Xue Li
School of Information Technology and Electronic Engineering, The University of Queensland
Attention-weighted Centered Kernel Alignment for Knowledge Distillation in Large Audio-Language Models Applied to Speech Emotion Recognition
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The emergence of Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) has advanced Speech Emotion Recognition (SER), but their size limits deployment in resource-constrained environments. While Knowledge Distillation is effective for LALM compression, existing methods remain underexplored in distilling the cross-modal projection module (Projector), and often struggle with alignment due to differences in feature dimensions. We propose PL-Distill, a KD framework that combines Projector-Level Distillation (PDist) to align audio embeddings and Logits-Level Distillation (LDist) to align output logits. PDist introduces Attention-weighted Centered Kernel Alignment, a novel approach we propose to highlight important time steps and address dimension mismatches. Meanwhile, LDist minimizes the Kullback-Leibler divergence between teacher and student logits from audio and text modalities. On IEMOCAP, RAVDESS, and SAVEE, PL-Distill compresses an 8.4B-parameter teacher to a compact 1.1B-parameter student, consistently outperforming the teacher, state-of-the-art pretrained models, and other KD baselines across all metrics.
DART: Diffusion-Inspired Speculative Decoding for Fast LLM Inference
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Speculative decoding is an effective and lossless approach for accelerating LLM inference. However, existing widely adopted model-based draft designs, such as EAGLE3, improve accuracy at the cost of multi-step autoregressive inference, resulting in high drafting latency and ultimately rendering the drafting stage itself a performance bottleneck. Inspired by diffusion-based large language models (dLLMs), we propose DART, which leverages parallel generation to reduce drafting latency. DART predicts logits for multiple future masked positions in parallel within a single forward pass based on hidden states of the target model, thereby eliminating autoregressive rollouts in the draft model while preserving a lightweight design. Based on these parallel logit predictions, we further introduce an efficient tree pruning algorithm that constructs high-quality draft token trees with N-gram-enforced semantic continuity. DART substantially reduces draft-stage overhead while preserving high draft accuracy, leading to significantly improved end-to-end decoding speed. Experimental results demonstrate that DART achieves a 2.03x--3.44x wall-clock time speedup across multiple datasets, surpassing EAGLE3 by 30% on average and offering a practical speculative decoding framework. Code is released at https://github.com/fvliang/DART.
MemWeaver: Weaving Hybrid Memories for Traceable Long-Horizon Agentic Reasoning
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Large language model-based agents operating in long-horizon interactions require memory systems that support temporal consistency, multi-hop reasoning, and evidence-grounded reuse across sessions. Existing approaches largely rely on unstructured retrieval or coarse abstractions, which often lead to temporal conflicts, brittle reasoning, and limited traceability. We propose MemWeaver, a unified memory framework that consolidates long-term agent experiences into three interconnected components: a temporally grounded graph memory for structured relational reasoning, an experience memory that abstracts recurring interaction patterns from repeated observations, and a passage memory that preserves original textual evidence. MemWeaver employs a dual-channel retrieval strategy that jointly retrieves structured knowledge and supporting evidence to construct compact yet information-dense contexts for reasoning. Experiments on the LoCoMo benchmark demonstrate that MemWeaver substantially improves multi-hop and temporal reasoning accuracy while reducing input context length by over 95\% compared to long-context baselines.
Are LLMs Smarter Than Chimpanzees? An Evaluation on Perspective Taking and Knowledge State Estimation
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Cognitive anthropology suggests that the distinction of human intelligence lies in the ability to infer other individuals' knowledge states and understand their intentions. In comparison, our closest animal relative, chimpanzees, lack the capacity to do so. With this paper, we aim to evaluate LLM performance in the area of knowledge state tracking and estimation. We design two tasks to test (1) if LLMs can detect when story characters, through their actions, demonstrate knowledge they should not possess, and (2) if LLMs can predict story characters' next actions based on their own knowledge vs. objective truths they do not know. Results reveal that most current state-of-the-art LLMs achieve near-random performance on both tasks, and are substantially inferior to humans. We argue future LLM research should place more weight on the abilities of knowledge estimation and intention understanding.
Efficient Vision-Language Reasoning via Adaptive Token Pruning
Dec 14, 2025

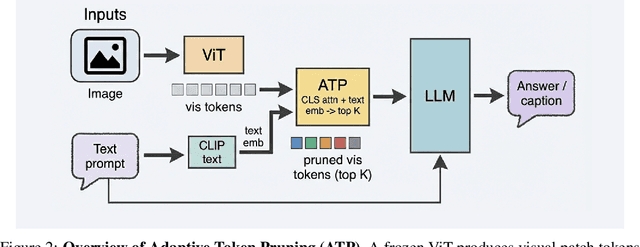
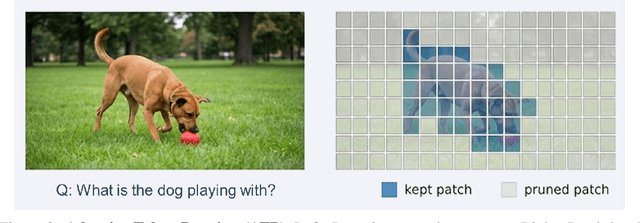
Abstract:Real-world deployment of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) is hindered by high computational demands, as existing architectures inefficiently process all tokens uniformly. We introduce Adaptive Token Pruning (ATP), a dynamic inference mechanism that retains only the most informative tokens based on contextual relevance. ATP operates at the vision-language interface, assigning a hybrid importance score combining ViT CLS attention (intra-modal saliency) and CLIP text-image similarity (inter-modal relevance) to keep top-K tokens for the LLM. Unlike static compression, ATP adapts to each input without modifying the backbone. Proposed as a lightweight gating module, ATP is compatible with popular backbones like BLIP-2, LLaVA, and Flamingo. Preliminary evaluations across VQAv2, GQA, and COCO indicate that ATP reduces inference FLOPs by around 40% and achieves roughly 1.5x speedups in end-to-end latency with negligible accuracy loss (less than 1%). Qualitative analyses suggest ATP preserves visual grounding and enhances interpretability. Beyond efficiency, we investigate robustness under corruptions; observations suggest adaptive pruning suppresses spurious correlations, improving stability. These findings imply that resource-constrained inference and model reliability are not competing objectives. Finally, we discuss ATP's role in efficient multimodal edge computing pipelines.
ReaKase-8B: Legal Case Retrieval via Knowledge and Reasoning Representations with LLMs
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Legal case retrieval (LCR) is a cornerstone of real-world legal decision making, as it enables practitioners to identify precedents for a given query case. Existing approaches mainly rely on traditional lexical models and pretrained language models to encode the texts of legal cases. Yet there are rich information in the relations among different legal entities as well as the crucial reasoning process that uncovers how legal facts and legal issues can lead to judicial decisions. Such relational reasoning process reflects the distinctive characteristics of each case that can distinguish one from another, mirroring the real-world judicial process. Naturally, incorporating such information into the precise case embedding could further enhance the accuracy of case retrieval. In this paper, a novel ReaKase-8B framework is proposed to leverage extracted legal facts, legal issues, legal relation triplets and legal reasoning for effective legal case retrieval. ReaKase-8B designs an in-context legal case representation learning paradigm with a fine-tuned large language model. Extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets from COLIEE 2022 and COLIEE 2023 demonstrate that our knowledge and reasoning augmented embeddings substantially improve retrieval performance over baseline models, highlighting the potential of integrating legal reasoning into legal case retrieval systems. The code has been released on https://github.com/yanran-tang/ReaKase-8B.
Attributed Graph Clustering with Multi-Scale Weight-Based Pairwise Coarsening and Contrastive Learning
Jul 28, 2025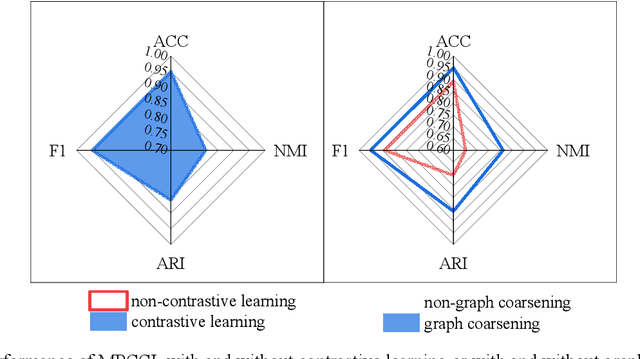
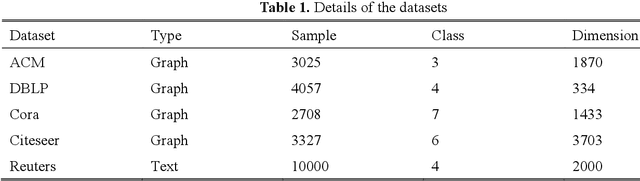
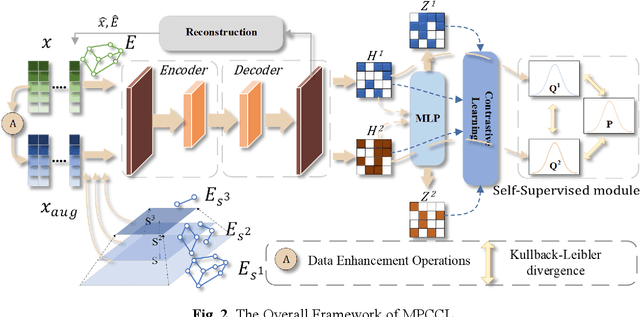
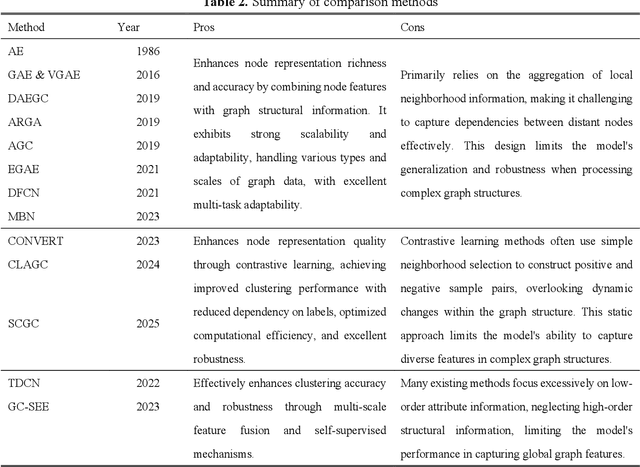
Abstract:This study introduces the Multi-Scale Weight-Based Pairwise Coarsening and Contrastive Learning (MPCCL) model, a novel approach for attributed graph clustering that effectively bridges critical gaps in existing methods, including long-range dependency, feature collapse, and information loss. Traditional methods often struggle to capture high-order graph features due to their reliance on low-order attribute information, while contrastive learning techniques face limitations in feature diversity by overemphasizing local neighborhood structures. Similarly, conventional graph coarsening methods, though reducing graph scale, frequently lose fine-grained structural details. MPCCL addresses these challenges through an innovative multi-scale coarsening strategy, which progressively condenses the graph while prioritizing the merging of key edges based on global node similarity to preserve essential structural information. It further introduces a one-to-many contrastive learning paradigm, integrating node embeddings with augmented graph views and cluster centroids to enhance feature diversity, while mitigating feature masking issues caused by the accumulation of high-frequency node weights during multi-scale coarsening. By incorporating a graph reconstruction loss and KL divergence into its self-supervised learning framework, MPCCL ensures cross-scale consistency of node representations. Experimental evaluations reveal that MPCCL achieves a significant improvement in clustering performance, including a remarkable 15.24% increase in NMI on the ACM dataset and notable robust gains on smaller-scale datasets such as Citeseer, Cora and DBLP.
* The source code for this study is available at https://github.com/YF-W/MPCCL
SAGE: A Visual Language Model for Anomaly Detection via Fact Enhancement and Entropy-aware Alignment
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown promising progress in general multimodal tasks, they often struggle in industrial anomaly detection and reasoning, particularly in delivering interpretable explanations and generalizing to unseen categories. This limitation stems from the inherently domain-specific nature of anomaly detection, which hinders the applicability of existing VLMs in industrial scenarios that require precise, structured, and context-aware analysis. To address these challenges, we propose SAGE, a VLM-based framework that enhances anomaly reasoning through Self-Guided Fact Enhancement (SFE) and Entropy-aware Direct Preference Optimization (E-DPO). SFE integrates domain-specific knowledge into visual reasoning via fact extraction and fusion, while E-DPO aligns model outputs with expert preferences using entropy-aware optimization. Additionally, we introduce AD-PL, a preference-optimized dataset tailored for industrial anomaly reasoning, consisting of 28,415 question-answering instances with expert-ranked responses. To evaluate anomaly reasoning models, we develop Multiscale Logical Evaluation (MLE), a quantitative framework analyzing model logic and consistency. SAGE demonstrates superior performance on industrial anomaly datasets under zero-shot and one-shot settings. The code, model and dataset are available at https://github.com/amoreZgx1n/SAGE.
FlashForge: Ultra-Efficient Prefix-Aware Attention for LLM Decoding
May 23, 2025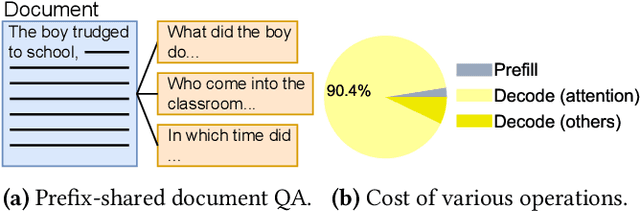
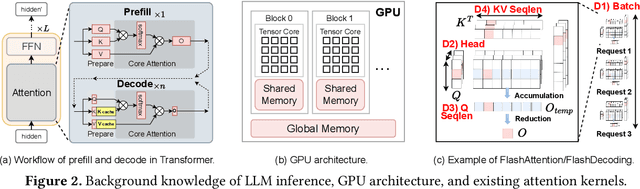
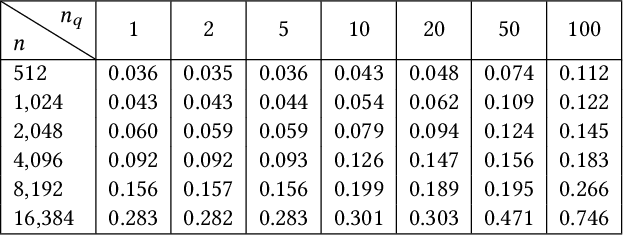
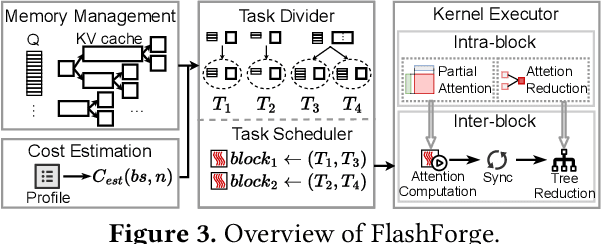
Abstract:Prefix-sharing among multiple prompts presents opportunities to combine the operations of the shared prefix, while attention computation in the decode stage, which becomes a critical bottleneck with increasing context lengths, is a memory-intensive process requiring heavy memory access on the key-value (KV) cache of the prefixes. Therefore, in this paper, we explore the potential of prefix-sharing in the attention computation of the decode stage. However, the tree structure of the prefix-sharing mechanism presents significant challenges for attention computation in efficiently processing shared KV cache access patterns while managing complex dependencies and balancing irregular workloads. To address the above challenges, we propose a dedicated attention kernel to combine the memory access of shared prefixes in the decoding stage, namely FlashForge. FlashForge delivers two key innovations: a novel shared-prefix attention kernel that optimizes memory hierarchy and exploits both intra-block and inter-block parallelism, and a comprehensive workload balancing mechanism that efficiently estimates cost, divides tasks, and schedules execution. Experimental results show that FlashForge achieves an average 1.9x speedup and 120.9x memory access reduction compared to the state-of-the-art FlashDecoding kernel regarding attention computation in the decode stage and 3.8x end-to-end time per output token compared to the vLLM.
From Embeddings to Accuracy: Comparing Foundation Models for Radiographic Classification
May 16, 2025Abstract:Foundation models, pretrained on extensive datasets, have significantly advanced machine learning by providing robust and transferable embeddings applicable to various domains, including medical imaging diagnostics. This study evaluates the utility of embeddings derived from both general-purpose and medical domain-specific foundation models for training lightweight adapter models in multi-class radiography classification, focusing specifically on tube placement assessment. A dataset comprising 8842 radiographs classified into seven distinct categories was employed to extract embeddings using six foundation models: DenseNet121, BiomedCLIP, Med-Flamingo, MedImageInsight, Rad-DINO, and CXR-Foundation. Adapter models were subsequently trained using classical machine learning algorithms. Among these combinations, MedImageInsight embeddings paired with an support vector machine adapter yielded the highest mean area under the curve (mAUC) at 93.8%, followed closely by Rad-DINO (91.1%) and CXR-Foundation (89.0%). In comparison, BiomedCLIP and DenseNet121 exhibited moderate performance with mAUC scores of 83.0% and 81.8%, respectively, whereas Med-Flamingo delivered the lowest performance at 75.1%. Notably, most adapter models demonstrated computational efficiency, achieving training within one minute and inference within seconds on CPU, underscoring their practicality for clinical applications. Furthermore, fairness analyses on adapters trained on MedImageInsight-derived embeddings indicated minimal disparities, with gender differences in performance within 2% and standard deviations across age groups not exceeding 3%. These findings confirm that foundation model embeddings-especially those from MedImageInsight-facilitate accurate, computationally efficient, and equitable diagnostic classification using lightweight adapters for radiographic image analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge