Shaobo Ma
APT-LLM: Exploiting Arbitrary-Precision Tensor Core Computing for LLM Acceleration
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized AI applications, yet their enormous computational demands severely limit deployment and real-time performance. Quantization methods can help reduce computational costs, however, attaining the extreme efficiency associated with ultra-low-bit quantized LLMs at arbitrary precision presents challenges on GPUs. This is primarily due to the limited support for GPU Tensor Cores, inefficient memory management, and inflexible kernel optimizations. To tackle these challenges, we propose a comprehensive acceleration scheme for arbitrary precision LLMs, namely APT-LLM. Firstly, we introduce a novel data format, bipolar-INT, which allows for efficient and lossless conversion with signed INT, while also being more conducive to parallel computation. We also develop a matrix multiplication (MatMul) method allowing for arbitrary precision by dismantling and reassembling matrices at the bit level. This method provides flexible precision and optimizes the utilization of GPU Tensor Cores. In addition, we propose a memory management system focused on data recovery, which strategically employs fast shared memory to substantially increase kernel execution speed and reduce memory access latency. Finally, we develop a kernel mapping method that dynamically selects the optimal configurable hyperparameters of kernels for varying matrix sizes, enabling optimal performance across different LLM architectures and precision settings. In LLM inference, APT-LLM achieves up to a 3.99$\times$ speedup compared to FP16 baselines and a 2.16$\times$ speedup over NVIDIA CUTLASS INT4 acceleration on RTX 3090. On RTX 4090 and H800, APT-LLM achieves up to 2.44$\times$ speedup over FP16 and 1.65$\times$ speedup over CUTLASS integer baselines.
FastMamba: A High-Speed and Efficient Mamba Accelerator on FPGA with Accurate Quantization
May 25, 2025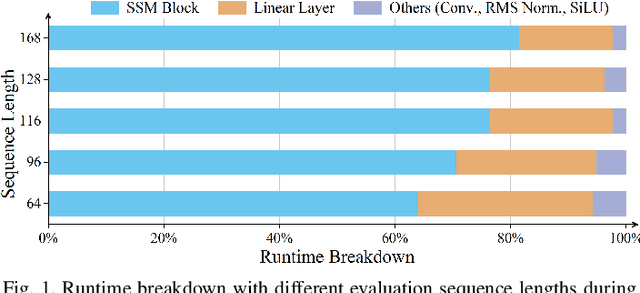
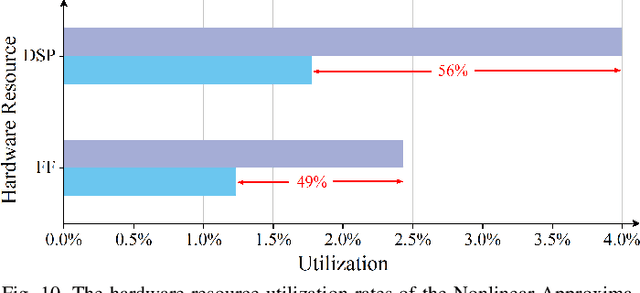
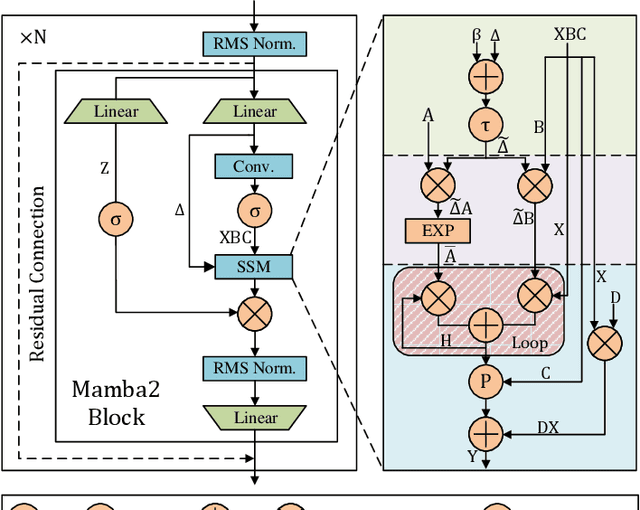
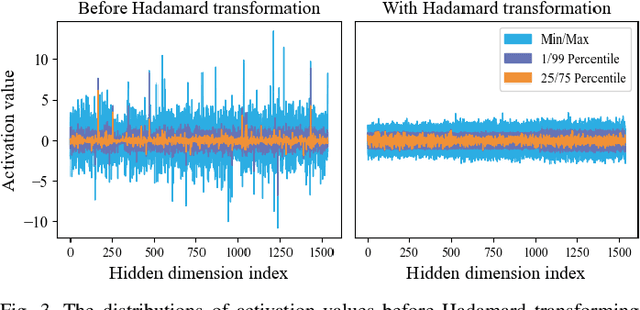
Abstract:State Space Models (SSMs), like recent Mamba2, have achieved remarkable performance and received extensive attention. However, deploying Mamba2 on resource-constrained edge devices encounters many problems: severe outliers within the linear layer challenging the quantization, diverse and irregular element-wise tensor operations, and hardware-unfriendly nonlinear functions in the SSM block. To address these issues, this paper presents FastMamba, a dedicated accelerator on FPGA with hardware-algorithm co-design to promote the deployment efficiency of Mamba2. Specifically, we successfully achieve 8-bit quantization for linear layers through Hadamard transformation to eliminate outliers. Moreover, a hardware-friendly and fine-grained power-of-two quantization framework is presented for the SSM block and convolution layer, and a first-order linear approximation is developed to optimize the nonlinear functions. Based on the accurate algorithm quantization, we propose an accelerator that integrates parallel vector processing units, pipelined execution dataflow, and an efficient SSM Nonlinear Approximation Unit, which enhances computational efficiency and reduces hardware complexity. Finally, we evaluate FastMamba on Xilinx VC709 FPGA. For the input prefill task on Mamba2-130M, FastMamba achieves 68.80\times and 8.90\times speedup over Intel Xeon 4210R CPU and NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPU, respectively. In the output decode experiment with Mamba2-2.7B, FastMamba attains 6\times higher energy efficiency than RTX 3090 GPU.
FlashForge: Ultra-Efficient Prefix-Aware Attention for LLM Decoding
May 23, 2025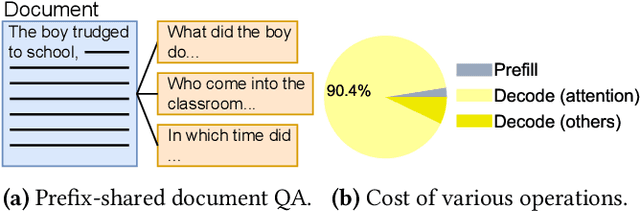
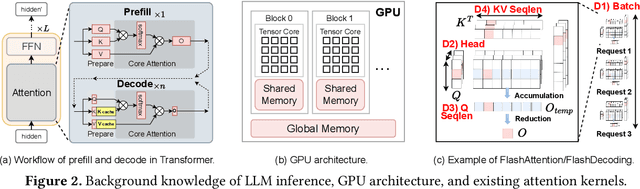
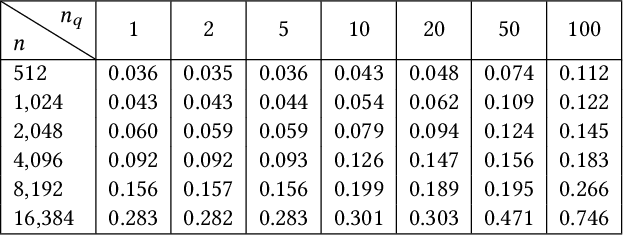
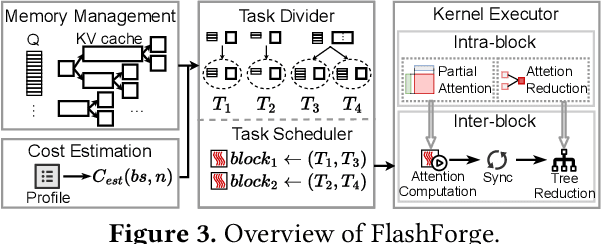
Abstract:Prefix-sharing among multiple prompts presents opportunities to combine the operations of the shared prefix, while attention computation in the decode stage, which becomes a critical bottleneck with increasing context lengths, is a memory-intensive process requiring heavy memory access on the key-value (KV) cache of the prefixes. Therefore, in this paper, we explore the potential of prefix-sharing in the attention computation of the decode stage. However, the tree structure of the prefix-sharing mechanism presents significant challenges for attention computation in efficiently processing shared KV cache access patterns while managing complex dependencies and balancing irregular workloads. To address the above challenges, we propose a dedicated attention kernel to combine the memory access of shared prefixes in the decoding stage, namely FlashForge. FlashForge delivers two key innovations: a novel shared-prefix attention kernel that optimizes memory hierarchy and exploits both intra-block and inter-block parallelism, and a comprehensive workload balancing mechanism that efficiently estimates cost, divides tasks, and schedules execution. Experimental results show that FlashForge achieves an average 1.9x speedup and 120.9x memory access reduction compared to the state-of-the-art FlashDecoding kernel regarding attention computation in the decode stage and 3.8x end-to-end time per output token compared to the vLLM.
Efficient Arbitrary Precision Acceleration for Large Language Models on GPU Tensor Cores
Sep 26, 2024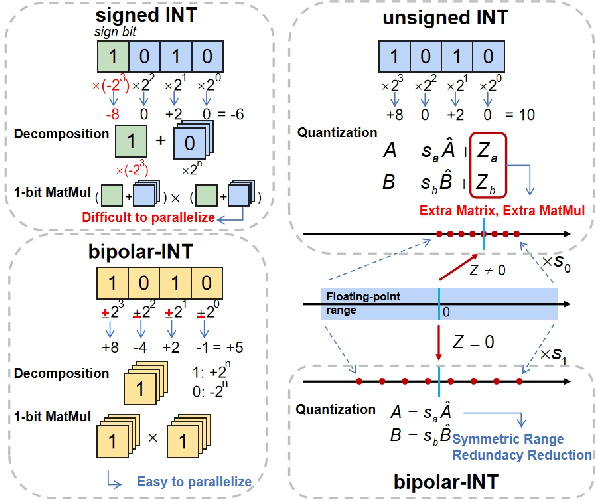
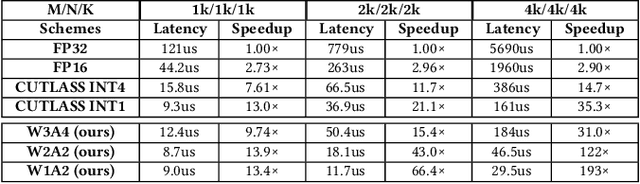
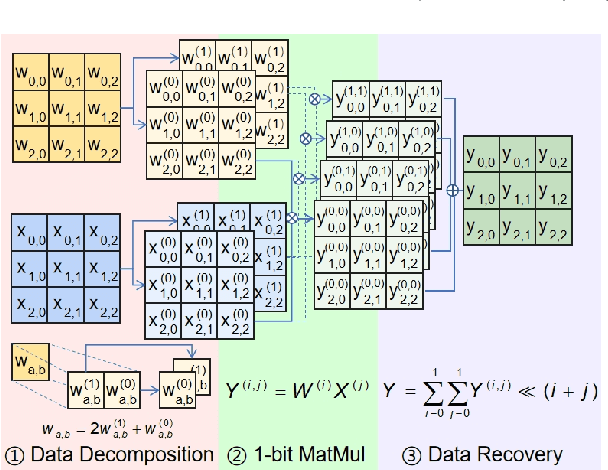
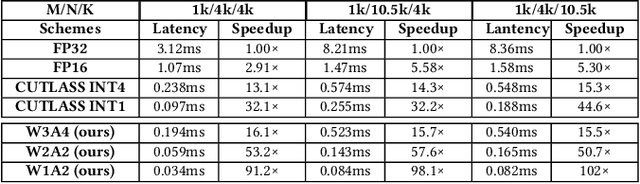
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been widely applied but face challenges in efficient inference. While quantization methods reduce computational demands, ultra-low bit quantization with arbitrary precision is hindered by limited GPU Tensor Core support and inefficient memory management, leading to suboptimal acceleration. To address these challenges, we propose a comprehensive acceleration scheme for arbitrary precision LLMs. At its core, we introduce a novel bipolar-INT data format that facilitates parallel computing and supports symmetric quantization, effectively reducing data redundancy. Building on this, we implement an arbitrary precision matrix multiplication scheme that decomposes and recovers matrices at the bit level, enabling flexible precision while maximizing GPU Tensor Core utilization. Furthermore, we develop an efficient matrix preprocessing method that optimizes data layout for subsequent computations. Finally, we design a data recovery-oriented memory management system that strategically utilizes fast shared memory, significantly enhancing kernel execution speed and minimizing memory access latency. Experimental results demonstrate our approach's effectiveness, with up to 13\times speedup in matrix multiplication compared to NVIDIA's CUTLASS. When integrated into LLMs, we achieve up to 6.7\times inference acceleration. These improvements significantly enhance LLM inference efficiency, enabling broader and more responsive applications of LLMs.
Co-Designing Binarized Transformer and Hardware Accelerator for Efficient End-to-End Edge Deployment
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:Transformer models have revolutionized AI tasks, but their large size hinders real-world deployment on resource-constrained and latency-critical edge devices. While binarized Transformers offer a promising solution by significantly reducing model size, existing approaches suffer from algorithm-hardware mismatches with limited co-design exploration, leading to suboptimal performance on edge devices. Hence, we propose a co-design method for efficient end-to-end edge deployment of Transformers from three aspects: algorithm, hardware, and joint optimization. First, we propose BMT, a novel hardware-friendly binarized Transformer with optimized quantization methods and components, and we further enhance its model accuracy by leveraging the weighted ternary weight splitting training technique. Second, we develop a streaming processor mixed binarized Transformer accelerator, namely BAT, which is equipped with specialized units and scheduling pipelines for efficient inference of binarized Transformers. Finally, we co-optimize the algorithm and hardware through a design space exploration approach to achieve a global trade-off between accuracy, latency, and robustness for real-world deployments. Experimental results show our co-design achieves up to 2.14-49.37x throughput gains and 3.72-88.53x better energy efficiency over state-of-the-art Transformer accelerators, enabling efficient end-to-end edge deployment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge