Binchi Zhang
GraphTOP: Graph Topology-Oriented Prompting for Graph Neural Networks
Oct 25, 2025Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have revolutionized the field of graph learning by learning expressive graph representations from massive graph data. As a common pattern to train powerful GNNs, the "pre-training, adaptation" scheme first pre-trains GNNs over unlabeled graph data and subsequently adapts them to specific downstream tasks. In the adaptation phase, graph prompting is an effective strategy that modifies input graph data with learnable prompts while keeping pre-trained GNN models frozen. Typically, existing graph prompting studies mainly focus on *feature-oriented* methods that apply graph prompts to node features or hidden representations. However, these studies often achieve suboptimal performance, as they consistently overlook the potential of *topology-oriented* prompting, which adapts pre-trained GNNs by modifying the graph topology. In this study, we conduct a pioneering investigation of graph prompting in terms of graph topology. We propose the first **Graph** **T**opology-**O**riented **P**rompting (GraphTOP) framework to effectively adapt pre-trained GNN models for downstream tasks. More specifically, we reformulate topology-oriented prompting as an edge rewiring problem within multi-hop local subgraphs and relax it into the continuous probability space through reparameterization while ensuring tight relaxation and preserving graph sparsity. Extensive experiments on five graph datasets under four pre-training strategies demonstrate that our proposed GraphTOP outshines six baselines on multiple node classification datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/xbfu/GraphTOP.
Virtual Nodes Can Help: Tackling Distribution Shifts in Federated Graph Learning
Dec 26, 2024Abstract:Federated Graph Learning (FGL) enables multiple clients to jointly train powerful graph learning models, e.g., Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), without sharing their local graph data for graph-related downstream tasks, such as graph property prediction. In the real world, however, the graph data can suffer from significant distribution shifts across clients as the clients may collect their graph data for different purposes. In particular, graph properties are usually associated with invariant label-relevant substructures (i.e., subgraphs) across clients, while label-irrelevant substructures can appear in a client-specific manner. The issue of distribution shifts of graph data hinders the efficiency of GNN training and leads to serious performance degradation in FGL. To tackle the aforementioned issue, we propose a novel FGL framework entitled FedVN that eliminates distribution shifts through client-specific graph augmentation strategies with multiple learnable Virtual Nodes (VNs). Specifically, FedVN lets the clients jointly learn a set of shared VNs while training a global GNN model. To eliminate distribution shifts, each client trains a personalized edge generator that determines how the VNs connect local graphs in a client-specific manner. Furthermore, we provide theoretical analyses indicating that FedVN can eliminate distribution shifts of graph data across clients. Comprehensive experiments on four datasets under five settings demonstrate the superiority of our proposed FedVN over nine baselines.
Federated Graph Learning with Graphless Clients
Nov 13, 2024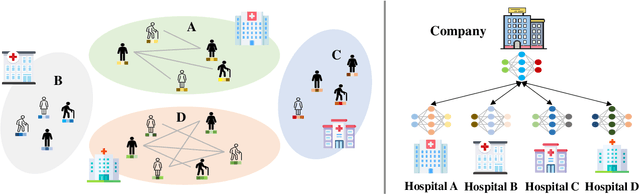
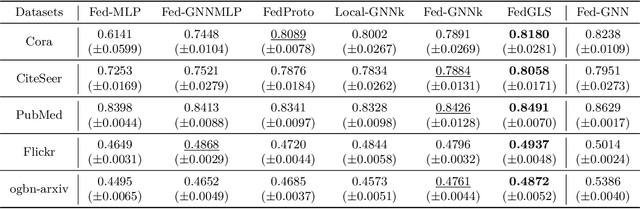
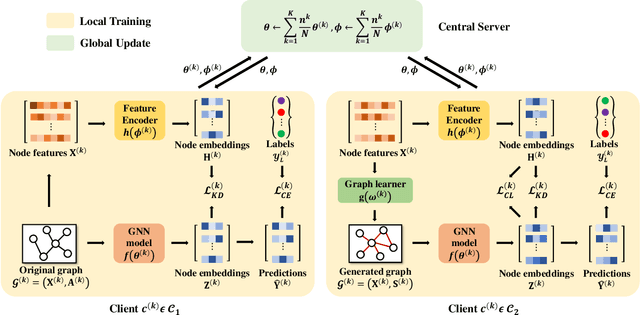
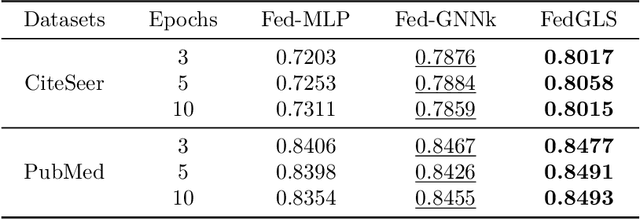
Abstract:Federated Graph Learning (FGL) is tasked with training machine learning models, such as Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), for multiple clients, each with its own graph data. Existing methods usually assume that each client has both node features and graph structure of its graph data. In real-world scenarios, however, there exist federated systems where only a part of the clients have such data while other clients (i.e. graphless clients) may only have node features. This naturally leads to a novel problem in FGL: how to jointly train a model over distributed graph data with graphless clients? In this paper, we propose a novel framework FedGLS to tackle the problem in FGL with graphless clients. In FedGLS, we devise a local graph learner on each graphless client which learns the local graph structure with the structure knowledge transferred from other clients. To enable structure knowledge transfer, we design a GNN model and a feature encoder on each client. During local training, the feature encoder retains the local graph structure knowledge together with the GNN model via knowledge distillation, and the structure knowledge is transferred among clients in global update. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of the proposed FedGLS over five baselines.
Federated Graph Learning with Structure Proxy Alignment
Aug 18, 2024



Abstract:Federated Graph Learning (FGL) aims to learn graph learning models over graph data distributed in multiple data owners, which has been applied in various applications such as social recommendation and financial fraud detection. Inherited from generic Federated Learning (FL), FGL similarly has the data heterogeneity issue where the label distribution may vary significantly for distributed graph data across clients. For instance, a client can have the majority of nodes from a class, while another client may have only a few nodes from the same class. This issue results in divergent local objectives and impairs FGL convergence for node-level tasks, especially for node classification. Moreover, FGL also encounters a unique challenge for the node classification task: the nodes from a minority class in a client are more likely to have biased neighboring information, which prevents FGL from learning expressive node embeddings with Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). To grapple with the challenge, we propose FedSpray, a novel FGL framework that learns local class-wise structure proxies in the latent space and aligns them to obtain global structure proxies in the server. Our goal is to obtain the aligned structure proxies that can serve as reliable, unbiased neighboring information for node classification. To achieve this, FedSpray trains a global feature-structure encoder and generates unbiased soft targets with structure proxies to regularize local training of GNN models in a personalized way. We conduct extensive experiments over four datasets, and experiment results validate the superiority of FedSpray compared with other baselines. Our code is available at https://github.com/xbfu/FedSpray.
Understanding and Modeling Job Marketplace with Pretrained Language Models
Aug 08, 2024Abstract:Job marketplace is a heterogeneous graph composed of interactions among members (job-seekers), companies, and jobs. Understanding and modeling job marketplace can benefit both job seekers and employers, ultimately contributing to the greater good of the society. However, existing graph neural network (GNN)-based methods have shallow understandings of the associated textual features and heterogeneous relations. To address the above challenges, we propose PLM4Job, a job marketplace foundation model that tightly couples pretrained language models (PLM) with job market graph, aiming to fully utilize the pretrained knowledge and reasoning ability to model member/job textual features as well as various member-job relations simultaneously. In the pretraining phase, we propose a heterogeneous ego-graph-based prompting strategy to model and aggregate member/job textual features based on the topological structure around the target member/job node, where entity type embeddings and graph positional embeddings are introduced accordingly to model different entities and their heterogeneous relations. Meanwhile, a proximity-aware attention alignment strategy is designed to dynamically adjust the attention of the PLM on ego-graph node tokens in the prompt, such that the attention can be better aligned with job marketplace semantics. Extensive experiments at LinkedIn demonstrate the effectiveness of PLM4Job.
Verification of Machine Unlearning is Fragile
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:As privacy concerns escalate in the realm of machine learning, data owners now have the option to utilize machine unlearning to remove their data from machine learning models, following recent legislation. To enhance transparency in machine unlearning and avoid potential dishonesty by model providers, various verification strategies have been proposed. These strategies enable data owners to ascertain whether their target data has been effectively unlearned from the model. However, our understanding of the safety issues of machine unlearning verification remains nascent. In this paper, we explore the novel research question of whether model providers can circumvent verification strategies while retaining the information of data supposedly unlearned. Our investigation leads to a pessimistic answer: \textit{the verification of machine unlearning is fragile}. Specifically, we categorize the current verification strategies regarding potential dishonesty among model providers into two types. Subsequently, we introduce two novel adversarial unlearning processes capable of circumventing both types. We validate the efficacy of our methods through theoretical analysis and empirical experiments using real-world datasets. This study highlights the vulnerabilities and limitations in machine unlearning verification, paving the way for further research into the safety of machine unlearning.
Towards Certified Unlearning for Deep Neural Networks
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:In the field of machine unlearning, certified unlearning has been extensively studied in convex machine learning models due to its high efficiency and strong theoretical guarantees. However, its application to deep neural networks (DNNs), known for their highly nonconvex nature, still poses challenges. To bridge the gap between certified unlearning and DNNs, we propose several simple techniques to extend certified unlearning methods to nonconvex objectives. To reduce the time complexity, we develop an efficient computation method by inverse Hessian approximation without compromising certification guarantees. In addition, we extend our discussion of certification to nonconvergence training and sequential unlearning, considering that real-world users can send unlearning requests at different time points. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate the efficacy of our method and the advantages of certified unlearning in DNNs.
IDEA: A Flexible Framework of Certified Unlearning for Graph Neural Networks
Jul 28, 2024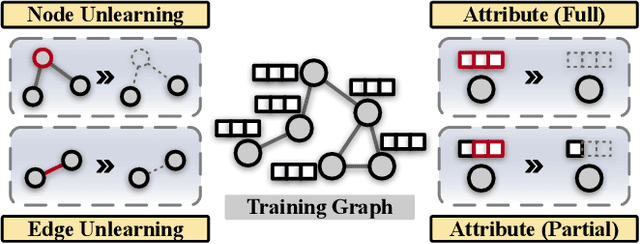
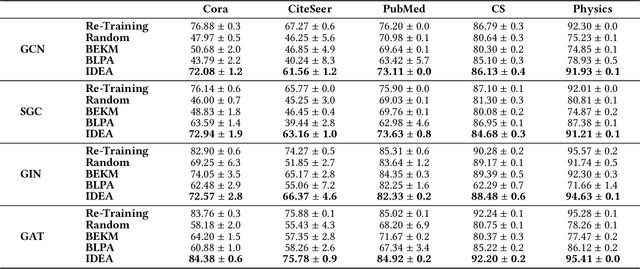
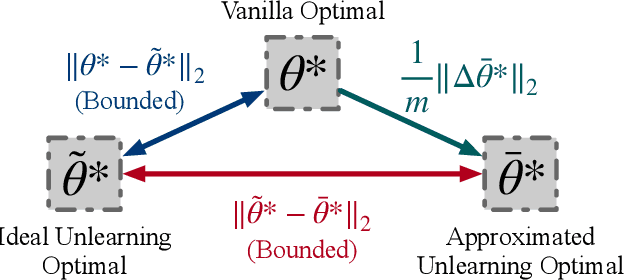
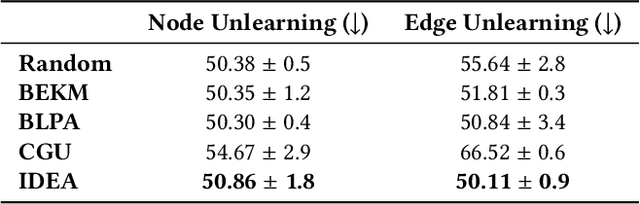
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have been increasingly deployed in a plethora of applications. However, the graph data used for training may contain sensitive personal information of the involved individuals. Once trained, GNNs typically encode such information in their learnable parameters. As a consequence, privacy leakage may happen when the trained GNNs are deployed and exposed to potential attackers. Facing such a threat, machine unlearning for GNNs has become an emerging technique that aims to remove certain personal information from a trained GNN. Among these techniques, certified unlearning stands out, as it provides a solid theoretical guarantee of the information removal effectiveness. Nevertheless, most of the existing certified unlearning methods for GNNs are only designed to handle node and edge unlearning requests. Meanwhile, these approaches are usually tailored for either a specific design of GNN or a specially designed training objective. These disadvantages significantly jeopardize their flexibility. In this paper, we propose a principled framework named IDEA to achieve flexible and certified unlearning for GNNs. Specifically, we first instantiate four types of unlearning requests on graphs, and then we propose an approximation approach to flexibly handle these unlearning requests over diverse GNNs. We further provide theoretical guarantee of the effectiveness for the proposed approach as a certification. Different from existing alternatives, IDEA is not designed for any specific GNNs or optimization objectives to perform certified unlearning, and thus can be easily generalized. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of IDEA in multiple key perspectives.
Safety in Graph Machine Learning: Threats and Safeguards
May 17, 2024Abstract:Graph Machine Learning (Graph ML) has witnessed substantial advancements in recent years. With their remarkable ability to process graph-structured data, Graph ML techniques have been extensively utilized across diverse applications, including critical domains like finance, healthcare, and transportation. Despite their societal benefits, recent research highlights significant safety concerns associated with the widespread use of Graph ML models. Lacking safety-focused designs, these models can produce unreliable predictions, demonstrate poor generalizability, and compromise data confidentiality. In high-stakes scenarios such as financial fraud detection, these vulnerabilities could jeopardize both individuals and society at large. Therefore, it is imperative to prioritize the development of safety-oriented Graph ML models to mitigate these risks and enhance public confidence in their applications. In this survey paper, we explore three critical aspects vital for enhancing safety in Graph ML: reliability, generalizability, and confidentiality. We categorize and analyze threats to each aspect under three headings: model threats, data threats, and attack threats. This novel taxonomy guides our review of effective strategies to protect against these threats. Our systematic review lays a groundwork for future research aimed at developing practical, safety-centered Graph ML models. Furthermore, we highlight the significance of safe Graph ML practices and suggest promising avenues for further investigation in this crucial area.
ELEGANT: Certified Defense on the Fairness of Graph Neural Networks
Nov 05, 2023Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as a prominent graph learning model in various graph-based tasks over the years. Nevertheless, due to the vulnerabilities of GNNs, it has been empirically proved that malicious attackers could easily corrupt the fairness level of their predictions by adding perturbations to the input graph data. In this paper, we take crucial steps to study a novel problem of certifiable defense on the fairness level of GNNs. Specifically, we propose a principled framework named ELEGANT and present a detailed theoretical certification analysis for the fairness of GNNs. ELEGANT takes any GNNs as its backbone, and the fairness level of such a backbone is theoretically impossible to be corrupted under certain perturbation budgets for attackers. Notably, ELEGANT does not have any assumption over the GNN structure or parameters, and does not require re-training the GNNs to realize certification. Hence it can serve as a plug-and-play framework for any optimized GNNs ready to be deployed. We verify the satisfactory effectiveness of ELEGANT in practice through extensive experiments on real-world datasets across different backbones of GNNs, where ELEGANT is also demonstrated to be beneficial for GNN debiasing. Open-source code can be found at https://github.com/yushundong/ELEGANT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge