Laura Coombs
American College of Radiology, USA
Fair Evaluation of Federated Learning Algorithms for Automated Breast Density Classification: The Results of the 2022 ACR-NCI-NVIDIA Federated Learning Challenge
May 22, 2024Abstract:The correct interpretation of breast density is important in the assessment of breast cancer risk. AI has been shown capable of accurately predicting breast density, however, due to the differences in imaging characteristics across mammography systems, models built using data from one system do not generalize well to other systems. Though federated learning (FL) has emerged as a way to improve the generalizability of AI without the need to share data, the best way to preserve features from all training data during FL is an active area of research. To explore FL methodology, the breast density classification FL challenge was hosted in partnership with the American College of Radiology, Harvard Medical School's Mass General Brigham, University of Colorado, NVIDIA, and the National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute. Challenge participants were able to submit docker containers capable of implementing FL on three simulated medical facilities, each containing a unique large mammography dataset. The breast density FL challenge ran from June 15 to September 5, 2022, attracting seven finalists from around the world. The winning FL submission reached a linear kappa score of 0.653 on the challenge test data and 0.413 on an external testing dataset, scoring comparably to a model trained on the same data in a central location.
* 16 pages, 9 figures
Federated Learning for Breast Density Classification: A Real-World Implementation
Sep 17, 2020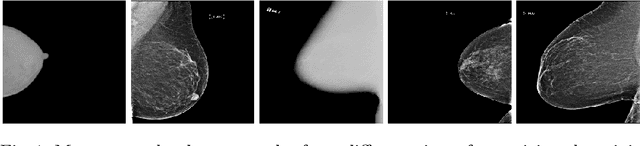
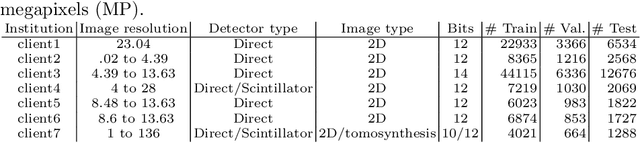
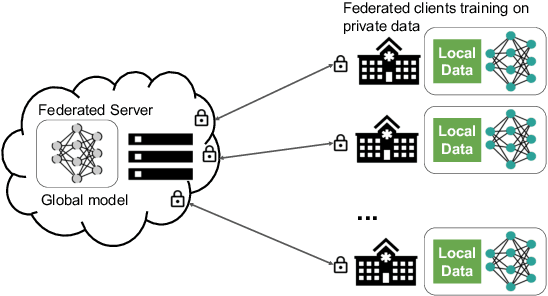
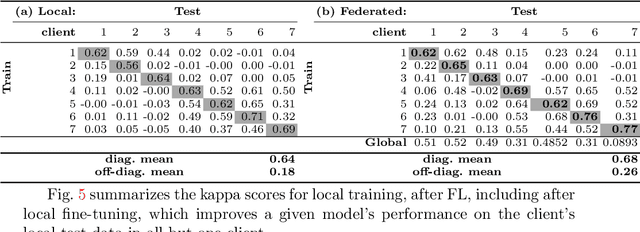
Abstract:Building robust deep learning-based models requires large quantities of diverse training data. In this study, we investigate the use of federated learning (FL) to build medical imaging classification models in a real-world collaborative setting. Seven clinical institutions from across the world joined this FL effort to train a model for breast density classification based on Breast Imaging, Reporting & Data System (BI-RADS). We show that despite substantial differences among the datasets from all sites (mammography system, class distribution, and data set size) and without centralizing data, we can successfully train AI models in federation. The results show that models trained using FL perform 6.3% on average better than their counterparts trained on an institute's local data alone. Furthermore, we show a 45.8% relative improvement in the models' generalizability when evaluated on the other participating sites' testing data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge