Honglong Yang
Radiology Workflow-Guided Hierarchical Reinforcement Fine-Tuning for Medical Report Generation
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Radiologists compose diagnostic reports through a structured workflow: they describe visual findings, summarize them into impressions, and carefully refine statements in clinically critical cases. However, most existing medical report generation (MRG) systems treat reports as flat sequences, overlooking this hierarchical organization and leading to inconsistencies between descriptive and diagnostic content. To align model behavior with real-world reporting practices, we propose RadFlow, a hierarchical workflow-guided reinforcement optimization framework that explicitly models the structured nature of clinical reporting. RadFlow introduces a clinically grounded reward hierarchy that mirrors the organization of radiological reports. At the global level, the reward integrates linguistic fluency, medical-domain correctness, and cross-sectional consistency between Finding and Impression, promoting coherent and clinically faithful narratives. At the local level, a section-specific reward emphasizes Impression quality, reflecting its central role in diagnostic accuracy. Furthermore, a critical-aware policy optimization mechanism adaptively regularizes learning for high-risk or clinically sensitive cases, emulating the cautious refinement behavior of radiologists when documenting critical findings. Together, these components translate the structured reporting paradigm into the reinforcement fine-tuning process, enabling the model to generate reports that are both linguistically consistent and clinically aligned. Experiments on chest X-ray and carotid ultrasound datasets demonstrate that RadFlow consistently improves diagnostic coherence and overall report quality compared with state-of-the-art baselines.
Multi-Modal Explainable Medical AI Assistant for Trustworthy Human-AI Collaboration
May 11, 2025Abstract:Generalist Medical AI (GMAI) systems have demonstrated expert-level performance in biomedical perception tasks, yet their clinical utility remains limited by inadequate multi-modal explainability and suboptimal prognostic capabilities. Here, we present XMedGPT, a clinician-centric, multi-modal AI assistant that integrates textual and visual interpretability to support transparent and trustworthy medical decision-making. XMedGPT not only produces accurate diagnostic and descriptive outputs, but also grounds referenced anatomical sites within medical images, bridging critical gaps in interpretability and enhancing clinician usability. To support real-world deployment, we introduce a reliability indexing mechanism that quantifies uncertainty through consistency-based assessment via interactive question-answering. We validate XMedGPT across four pillars: multi-modal interpretability, uncertainty quantification, and prognostic modeling, and rigorous benchmarking. The model achieves an IoU of 0.703 across 141 anatomical regions, and a Kendall's tau-b of 0.479, demonstrating strong alignment between visual rationales and clinical outcomes. For uncertainty estimation, it attains an AUC of 0.862 on visual question answering and 0.764 on radiology report generation. In survival and recurrence prediction for lung and glioma cancers, it surpasses prior leading models by 26.9%, and outperforms GPT-4o by 25.0%. Rigorous benchmarking across 347 datasets covers 40 imaging modalities and external validation spans 4 anatomical systems confirming exceptional generalizability, with performance gains surpassing existing GMAI by 20.7% for in-domain evaluation and 16.7% on 11,530 in-house data evaluation. Together, XMedGPT represents a significant leap forward in clinician-centric AI integration, offering trustworthy and scalable support for diverse healthcare applications.
DDaTR: Dynamic Difference-aware Temporal Residual Network for Longitudinal Radiology Report Generation
May 06, 2025Abstract:Radiology Report Generation (RRG) automates the creation of radiology reports from medical imaging, enhancing the efficiency of the reporting process. Longitudinal Radiology Report Generation (LRRG) extends RRG by incorporating the ability to compare current and prior exams, facilitating the tracking of temporal changes in clinical findings. Existing LRRG approaches only extract features from prior and current images using a visual pre-trained encoder, which are then concatenated to generate the final report. However, these methods struggle to effectively capture both spatial and temporal correlations during the feature extraction process. Consequently, the extracted features inadequately capture the information of difference across exams and thus underrepresent the expected progressions, leading to sub-optimal performance in LRRG. To address this, we develop a novel dynamic difference-aware temporal residual network (DDaTR). In DDaTR, we introduce two modules at each stage of the visual encoder to capture multi-level spatial correlations. The Dynamic Feature Alignment Module (DFAM) is designed to align prior features across modalities for the integrity of prior clinical information. Prompted by the enriched prior features, the dynamic difference-aware module (DDAM) captures favorable difference information by identifying relationships across exams. Furthermore, our DDaTR employs the dynamic residual network to unidirectionally transmit longitudinal information, effectively modelling temporal correlations. Extensive experiments demonstrated superior performance over existing methods on three benchmarks, proving its efficacy in both RRG and LRRG tasks.
Interpretable Bilingual Multimodal Large Language Model for Diverse Biomedical Tasks
Oct 24, 2024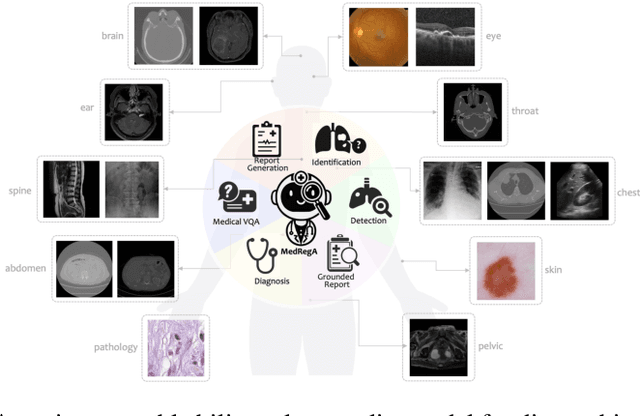

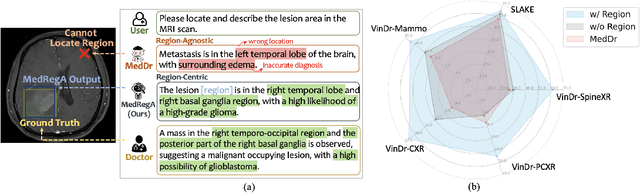

Abstract:Several medical Multimodal Large Languange Models (MLLMs) have been developed to address tasks involving visual images with textual instructions across various medical modalities, achieving impressive results. Most current medical generalist models are region-agnostic, treating the entire image as a holistic representation. However, they struggle to identify which specific regions they are focusing on when generating a sentence.To mimic the behavior of doctors, who typically begin by reviewing the entire image before concentrating on specific regions for a thorough evaluation, we aim to enhance the capability of medical MLLMs in understanding anatomical regions within entire medical scans. To achieve it, we first formulate Region-Centric tasks and construct a large-scale dataset, MedRegInstruct, to incorporate regional information into training. Combining our collected dataset with other medical multimodal corpora for training, we propose a Region-Aware medical MLLM, MedRegA, which is the first bilingual generalist medical AI system to simultaneously handle image-level and region-level medical vision-language tasks across a broad range of modalities. Our MedRegA not only enables three region-centric tasks, but also achieves the best performance for visual question answering, report generation and medical image classification over 8 modalities, showcasing significant versatility. Experiments demonstrate that our model can not only accomplish powerful performance across various medical vision-language tasks in bilingual settings, but also recognize and detect structures in multimodal medical scans, boosting the interpretability and user interactivity of medical MLLMs. Our project page is https://medrega.github.io.
FITA: Fine-grained Image-Text Aligner for Radiology Report Generation
May 02, 2024Abstract:Radiology report generation aims to automatically generate detailed and coherent descriptive reports alongside radiology images. Previous work mainly focused on refining fine-grained image features or leveraging external knowledge. However, the precise alignment of fine-grained image features with corresponding text descriptions has not been considered. This paper presents a novel method called Fine-grained Image-Text Aligner (FITA) to construct fine-grained alignment for image and text features. It has three novel designs: Image Feature Refiner (IFR), Text Feature Refiner (TFR) and Contrastive Aligner (CA). IFR and TFR aim to learn fine-grained image and text features, respectively. We achieve this by leveraging saliency maps to effectively fuse symptoms with corresponding abnormal visual regions, and by utilizing a meticulously constructed triplet set for training. Finally, CA module aligns fine-grained image and text features using contrastive loss for precise alignment. Results show that our method surpasses existing methods on the widely used benchmark
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge