments.
Collision-Free Navigation of Mobile Robots via Quadtree-Based Model Predictive Control
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an integrated navigation framework for Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) that unifies environment representation, trajectory generation, and Model Predictive Control (MPC). The proposed approach incorporates a quadtree-based method to generate structured, axis-aligned collision-free regions from occupancy maps. These regions serve as both a basis for developing safe corridors and as linear constraints within the MPC formulation, enabling efficient and reliable navigation without requiring direct obstacle encoding. The complete pipeline combines safe-area extraction, connectivity graph construction, trajectory generation, and B-spline smoothing into one coherent system. Experimental results demonstrate consistent success and superior performance compared to baseline approaches across complex environments.
AdapSCA-PSO: An Adaptive Localization Algorithm with AI-Based Hybrid SCA-PSO for IoT WSNs
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:The accurate localization of sensor nodes is a fundamental requirement for the practical application of the Internet of Things (IoT). To enable robust localization across diverse environments, this paper proposes a hybrid meta-heuristic localization algorithm. Specifically, the algorithm integrates the Sine Cosine Algorithm (SCA), which is effective in global search, with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), which excels at local search. An adaptive switching module is introduced to dynamically select between the two algorithms. Furthermore, the initialization, fitness evaluation, and parameter settings of the algorithm have been specifically redesigned and optimized to address the characteristics of the node localization problem. Simulation results across varying numbers of sensor nodes demonstrate that, compared to standalone PSO and the unoptimized SCAPSO algorithm, the proposed method significantly reduces the number of required iterations and achieves an average localization error reduction of 84.97%.
AMSbench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating MLLM Capabilities in AMS Circuits
May 30, 2025Abstract:Analog/Mixed-Signal (AMS) circuits play a critical role in the integrated circuit (IC) industry. However, automating Analog/Mixed-Signal (AMS) circuit design has remained a longstanding challenge due to its difficulty and complexity. Recent advances in Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) offer promising potential for supporting AMS circuit analysis and design. However, current research typically evaluates MLLMs on isolated tasks within the domain, lacking a comprehensive benchmark that systematically assesses model capabilities across diverse AMS-related challenges. To address this gap, we introduce AMSbench, a benchmark suite designed to evaluate MLLM performance across critical tasks including circuit schematic perception, circuit analysis, and circuit design. AMSbench comprises approximately 8000 test questions spanning multiple difficulty levels and assesses eight prominent models, encompassing both open-source and proprietary solutions such as Qwen 2.5-VL and Gemini 2.5 Pro. Our evaluation highlights significant limitations in current MLLMs, particularly in complex multi-modal reasoning and sophisticated circuit design tasks. These results underscore the necessity of advancing MLLMs' understanding and effective application of circuit-specific knowledge, thereby narrowing the existing performance gap relative to human expertise and moving toward fully automated AMS circuit design workflows. Our data is released at https://huggingface.co/datasets/wwhhyy/AMSBench
Future-Oriented Navigation: Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance with One-Shot Energy-Based Multimodal Motion Prediction
May 01, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes an integrated approach for the safe and efficient control of mobile robots in dynamic and uncertain environments. The approach consists of two key steps: one-shot multimodal motion prediction to anticipate motions of dynamic obstacles and model predictive control to incorporate these predictions into the motion planning process. Motion prediction is driven by an energy-based neural network that generates high-resolution, multi-step predictions in a single operation. The prediction outcomes are further utilized to create geometric shapes formulated as mathematical constraints. Instead of treating each dynamic obstacle individually, predicted obstacles are grouped by proximity in an unsupervised way to improve performance and efficiency. The overall collision-free navigation is handled by model predictive control with a specific design for proactive dynamic obstacle avoidance. The proposed approach allows mobile robots to navigate effectively in dynamic environments. Its performance is accessed across various scenarios that represent typical warehouse settings. The results demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms other existing dynamic obstacle avoidance methods.
Gradient Field-Based Dynamic Window Approach for Collision Avoidance in Complex Environments
Apr 04, 2025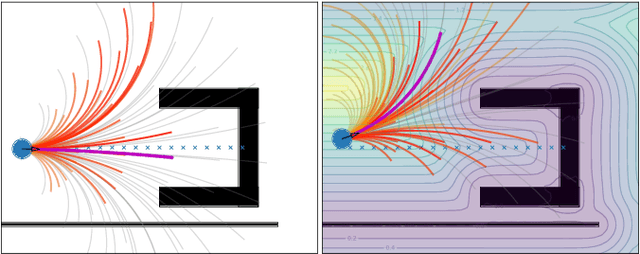
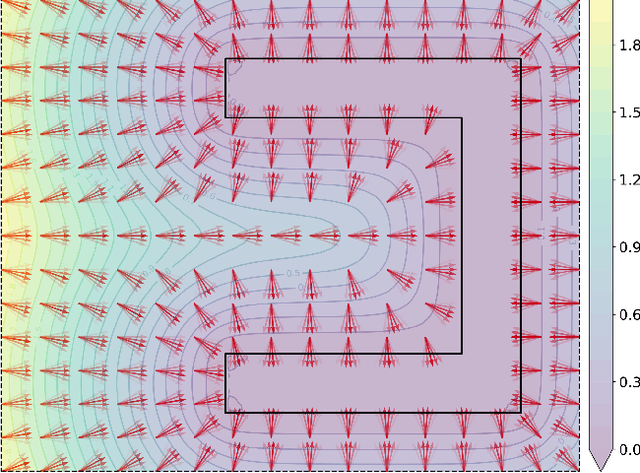
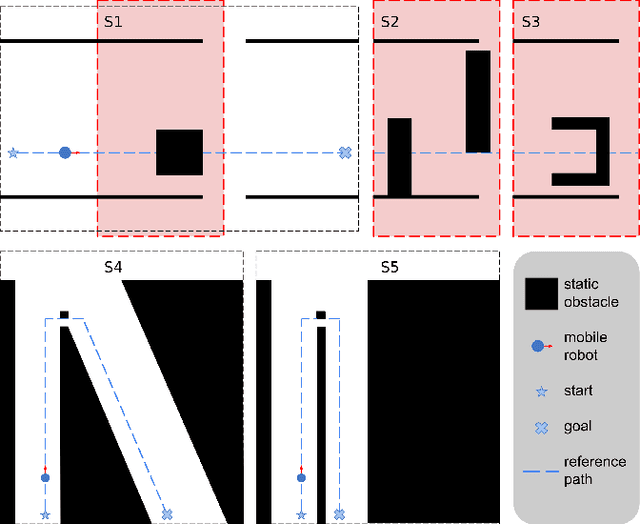
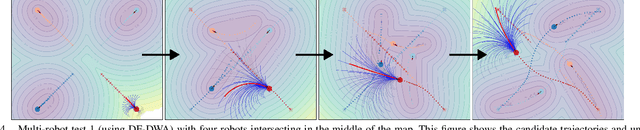
Abstract:For safe and flexible navigation in multi-robot systems, this paper presents an enhanced and predictive sampling-based trajectory planning approach in complex environments, the Gradient Field-based Dynamic Window Approach (GF-DWA). Building upon the dynamic window approach, the proposed method utilizes gradient information of obstacle distances as a new cost term to anticipate potential collisions. This enhancement enables the robot to improve awareness of obstacles, including those with non-convex shapes. The gradient field is derived from the Gaussian process distance field, which generates both the distance field and gradient field by leveraging Gaussian process regression to model the spatial structure of the environment. Through several obstacle avoidance and fleet collision avoidance scenarios, the proposed GF-DWA is shown to outperform other popular trajectory planning and control methods in terms of safety and flexibility, especially in complex environments with non-convex obstacles.
Refined Geometry-guided Head Avatar Reconstruction from Monocular RGB Video
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:High-fidelity reconstruction of head avatars from monocular videos is highly desirable for virtual human applications, but it remains a challenge in the fields of computer graphics and computer vision. In this paper, we propose a two-phase head avatar reconstruction network that incorporates a refined 3D mesh representation. Our approach, in contrast to existing methods that rely on coarse template-based 3D representations derived from 3DMM, aims to learn a refined mesh representation suitable for a NeRF that captures complex facial nuances. In the first phase, we train 3DMM-stored NeRF with an initial mesh to utilize geometric priors and integrate observations across frames using a consistent set of latent codes. In the second phase, we leverage a novel mesh refinement procedure based on an SDF constructed from the density field of the initial NeRF. To mitigate the typical noise in the NeRF density field without compromising the features of the 3DMM, we employ Laplace smoothing on the displacement field. Subsequently, we apply a second-phase training with these refined meshes, directing the learning process of the network towards capturing intricate facial details. Our experiments demonstrate that our method further enhances the NeRF rendering based on the initial mesh and achieves performance superior to state-of-the-art methods in reconstructing high-fidelity head avatars with such input.
Copy-Move Forgery Detection and Question Answering for Remote Sensing Image
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces the task of Remote Sensing Copy-Move Question Answering (RSCMQA). Unlike traditional Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering (RSVQA), RSCMQA focuses on interpreting complex tampering scenarios and inferring relationships between objects. Based on the practical needs of national defense security and land resource monitoring, we have developed an accurate and comprehensive global dataset for remote sensing image copy-move question answering, named RS-CMQA-2.1M. These images were collected from 29 different regions across 14 countries. Additionally, we have refined a balanced dataset, RS-CMQA-B, to address the long-standing issue of long-tail data in the remote sensing field. Furthermore, we propose a region-discriminative guided multimodal CMQA model, which enhances the accuracy of answering questions about tampered images by leveraging prompt about the differences and connections between the source and tampered domains. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method provides a stronger benchmark for RS-CMQA compared to general VQA and RSVQA models. Our dataset and code are available at https://github.com/shenyedepisa/RSCMQA.
3D Programming of Patterned Heterogeneous Interface for 4D Smart Robotics
Dec 22, 2023Abstract:Shape memory structures are playing an important role in many cutting-edge intelligent fields. However, the existing technologies can only realize 4D printing of a single polymer or metal, which limits practical applications. Here, we report a construction strategy for TSMP/M heterointerface, which uses Pd2+-containing shape memory polymer (AP-SMR) to induce electroless plating reaction and relies on molecular dynamics, which has both shape memory properties and metal activity and information processing power. Through multi-material DLP 3D printing technology, the interface can be 3D selectively programmed on functional substrate parts of arbitrary shapes to become 4D electronic smart devices (Robotics). Microscopically, this type of interface appears as a composite structure with a nanometer-micrometer interface height, which is composed of a pure substrate layer (smart materials), an intermediate layer (a composite structure in which metal particles are embedded in a polymer cross-linked network) and a pure metal layer. The structure programmed by TSMP/M heterointerface exhibits both SMA characteristics and metal properties, thus having more intelligent functions (electroactive, electrothermal deformation, electronically controlled denaturation) and higher performance (selectivity of shape memory structures can be realized control, remote control, inline control and low voltage control). This is expected to provide a more flexible manufacturing process as platform technology for designing, manufacturing and applying smart devices with new concepts, and promote the development of cutting-edge industries such as smart robots and smart electronics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge