Alvin Ihsani
DeepEdit: Deep Editable Learning for Interactive Segmentation of 3D Medical Images
May 18, 2023Abstract:Automatic segmentation of medical images is a key step for diagnostic and interventional tasks. However, achieving this requires large amounts of annotated volumes, which can be tedious and time-consuming task for expert annotators. In this paper, we introduce DeepEdit, a deep learning-based method for volumetric medical image annotation, that allows automatic and semi-automatic segmentation, and click-based refinement. DeepEdit combines the power of two methods: a non-interactive (i.e. automatic segmentation using nnU-Net, UNET or UNETR) and an interactive segmentation method (i.e. DeepGrow), into a single deep learning model. It allows easy integration of uncertainty-based ranking strategies (i.e. aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty computation) and active learning. We propose and implement a method for training DeepEdit by using standard training combined with user interaction simulation. Once trained, DeepEdit allows clinicians to quickly segment their datasets by using the algorithm in auto segmentation mode or by providing clicks via a user interface (i.e. 3D Slicer, OHIF). We show the value of DeepEdit through evaluation on the PROSTATEx dataset for prostate/prostatic lesions and the Multi-Atlas Labeling Beyond the Cranial Vault (BTCV) dataset for abdominal CT segmentation, using state-of-the-art network architectures as baseline for comparison. DeepEdit could reduce the time and effort annotating 3D medical images compared to DeepGrow alone. Source code is available at https://github.com/Project-MONAI/MONAILabel
MONAI Label: A framework for AI-assisted Interactive Labeling of 3D Medical Images
Mar 23, 2022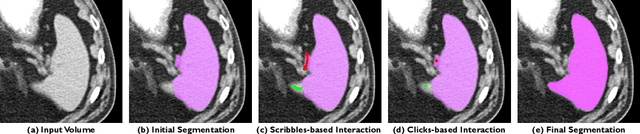
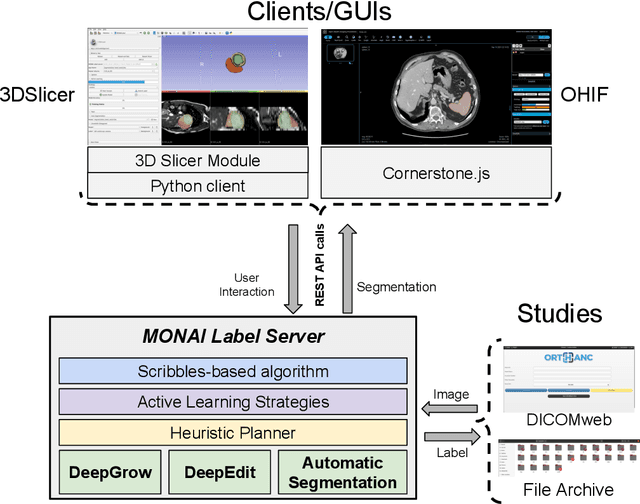
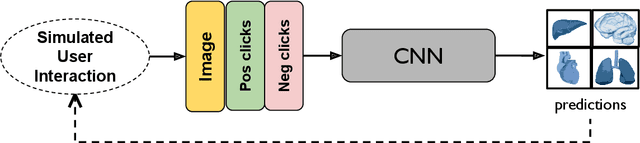
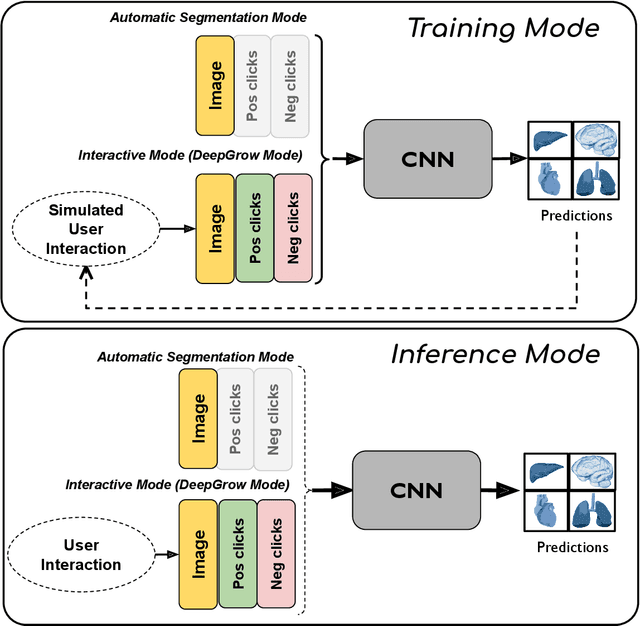
Abstract:The lack of annotated datasets is a major challenge in training new task-specific supervised AI algorithms as manual annotation is expensive and time-consuming. To address this problem, we present MONAI Label, a free and open-source platform that facilitates the development of AI-based applications that aim at reducing the time required to annotate 3D medical image datasets. Through MONAI Label researchers can develop annotation applications focusing on their domain of expertise. It allows researchers to readily deploy their apps as services, which can be made available to clinicians via their preferred user-interface. Currently, MONAI Label readily supports locally installed (3DSlicer) and web-based (OHIF) frontends, and offers two Active learning strategies to facilitate and speed up the training of segmentation algorithms. MONAI Label allows researchers to make incremental improvements to their labeling apps by making them available to other researchers and clinicians alike. Lastly, MONAI Label provides sample labeling apps, namely DeepEdit and DeepGrow, demonstrating dramatically reduced annotation times.
Artificial Intelligence in PET: an Industry Perspective
Jul 14, 2021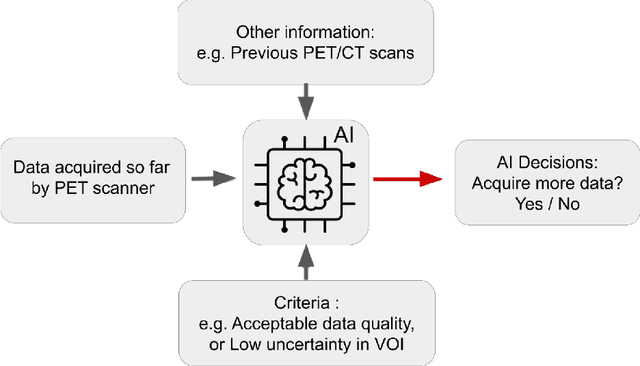
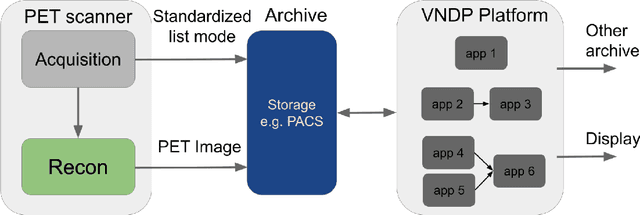
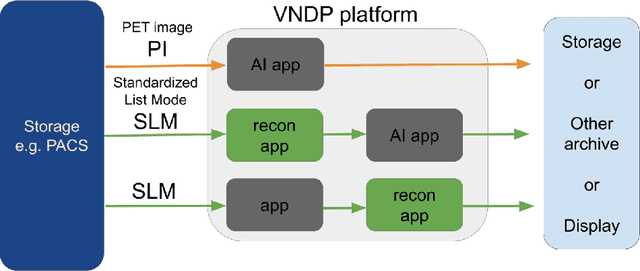
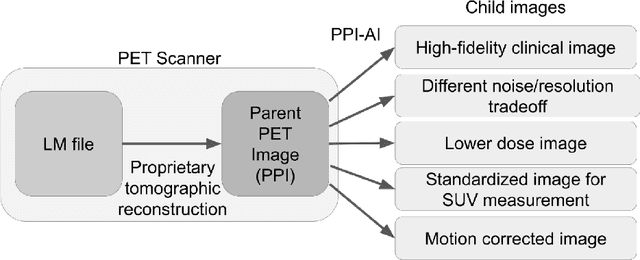
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) has significant potential to positively impact and advance medical imaging, including positron emission tomography (PET) imaging applications. AI has the ability to enhance and optimize all aspects of the PET imaging chain from patient scheduling, patient setup, protocoling, data acquisition, detector signal processing, reconstruction, image processing and interpretation. AI poses industry-specific challenges which will need to be addressed and overcome to maximize the future potentials of AI in PET. This paper provides an overview of these industry-specific challenges for the development, standardization, commercialization, and clinical adoption of AI, and explores the potential enhancements to PET imaging brought on by AI in the near future. In particular, the combination of on-demand image reconstruction, AI, and custom designed data processing workflows may open new possibilities for innovation which would positively impact the industry and ultimately patients.
Federated Learning for Breast Density Classification: A Real-World Implementation
Sep 17, 2020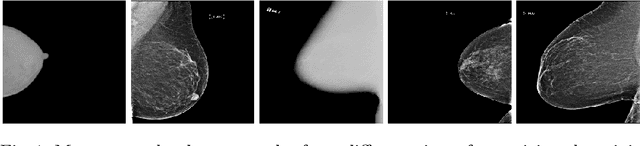
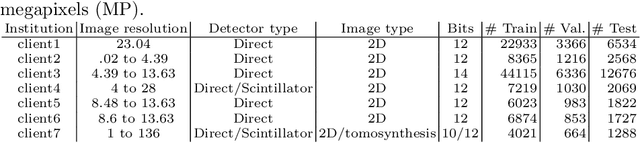
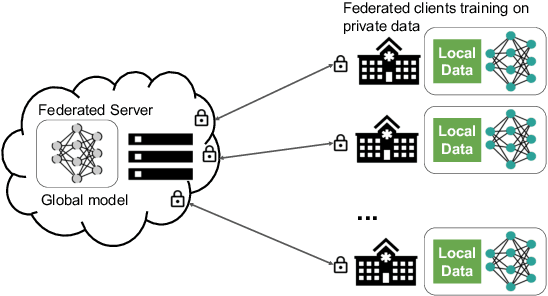
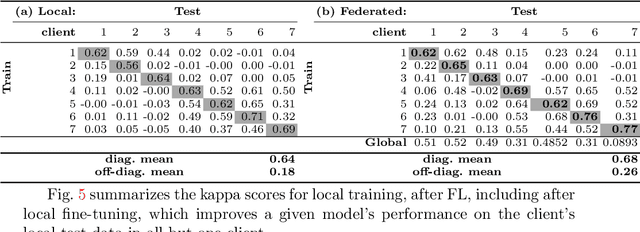
Abstract:Building robust deep learning-based models requires large quantities of diverse training data. In this study, we investigate the use of federated learning (FL) to build medical imaging classification models in a real-world collaborative setting. Seven clinical institutions from across the world joined this FL effort to train a model for breast density classification based on Breast Imaging, Reporting & Data System (BI-RADS). We show that despite substantial differences among the datasets from all sites (mammography system, class distribution, and data set size) and without centralizing data, we can successfully train AI models in federation. The results show that models trained using FL perform 6.3% on average better than their counterparts trained on an institute's local data alone. Furthermore, we show a 45.8% relative improvement in the models' generalizability when evaluated on the other participating sites' testing data.
GANDALF: Generative Adversarial Networks with Discriminator-Adaptive Loss Fine-tuning for Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis from MRI
Aug 10, 2020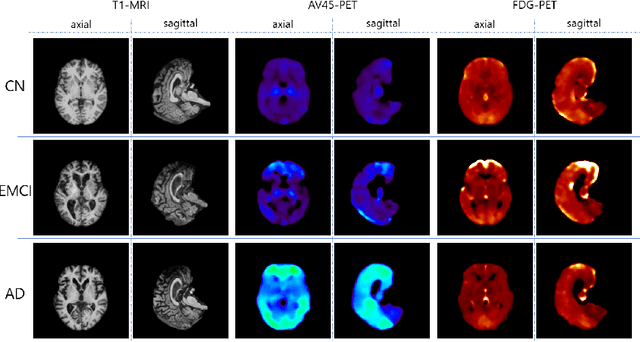
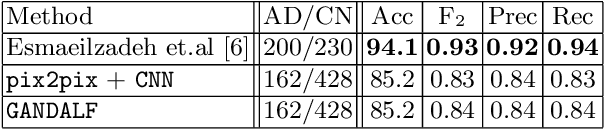
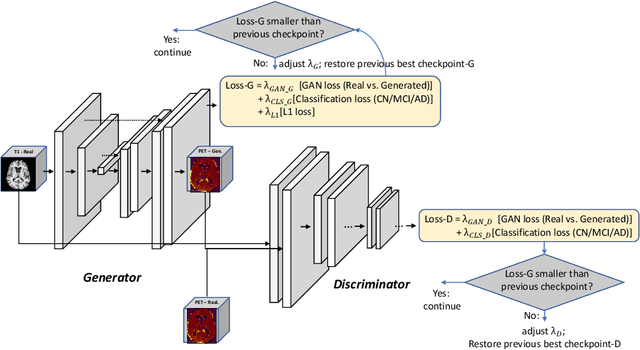
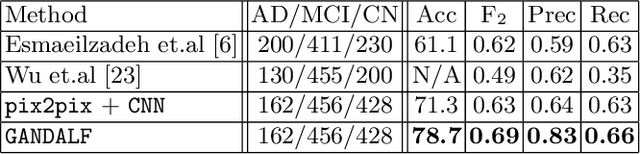
Abstract:Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is now regarded as the gold standard for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease (AD). However, PET imaging can be prohibitive in terms of cost and planning, and is also among the imaging techniques with the highest dosage of radiation. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), in contrast, is more widely available and provides more flexibility when setting the desired image resolution. Unfortunately, the diagnosis of AD using MRI is difficult due to the very subtle physiological differences between healthy and AD subjects visible on MRI. As a result, many attempts have been made to synthesize PET images from MR images using generative adversarial networks (GANs) in the interest of enabling the diagnosis of AD from MR. Existing work on PET synthesis from MRI has largely focused on Conditional GANs, where MR images are used to generate PET images and subsequently used for AD diagnosis. There is no end-to-end training goal. This paper proposes an alternative approach to the aforementioned, where AD diagnosis is incorporated in the GAN training objective to achieve the best AD classification performance. Different GAN lossesare fine-tuned based on the discriminator performance, and the overall training is stabilized. The proposed network architecture and training regime show state-of-the-art performance for three- and four- class AD classification tasks.
GANBERT: Generative Adversarial Networks with Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers for MRI to PET synthesis
Aug 10, 2020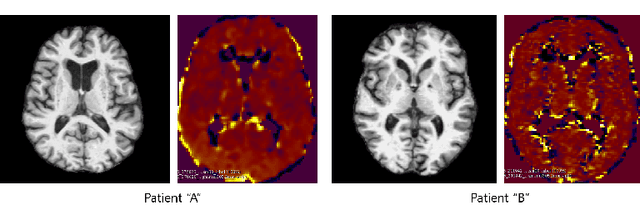
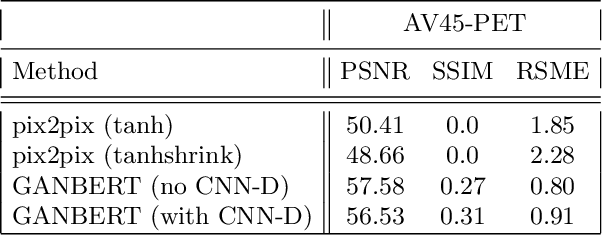
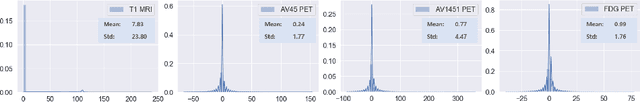
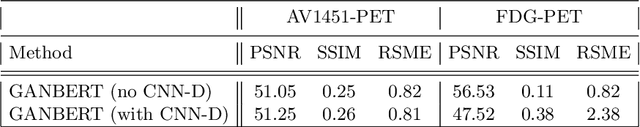
Abstract:Synthesizing medical images, such as PET, is a challenging task due to the fact that the intensity range is much wider and denser than those in photographs and digital renderings and are often heavily biased toward zero. Above all, intensity values in PET have absolute significance, and are used to compute parameters that are reproducible across the population. Yet, usually much manual adjustment has to be made in pre-/post- processing when synthesizing PET images, because its intensity ranges can vary a lot, e.g., between -100 to 1000 in floating point values. To overcome these challenges, we adopt the Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) algorithm that has had great success in natural language processing (NLP), where wide-range floating point intensity values are represented as integers ranging between 0 to 10000 that resemble a dictionary of natural language vocabularies. BERT is then trained to predict a proportion of masked values images, where its "next sentence prediction (NSP)" acts as GAN discriminator. Our proposed approach, is able to generate PET images from MRI images in wide intensity range, with no manual adjustments in pre-/post- processing. It is a method that can scale and ready to deploy.
4D CNN for semantic segmentation of cardiac volumetric sequences
Jun 17, 2019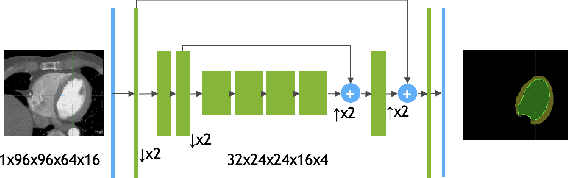
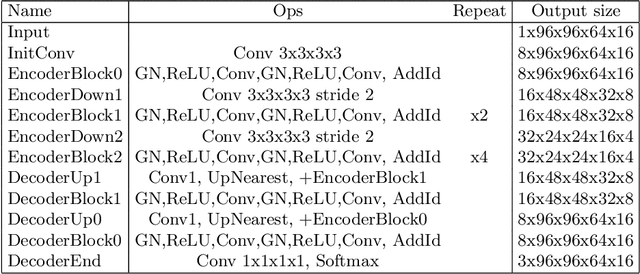
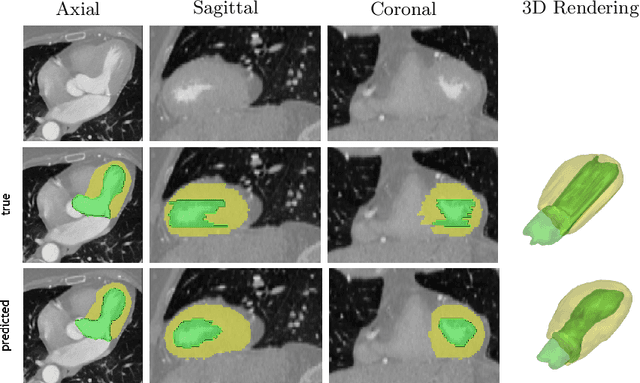
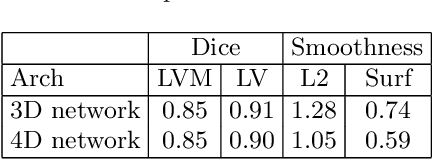
Abstract:We propose a 4D convolutional neural network (CNN) for the segmentation of retrospective ECG-gated cardiac CT, a series of single-channel volumetric data over time. While only a small subset of volumes in the temporal sequence are annotated, we define a sparse loss function on available labels to allow the network to leverage unlabeled images during training and generate a fully segmented sequence. We investigate the accuracy of the proposed 4D network to predict temporally consistent segmentations and compare with traditional 3D segmentation approaches. We demonstrate the feasibility of the 4D CNN and establish its performance on cardiac 4D CCTA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge