Yi Qin
Electronic and Computer Engineering, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, China
Detecting Misbehaviors of Large Vision-Language Models by Evidential Uncertainty Quantification
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) have shown substantial advances in multimodal understanding and generation. However, when presented with incompetent or adversarial inputs, they frequently produce unreliable or even harmful content, such as fact hallucinations or dangerous instructions. This misalignment with human expectations, referred to as \emph{misbehaviors} of LVLMs, raises serious concerns for deployment in critical applications. These misbehaviors are found to stem from epistemic uncertainty, specifically either conflicting internal knowledge or the absence of supporting information. However, existing uncertainty quantification methods, which typically capture only overall epistemic uncertainty, have shown limited effectiveness in identifying such issues. To address this gap, we propose Evidential Uncertainty Quantification (EUQ), a fine-grained method that captures both information conflict and ignorance for effective detection of LVLM misbehaviors. In particular, we interpret features from the model output head as either supporting (positive) or opposing (negative) evidence. Leveraging Evidence Theory, we model and aggregate this evidence to quantify internal conflict and knowledge gaps within a single forward pass. We extensively evaluate our method across four categories of misbehavior, including hallucinations, jailbreaks, adversarial vulnerabilities, and out-of-distribution (OOD) failures, using state-of-the-art LVLMs, and find that EUQ consistently outperforms strong baselines, showing that hallucinations correspond to high internal conflict and OOD failures to high ignorance. Furthermore, layer-wise evidential uncertainty dynamics analysis helps interpret the evolution of internal representations from a new perspective. The source code is available at https://github.com/HT86159/EUQ.
Incentivizing Cardiologist-Like Reasoning in MLLMs for Interpretable Echocardiographic Diagnosis
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Echocardiographic diagnosis is vital for cardiac screening yet remains challenging. Existing echocardiography foundation models do not effectively capture the relationships between quantitative measurements and clinical manifestations, whereas medical reasoning multimodal large language models (MLLMs) require costly construction of detailed reasoning paths and remain ineffective at directly incorporating such echocardiographic priors into their reasoning. To address these limitations, we propose a novel approach comprising Cardiac Reasoning Template (CRT) and CardiacMind to enhance MLLM's echocardiographic reasoning by introducing cardiologist-like mindset. Specifically, CRT provides stepwise canonical diagnostic procedures for complex cardiac diseases to streamline reasoning path construction without the need for costly case-by-case verification. To incentivize reasoning MLLM under CRT, we develop CardiacMind, a new reinforcement learning scheme with three novel rewards: Procedural Quantity Reward (PQtR), Procedural Quality Reward (PQlR), and Echocardiographic Semantic Reward (ESR). PQtR promotes detailed reasoning; PQlR promotes integration of evidence across views and modalities, while ESR grounds stepwise descriptions in visual content. Our methods show a 48% improvement in multiview echocardiographic diagnosis for 15 complex cardiac diseases and a 5% improvement on CardiacNet-PAH over prior methods. The user study on our method's reasoning outputs shows 93.33% clinician agreement with cardiologist-like reasoning logic. Our code will be available.
Cross-view Generalized Diffusion Model for Sparse-view CT Reconstruction
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Sparse-view computed tomography (CT) reduces radiation exposure by subsampling projection views, but conventional reconstruction methods produce severe streak artifacts with undersampled data. While deep-learning-based methods enable single-step artifact suppression, they often produce over-smoothed results under significant sparsity. Though diffusion models improve reconstruction via iterative refinement and generative priors, they require hundreds of sampling steps and struggle with stability in highly sparse regimes. To tackle these concerns, we present the Cross-view Generalized Diffusion Model (CvG-Diff), which reformulates sparse-view CT reconstruction as a generalized diffusion process. Unlike existing diffusion approaches that rely on stochastic Gaussian degradation, CvG-Diff explicitly models image-domain artifacts caused by angular subsampling as a deterministic degradation operator, leveraging correlations across sparse-view CT at different sample rates. To address the inherent artifact propagation and inefficiency of sequential sampling in generalized diffusion model, we introduce two innovations: Error-Propagating Composite Training (EPCT), which facilitates identifying error-prone regions and suppresses propagated artifacts, and Semantic-Prioritized Dual-Phase Sampling (SPDPS), an adaptive strategy that prioritizes semantic correctness before detail refinement. Together, these innovations enable CvG-Diff to achieve high-quality reconstructions with minimal iterations, achieving 38.34 dB PSNR and 0.9518 SSIM for 18-view CT using only \textbf{10} steps on AAPM-LDCT dataset. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of CvG-Diff over state-of-the-art sparse-view CT reconstruction methods. The code is available at https://github.com/xmed-lab/CvG-Diff.
SAM Encoder Breach by Adversarial Simplicial Complex Triggers Downstream Model Failures
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:While the Segment Anything Model (SAM) transforms interactive segmentation with zero-shot abilities, its inherent vulnerabilities present a single-point risk, potentially leading to the failure of numerous downstream applications. Proactively evaluating these transferable vulnerabilities is thus imperative. Prior adversarial attacks on SAM often present limited transferability due to insufficient exploration of common weakness across domains. To address this, we propose Vertex-Refining Simplicial Complex Attack (VeSCA), a novel method that leverages only the encoder of SAM for generating transferable adversarial examples. Specifically, it achieves this by explicitly characterizing the shared vulnerable regions between SAM and downstream models through a parametric simplicial complex. Our goal is to identify such complexes within adversarially potent regions by iterative vertex-wise refinement. A lightweight domain re-adaptation strategy is introduced to bridge domain divergence using minimal reference data during the initialization of simplicial complex. Ultimately, VeSCA generates consistently transferable adversarial examples through random simplicial complex sampling. Extensive experiments demonstrate that VeSCA achieves performance improved by 12.7% compared to state-of-the-art methods across three downstream model categories across five domain-specific datasets. Our findings further highlight the downstream model risks posed by SAM's vulnerabilities and emphasize the urgency of developing more robust foundation models.
Multi-Modal Explainable Medical AI Assistant for Trustworthy Human-AI Collaboration
May 11, 2025Abstract:Generalist Medical AI (GMAI) systems have demonstrated expert-level performance in biomedical perception tasks, yet their clinical utility remains limited by inadequate multi-modal explainability and suboptimal prognostic capabilities. Here, we present XMedGPT, a clinician-centric, multi-modal AI assistant that integrates textual and visual interpretability to support transparent and trustworthy medical decision-making. XMedGPT not only produces accurate diagnostic and descriptive outputs, but also grounds referenced anatomical sites within medical images, bridging critical gaps in interpretability and enhancing clinician usability. To support real-world deployment, we introduce a reliability indexing mechanism that quantifies uncertainty through consistency-based assessment via interactive question-answering. We validate XMedGPT across four pillars: multi-modal interpretability, uncertainty quantification, and prognostic modeling, and rigorous benchmarking. The model achieves an IoU of 0.703 across 141 anatomical regions, and a Kendall's tau-b of 0.479, demonstrating strong alignment between visual rationales and clinical outcomes. For uncertainty estimation, it attains an AUC of 0.862 on visual question answering and 0.764 on radiology report generation. In survival and recurrence prediction for lung and glioma cancers, it surpasses prior leading models by 26.9%, and outperforms GPT-4o by 25.0%. Rigorous benchmarking across 347 datasets covers 40 imaging modalities and external validation spans 4 anatomical systems confirming exceptional generalizability, with performance gains surpassing existing GMAI by 20.7% for in-domain evaluation and 16.7% on 11,530 in-house data evaluation. Together, XMedGPT represents a significant leap forward in clinician-centric AI integration, offering trustworthy and scalable support for diverse healthcare applications.
Concept-Based Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
May 08, 2025Abstract:Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) enhance interpretability by explaining predictions through human-understandable concepts but typically assume that training and test data share the same distribution. This assumption often fails under domain shifts, leading to degraded performance and poor generalization. To address these limitations and improve the robustness of CBMs, we propose the Concept-based Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (CUDA) framework. CUDA is designed to: (1) align concept representations across domains using adversarial training, (2) introduce a relaxation threshold to allow minor domain-specific differences in concept distributions, thereby preventing performance drop due to over-constraints of these distributions, (3) infer concepts directly in the target domain without requiring labeled concept data, enabling CBMs to adapt to diverse domains, and (4) integrate concept learning into conventional domain adaptation (DA) with theoretical guarantees, improving interpretability and establishing new benchmarks for DA. Experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art CBM and DA methods on real-world datasets.
Reinforced Correlation Between Vision and Language for Precise Medical AI Assistant
May 06, 2025Abstract:Medical AI assistants support doctors in disease diagnosis, medical image analysis, and report generation. However, they still face significant challenges in clinical use, including limited accuracy with multimodal content and insufficient validation in real-world settings. We propose RCMed, a full-stack AI assistant that improves multimodal alignment in both input and output, enabling precise anatomical delineation, accurate localization, and reliable diagnosis through hierarchical vision-language grounding. A self-reinforcing correlation mechanism allows visual features to inform language context, while language semantics guide pixel-wise attention, forming a closed loop that refines both modalities. This correlation is enhanced by a color region description strategy, translating anatomical structures into semantically rich text to learn shape-location-text relationships across scales. Trained on 20 million image-mask-description triplets, RCMed achieves state-of-the-art precision in contextualizing irregular lesions and subtle anatomical boundaries, excelling in 165 clinical tasks across 9 modalities. It achieved a 23.5% relative improvement in cell segmentation from microscopy images over prior methods. RCMed's strong vision-language alignment enables exceptional generalization, with state-of-the-art performance in external validation across 20 clinically significant cancer types, including novel tasks. This work demonstrates how integrated multimodal models capture fine-grained patterns, enabling human-level interpretation in complex scenarios and advancing human-centric AI healthcare.
Improved ICNN-LSTM Model Classification Based on Attitude Sensor Data for Hazardous State Assessment of Magnetic Adhesion Climbing Wall Robots
Dec 30, 2024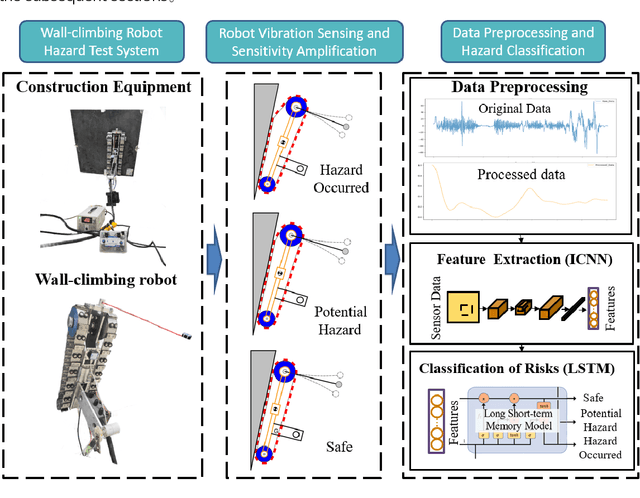
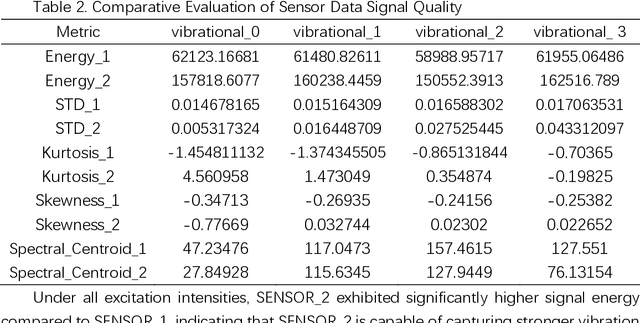
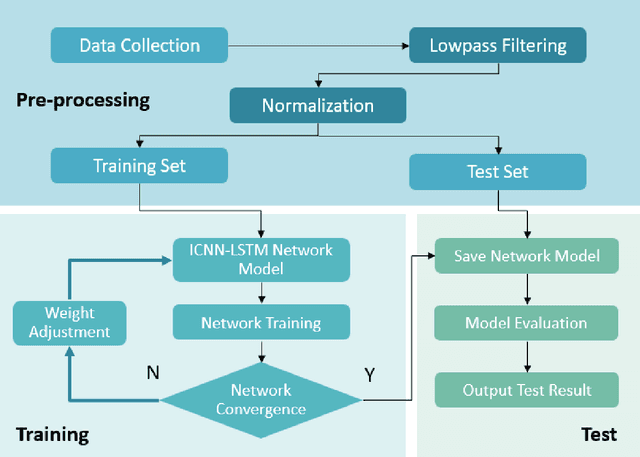
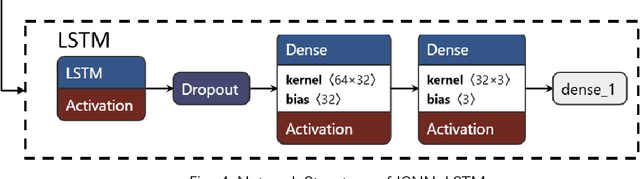
Abstract:Magnetic adhesion tracked climbing robots are widely utilized in high-altitude inspection, welding, and cleaning tasks due to their ability to perform various operations against gravity on vertical or inclined walls. However, during operation, the robot may experience overturning torque caused by its own weight and load, which can lead to the detachment of magnetic plates and subsequently pose safety risks. This paper proposes an improved ICNN-LSTM network classification method based on Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) attitude sensor data for real-time monitoring and assessment of hazardous states in magnetic adhesion tracked climbing robots. Firstly, a data acquisition strategy for attitude sensors capable of capturing minute vibrations is designed. Secondly, a feature extraction and classification model combining an Improved Convolutional Neural Network (ICNN) with a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network is proposed. Experimental validation demonstrates that the proposed minute vibration sensing method achieves significant results, and the proposed classification model consistently exhibits high accuracy compared to other models. The research findings provide effective technical support for the safe operation of climbing robots
FoAM: Foresight-Augmented Multi-Task Imitation Policy for Robotic Manipulation
Sep 29, 2024



Abstract:Multi-task imitation learning (MTIL) has shown significant potential in robotic manipulation by enabling agents to perform various tasks using a unified policy. This simplifies the policy deployment and enhances the agent's adaptability across different contexts. However, key challenges remain, such as maintaining action reliability (e.g., avoiding abnormal action sequences that deviate from nominal task trajectories), distinguishing between similar tasks, and generalizing to unseen scenarios. To address these challenges, we introduce the Foresight-Augmented Manipulation Policy (FoAM), an innovative MTIL framework. FoAM not only learns to mimic expert actions but also predicts the visual outcomes of those actions to enhance decision-making. Additionally, it integrates multi-modal goal inputs, such as visual and language prompts, overcoming the limitations of single-conditioned policies. We evaluated FoAM across over 100 tasks in both simulation and real-world settings, demonstrating that it significantly improves IL policy performance, outperforming current state-of-the-art IL baselines by up to 41% in success rate. Furthermore, we released a simulation benchmark for robotic manipulation, featuring 10 task suites and over 80 challenging tasks designed for multi-task policy training and evaluation. See project homepage https://projFoAM.github.io/ for project details.
Fair Evaluation of Federated Learning Algorithms for Automated Breast Density Classification: The Results of the 2022 ACR-NCI-NVIDIA Federated Learning Challenge
May 22, 2024Abstract:The correct interpretation of breast density is important in the assessment of breast cancer risk. AI has been shown capable of accurately predicting breast density, however, due to the differences in imaging characteristics across mammography systems, models built using data from one system do not generalize well to other systems. Though federated learning (FL) has emerged as a way to improve the generalizability of AI without the need to share data, the best way to preserve features from all training data during FL is an active area of research. To explore FL methodology, the breast density classification FL challenge was hosted in partnership with the American College of Radiology, Harvard Medical School's Mass General Brigham, University of Colorado, NVIDIA, and the National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute. Challenge participants were able to submit docker containers capable of implementing FL on three simulated medical facilities, each containing a unique large mammography dataset. The breast density FL challenge ran from June 15 to September 5, 2022, attracting seven finalists from around the world. The winning FL submission reached a linear kappa score of 0.653 on the challenge test data and 0.413 on an external testing dataset, scoring comparably to a model trained on the same data in a central location.
* 16 pages, 9 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge