Yuyang Bai
MoCo: A One-Stop Shop for Model Collaboration Research
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Advancing beyond single monolithic language models (LMs), recent research increasingly recognizes the importance of model collaboration, where multiple LMs collaborate, compose, and complement each other. Existing research on this topic has mostly been disparate and disconnected, from different research communities, and lacks rigorous comparison. To consolidate existing research and establish model collaboration as a school of thought, we present MoCo: a one-stop Python library of executing, benchmarking, and comparing model collaboration algorithms at scale. MoCo features 26 model collaboration methods, spanning diverse levels of cross-model information exchange such as routing, text, logit, and model parameters. MoCo integrates 25 evaluation datasets spanning reasoning, QA, code, safety, and more, while users could flexibly bring their own data. Extensive experiments with MoCo demonstrate that most collaboration strategies outperform models without collaboration in 61.0% of (model, data) settings on average, with the most effective methods outperforming by up to 25.8%. We further analyze the scaling of model collaboration strategies, the training/inference efficiency of diverse methods, highlight that the collaborative system solves problems where single LMs struggle, and discuss future work in model collaboration, all made possible by MoCo. We envision MoCo as a valuable toolkit to facilitate and turbocharge the quest for an open, modular, decentralized, and collaborative AI future.
GraphDancer: Training LLMs to Explore and Reason over Graphs via Curriculum Reinforcement Learning
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) increasingly rely on external knowledge to improve factuality, yet many real-world knowledge sources are organized as heterogeneous graphs rather than plain text. Reasoning over such graph-structured knowledge poses two key challenges: (1) navigating structured, schema-defined relations requires precise function calls rather than similarity-based retrieval, and (2) answering complex questions often demands multi-hop evidence aggregation through iterative information seeking. We propose GraphDancer, a reinforcement learning (RL) framework that teaches LLMs to navigate graphs by interleaving reasoning and function execution. To make RL effective for moderate-sized LLMs, we introduce a graph-aware curriculum that schedules training by the structural complexity of information-seeking trajectories using an easy-to-hard biased sampler. We evaluate GraphDancer on a multi-domain benchmark by training on one domain only and testing on unseen domains and out-of-distribution question types. Despite using only a 3B backbone, GraphDancer outperforms baselines equipped with either a 14B backbone or GPT-4o-mini, demonstrating robust cross-domain generalization of graph exploration and reasoning skills. Our code and models can be found at https://yuyangbai.com/graphdancer/ .
Continuously Steering LLMs Sensitivity to Contextual Knowledge with Proxy Models
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:In Large Language Models (LLMs) generation, there exist knowledge conflicts and scenarios where parametric knowledge contradicts knowledge provided in the context. Previous works studied tuning, decoding algorithms, or locating and editing context-aware neurons to adapt LLMs to be faithful to new contextual knowledge. However, they are usually inefficient or ineffective for large models, not workable for black-box models, or unable to continuously adjust LLMs' sensitivity to the knowledge provided in the context. To mitigate these problems, we propose CSKS (Continuously Steering Knowledge Sensitivity), a simple framework that can steer LLMs' sensitivity to contextual knowledge continuously at a lightweight cost. Specifically, we tune two small LMs (i.e. proxy models) and use the difference in their output distributions to shift the original distribution of an LLM without modifying the LLM weights. In the evaluation process, we not only design synthetic data and fine-grained metrics to measure models' sensitivity to contextual knowledge but also use a real conflict dataset to validate CSKS's practical efficacy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework achieves continuous and precise control over LLMs' sensitivity to contextual knowledge, enabling both increased sensitivity and reduced sensitivity, thereby allowing LLMs to prioritize either contextual or parametric knowledge as needed flexibly. Our data and code are available at https://github.com/OliveJuiceLin/CSKS.
CodeTaxo: Enhancing Taxonomy Expansion with Limited Examples via Code Language Prompts
Aug 17, 2024



Abstract:Taxonomies play a crucial role in various applications by providing a structural representation of knowledge. The task of taxonomy expansion involves integrating emerging concepts into existing taxonomies by identifying appropriate parent concepts for these new query concepts. Previous approaches typically relied on self-supervised methods that generate annotation data from existing taxonomies. However, these methods are less effective when the existing taxonomy is small (fewer than 100 entities). In this work, we introduce \textsc{CodeTaxo}, a novel approach that leverages large language models through code language prompts to capture the taxonomic structure. Extensive experiments on five real-world benchmarks from different domains demonstrate that \textsc{CodeTaxo} consistently achieves superior performance across all evaluation metrics, significantly outperforming previous state-of-the-art methods. The code and data are available at \url{https://github.com/QingkaiZeng/CodeTaxo-Pub}.
Chain-of-Layer: Iteratively Prompting Large Language Models for Taxonomy Induction from Limited Examples
Feb 12, 2024



Abstract:Automatic taxonomy induction is crucial for web search, recommendation systems, and question answering. Manual curation of taxonomies is expensive in terms of human effort, making automatic taxonomy construction highly desirable. In this work, we introduce Chain-of-Layer which is an in-context learning framework designed to induct taxonomies from a given set of entities. Chain-of-Layer breaks down the task into selecting relevant candidate entities in each layer and gradually building the taxonomy from top to bottom. To minimize errors, we introduce the Ensemble-based Ranking Filter to reduce the hallucinated content generated at each iteration. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that Chain-of-Layer achieves state-of-the-art performance on four real-world benchmarks.
KGQuiz: Evaluating the Generalization of Encoded Knowledge in Large Language Models
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable performance on knowledge-intensive tasks, suggesting that real-world knowledge is encoded in their model parameters. However, besides explorations on a few probing tasks in limited knowledge domains, it is not well understood how to evaluate LLMs' knowledge systematically and how well their knowledge abilities generalize, across a spectrum of knowledge domains and progressively complex task formats. To this end, we propose KGQuiz, a knowledge-intensive benchmark to comprehensively investigate the knowledge generalization abilities of LLMs. KGQuiz is a scalable framework constructed from triplet-based knowledge, which covers three knowledge domains and consists of five tasks with increasing complexity: true-or-false, multiple-choice QA, blank filling, factual editing, and open-ended knowledge generation. To gain a better understanding of LLMs' knowledge abilities and their generalization, we evaluate 10 open-source and black-box LLMs on the KGQuiz benchmark across the five knowledge-intensive tasks and knowledge domains. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LLMs achieve impressive performance in straightforward knowledge QA tasks, while settings and contexts requiring more complex reasoning or employing domain-specific facts still present significant challenges. We envision KGQuiz as a testbed to analyze such nuanced variations in performance across domains and task formats, and ultimately to understand, evaluate, and improve LLMs' knowledge abilities across a wide spectrum of knowledge domains and tasks.
CooK: Empowering General-Purpose Language Models with Modular and Collaborative Knowledge
May 17, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly adopted for knowledge-intensive tasks and contexts. Existing approaches improve the knowledge capabilities of general-purpose LLMs through retrieval or generated knowledge prompting, but they fall short of reflecting two key properties of knowledge-rich models: knowledge should be modular, ever-growing, sourced from diverse domains; knowledge acquisition and production should be a collaborative process, where diverse stakeholders contribute new information. To this end, we propose CooK, a novel framework to empower general-purpose large language models with modular and collaboratively sourced knowledge. We first introduce specialized language models, autoregressive models trained on corpora from a wide range of domains and sources. These specialized LMs serve as parametric knowledge repositories that are later prompted to generate background knowledge for general-purpose LLMs. We then propose three knowledge filters to dynamically select and retain information in generated documents by controlling for relevance, brevity, and factuality. Finally, we propose bottom-up and top-down knowledge integration approaches to augment general-purpose LLMs with the curated (relevant, factual) knowledge from community-driven specialized LMs that enable multi-domain knowledge synthesis and on-demand knowledge requests. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that CooK achieves state-of-the-art performance on six benchmark datasets. Our results highlight the potential of enriching general-purpose LLMs with evolving and modular knowledge -- relevant knowledge that can be continuously updated through the collective efforts of the research community.
FactKB: Generalizable Factuality Evaluation using Language Models Enhanced with Factual Knowledge
May 14, 2023Abstract:Evaluating the factual consistency of automatically generated summaries is essential for the progress and adoption of reliable summarization systems. Despite recent advances, existing factuality evaluation models are not robust, being especially prone to entity and relation errors in new domains. We propose FactKB, a simple new approach to factuality evaluation that is generalizable across domains, in particular with respect to entities and relations. FactKB is based on language models pretrained using facts extracted from external knowledge bases. We introduce three types of complementary factuality pretraining objectives based on direct entity facts, facts grounded in auxiliary knowledge about entities, and facts constructed compositionally through knowledge base walks. The resulting factuality evaluation model achieves state-of-the-art performance on two in-domain news summarization benchmarks as well as on three out-of-domain scientific literature datasets. Further analysis of FactKB shows improved ability to detect erroneous entities and relations in summaries and is robust and generalizable across domains.
Detecting Spoilers in Movie Reviews with External Movie Knowledge and User Networks
Apr 22, 2023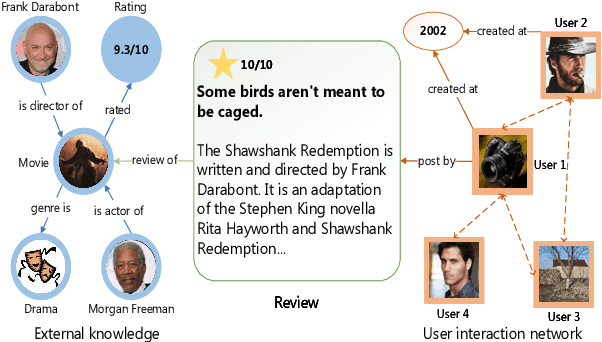
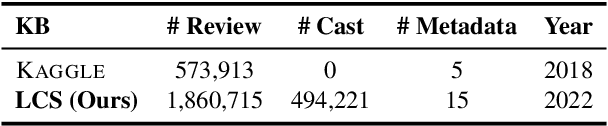

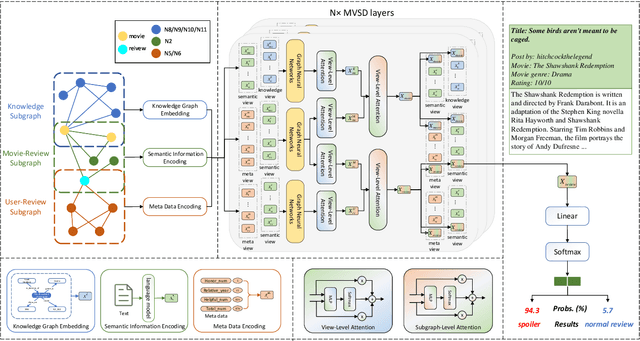
Abstract:Online movie review platforms are providing crowdsourced feedback for the film industry and the general public, while spoiler reviews greatly compromise user experience. Although preliminary research efforts were made to automatically identify spoilers, they merely focus on the review content itself, while robust spoiler detection requires putting the review into the context of facts and knowledge regarding movies, user behavior on film review platforms, and more. In light of these challenges, we first curate a large-scale network-based spoiler detection dataset LCS and a comprehensive and up-to-date movie knowledge base UKM. We then propose MVSD, a novel Multi-View Spoiler Detection framework that takes into account the external knowledge about movies and user activities on movie review platforms. Specifically, MVSD constructs three interconnecting heterogeneous information networks to model diverse data sources and their multi-view attributes, while we design and employ a novel heterogeneous graph neural network architecture for spoiler detection as node-level classification. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MVSD advances the state-of-the-art on two spoiler detection datasets, while the introduction of external knowledge and user interactions help ground robust spoiler detection. Our data and code are available at https://github.com/Arthur-Heng/Spoiler-Detection
TwiBot-22: Towards Graph-Based Twitter Bot Detection
Jun 12, 2022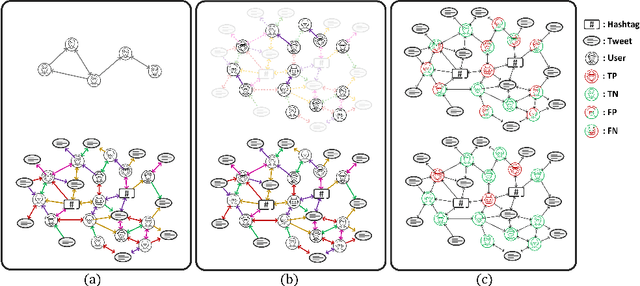
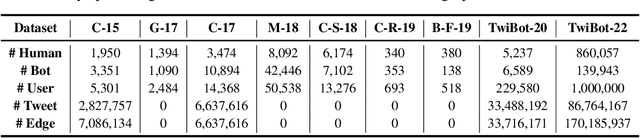
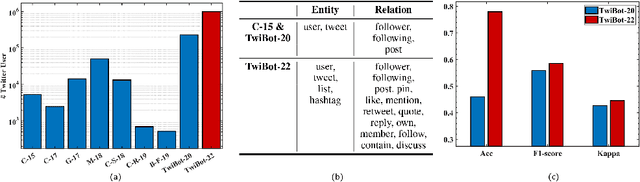
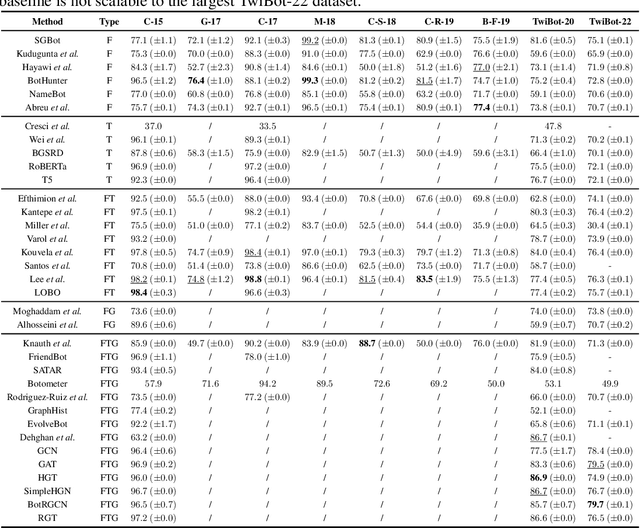
Abstract:Twitter bot detection has become an increasingly important task to combat misinformation, facilitate social media moderation, and preserve the integrity of the online discourse. State-of-the-art bot detection methods generally leverage the graph structure of the Twitter network, and they exhibit promising performance when confronting novel Twitter bots that traditional methods fail to detect. However, very few of the existing Twitter bot detection datasets are graph-based, and even these few graph-based datasets suffer from limited dataset scale, incomplete graph structure, as well as low annotation quality. In fact, the lack of a large-scale graph-based Twitter bot detection benchmark that addresses these issues has seriously hindered the development and evaluation of novel graph-based bot detection approaches. In this paper, we propose TwiBot-22, a comprehensive graph-based Twitter bot detection benchmark that presents the largest dataset to date, provides diversified entities and relations on the Twitter network, and has considerably better annotation quality than existing datasets. In addition, we re-implement 35 representative Twitter bot detection baselines and evaluate them on 9 datasets, including TwiBot-22, to promote a fair comparison of model performance and a holistic understanding of research progress. To facilitate further research, we consolidate all implemented codes and datasets into the TwiBot-22 evaluation framework, where researchers could consistently evaluate new models and datasets. The TwiBot-22 Twitter bot detection benchmark and evaluation framework are publicly available at https://twibot22.github.io/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge