Yuxi Hu
${C}^{3}$-GS: Learning Context-aware, Cross-dimension, Cross-scale Feature for Generalizable Gaussian Splatting
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Generalizable Gaussian Splatting aims to synthesize novel views for unseen scenes without per-scene optimization. In particular, recent advancements utilize feed-forward networks to predict per-pixel Gaussian parameters, enabling high-quality synthesis from sparse input views. However, existing approaches fall short in encoding discriminative, multi-view consistent features for Gaussian predictions, which struggle to construct accurate geometry with sparse views. To address this, we propose $\mathbf{C}^{3}$-GS, a framework that enhances feature learning by incorporating context-aware, cross-dimension, and cross-scale constraints. Our architecture integrates three lightweight modules into a unified rendering pipeline, improving feature fusion and enabling photorealistic synthesis without requiring additional supervision. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets validate that $\mathbf{C}^{3}$-GS achieves state-of-the-art rendering quality and generalization ability. Code is available at: https://github.com/YuhsiHu/C3-GS.
Two-dimensional Sparse Parallelism for Large Scale Deep Learning Recommendation Model Training
Aug 05, 2025Abstract:The increasing complexity of deep learning recommendation models (DLRM) has led to a growing need for large-scale distributed systems that can efficiently train vast amounts of data. In DLRM, the sparse embedding table is a crucial component for managing sparse categorical features. Typically, these tables in industrial DLRMs contain trillions of parameters, necessitating model parallelism strategies to address memory constraints. However, as training systems expand with massive GPUs, the traditional fully parallelism strategies for embedding table post significant scalability challenges, including imbalance and straggler issues, intensive lookup communication, and heavy embedding activation memory. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel two-dimensional sparse parallelism approach. Rather than fully sharding tables across all GPUs, our solution introduces data parallelism on top of model parallelism. This enables efficient all-to-all communication and reduces peak memory consumption. Additionally, we have developed the momentum-scaled row-wise AdaGrad algorithm to mitigate performance losses associated with the shift in training paradigms. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach significantly enhances training efficiency while maintaining model performance parity. It achieves nearly linear training speed scaling up to 4K GPUs, setting a new state-of-the-art benchmark for recommendation model training.
ICG-MVSNet: Learning Intra-view and Cross-view Relationships for Guidance in Multi-View Stereo
Mar 27, 2025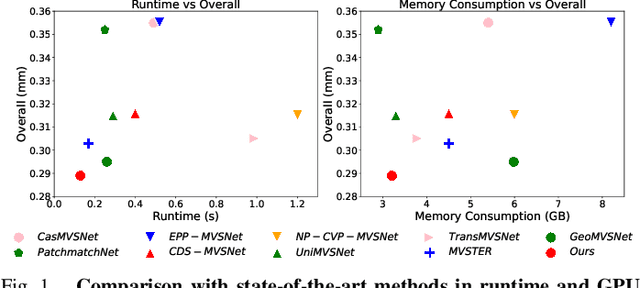
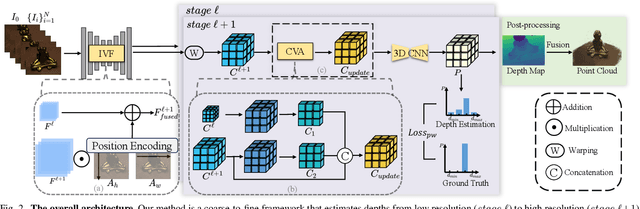
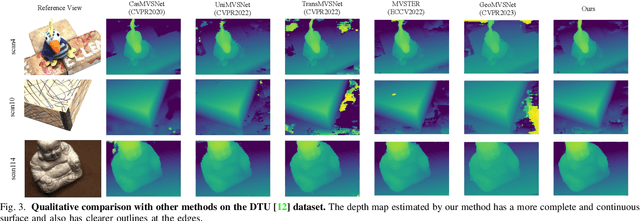
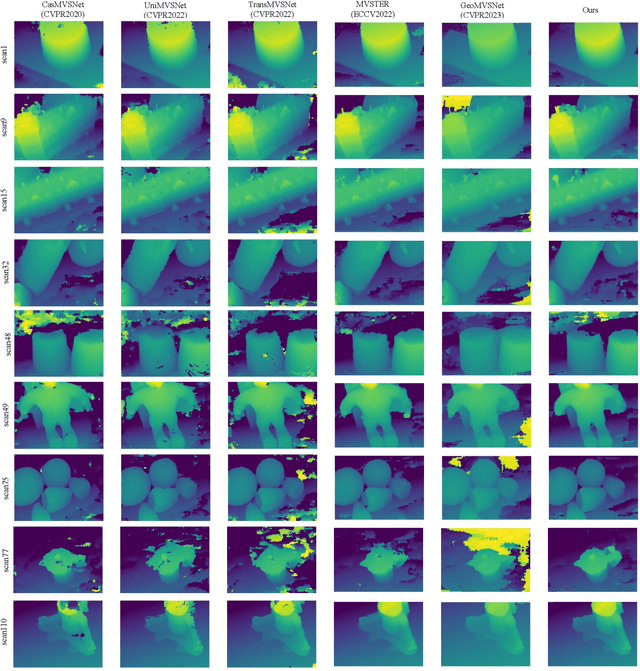
Abstract:Multi-view Stereo (MVS) aims to estimate depth and reconstruct 3D point clouds from a series of overlapping images. Recent learning-based MVS frameworks overlook the geometric information embedded in features and correlations, leading to weak cost matching. In this paper, we propose ICG-MVSNet, which explicitly integrates intra-view and cross-view relationships for depth estimation. Specifically, we develop an intra-view feature fusion module that leverages the feature coordinate correlations within a single image to enhance robust cost matching. Additionally, we introduce a lightweight cross-view aggregation module that efficiently utilizes the contextual information from volume correlations to guide regularization. Our method is evaluated on the DTU dataset and Tanks and Temples benchmark, consistently achieving competitive performance against state-of-the-art works, while requiring lower computational resources.
External Large Foundation Model: How to Efficiently Serve Trillions of Parameters for Online Ads Recommendation
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Ads recommendation is a prominent service of online advertising systems and has been actively studied. Recent studies indicate that scaling-up and advanced design of the recommendation model can bring significant performance improvement. However, with a larger model scale, such prior studies have a significantly increasing gap from industry as they often neglect two fundamental challenges in industrial-scale applications. First, training and inference budgets are restricted for the model to be served, exceeding which may incur latency and impair user experience. Second, large-volume data arrive in a streaming mode with data distributions dynamically shifting, as new users/ads join and existing users/ads leave the system. We propose the External Large Foundation Model (ExFM) framework to address the overlooked challenges. Specifically, we develop external distillation and a data augmentation system (DAS) to control the computational cost of training/inference while maintaining high performance. We design the teacher in a way like a foundation model (FM) that can serve multiple students as vertical models (VMs) to amortize its building cost. We propose Auxiliary Head and Student Adapter to mitigate the data distribution gap between FM and VMs caused by the streaming data issue. Comprehensive experiments on internal industrial-scale applications and public datasets demonstrate significant performance gain by ExFM.
Fine-Grained Embedding Dimension Optimization During Training for Recommender Systems
Jan 09, 2024



Abstract:Huge embedding tables in modern Deep Learning Recommender Models (DLRM) require prohibitively large memory during training and inference. Aiming to reduce the memory footprint of training, this paper proposes FIne-grained In-Training Embedding Dimension optimization (FIITED). Given the observation that embedding vectors are not equally important, FIITED adjusts the dimension of each individual embedding vector continuously during training, assigning longer dimensions to more important embeddings while adapting to dynamic changes in data. A novel embedding storage system based on virtually-hashed physically-indexed hash tables is designed to efficiently implement the embedding dimension adjustment and effectively enable memory saving. Experiments on two industry models show that FIITED is able to reduce the size of embeddings by more than 65% while maintaining the trained model's quality, saving significantly more memory than a state-of-the-art in-training embedding pruning method. On public click-through rate prediction datasets, FIITED is able to prune up to 93.75%-99.75% embeddings without significant accuracy loss.
High-performance, Distributed Training of Large-scale Deep Learning Recommendation Models
Apr 15, 2021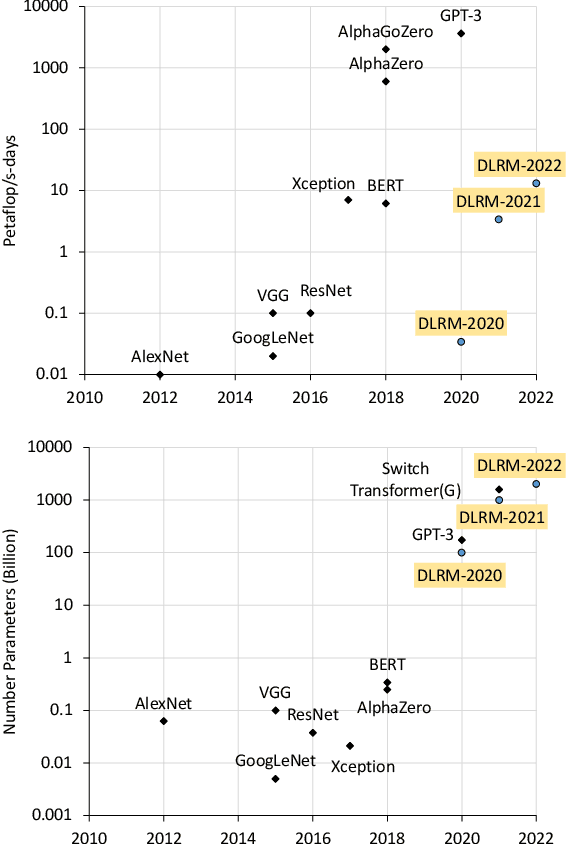

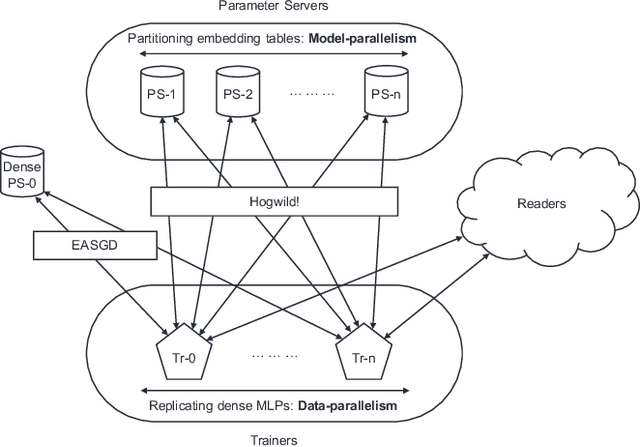
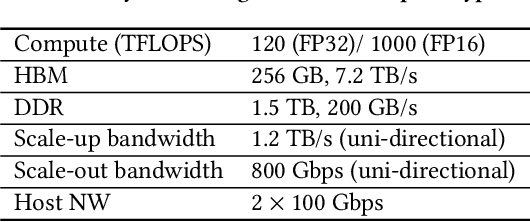
Abstract:Deep learning recommendation models (DLRMs) are used across many business-critical services at Facebook and are the single largest AI application in terms of infrastructure demand in its data-centers. In this paper we discuss the SW/HW co-designed solution for high-performance distributed training of large-scale DLRMs. We introduce a high-performance scalable software stack based on PyTorch and pair it with the new evolution of Zion platform, namely ZionEX. We demonstrate the capability to train very large DLRMs with up to 12 Trillion parameters and show that we can attain 40X speedup in terms of time to solution over previous systems. We achieve this by (i) designing the ZionEX platform with dedicated scale-out network, provisioned with high bandwidth, optimal topology and efficient transport (ii) implementing an optimized PyTorch-based training stack supporting both model and data parallelism (iii) developing sharding algorithms capable of hierarchical partitioning of the embedding tables along row, column dimensions and load balancing them across multiple workers; (iv) adding high-performance core operators while retaining flexibility to support optimizers with fully deterministic updates (v) leveraging reduced precision communications, multi-level memory hierarchy (HBM+DDR+SSD) and pipelining. Furthermore, we develop and briefly comment on distributed data ingestion and other supporting services that are required for the robust and efficient end-to-end training in production environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge