Lei Wu
KOCOBrain: Kuramoto-Guided Graph Network for Uncovering Structure-Function Coupling in Adolescent Prenatal Drug Exposure
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Exposure to psychoactive substances during pregnancy, such as cannabis, can disrupt neurodevelopment and alter large-scale brain networks, yet identifying their neural signatures remains challenging. We introduced KOCOBrain: KuramotO COupled Brain Graph Network; a unified graph neural network framework that integrates structural and functional connectomes via Kuramoto-based phase dynamics and cognition-aware attention. The Kuramoto layer models neural synchronization over anatomical connections, generating phase-informed embeddings that capture structure-function coupling, while cognitive scores modulate information routing in a subject-specific manner followed by a joint objective enhancing robustness under class imbalance scenario. Applied to the ABCD cohort, KOCOBrain improved prenatal drug exposure prediction over relevant baselines and revealed interpretable structure-function patterns that reflect disrupted brain network coordination associated with early exposure.
Esim: EVM Bytecode Similarity Detection Based on Stable-Semantic Graph
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Decentralized finance (DeFi) is experiencing rapid expansion. However, prevalent code reuse and limited open-source contributions have introduced significant challenges to the blockchain ecosystem, including plagiarism and the propagation of vulnerable code. Consequently, an effective and accurate similarity detection method for EVM bytecode is urgently needed to identify similar contracts. Traditional binary similarity detection methods are typically based on instruction stream or control flow graph (CFG), which have limitations on EVM bytecode due to specific features like low-level EVM bytecode and heavily-reused basic blocks. Moreover, the highly-diverse Solidity Compiler (Solc) versions further complicate accurate similarity detection. Motivated by these challenges, we propose a novel EVM bytecode representation called Stable-Semantic Graph (SSG), which captures relationships between 'stable instructions' (special instructions identified by our study). Moreover, we implement a prototype, Esim, which embeds SSG into matrices for similarity detection using a heterogeneous graph neural network. Esim demonstrates high accuracy in SSG construction, achieving F1-scores of 100% for control flow and 95.16% for data flow, and its similarity detection performance reaches 96.3% AUC, surpassing traditional approaches. Our large-scale study, analyzing 2,675,573 smart contracts on six EVM-compatible chains over a one-year period, also demonstrates that Esim outperforms the SOTA tool Etherscan in vulnerability search.
GradPower: Powering Gradients for Faster Language Model Pre-Training
May 30, 2025



Abstract:We propose GradPower, a lightweight gradient-transformation technique for accelerating language model pre-training. Given a gradient vector $g=(g_i)_i$, GradPower first applies the elementwise sign-power transformation: $\varphi_p(g)=({\rm sign}(g_i)|g_i|^p)_{i}$ for a fixed $p>0$, and then feeds the transformed gradient into a base optimizer. Notably, GradPower requires only a single-line code change and no modifications to the base optimizer's internal logic, including the hyperparameters. When applied to Adam (termed AdamPower), GradPower consistently achieves lower terminal loss across diverse architectures (LLaMA, Qwen2MoE), parameter scales (66M to 2B), datasets (C4, OpenWebText), and learning-rate schedules (cosine, warmup-stable-decay). The most pronounced gains are observed when training modern mixture-of-experts models with warmup-stable-decay schedules. GradPower also integrates seamlessly with other state-of-the-art optimizers, such as Muon, yielding further improvements. Finally, we provide theoretical analyses that reveal the underlying mechanism of GradPower and highlights the influence of gradient noise.
Physics-Guided Multi-View Graph Neural Network for Schizophrenia Classification via Structural-Functional Coupling
May 21, 2025Abstract:Clinical studies reveal disruptions in brain structural connectivity (SC) and functional connectivity (FC) in neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia (SZ). Traditional approaches might rely solely on SC due to limited functional data availability, hindering comprehension of cognitive and behavioral impairments in individuals with SZ by neglecting the intricate SC-FC interrelationship. To tackle the challenge, we propose a novel physics-guided deep learning framework that leverages a neural oscillation model to describe the dynamics of a collection of interconnected neural oscillators, which operate via nerve fibers dispersed across the brain's structure. Our proposed framework utilizes SC to simultaneously generate FC by learning SC-FC coupling from a system dynamics perspective. Additionally, it employs a novel multi-view graph neural network (GNN) with a joint loss to perform correlation-based SC-FC fusion and classification of individuals with SZ. Experiments conducted on a clinical dataset exhibited improved performance, demonstrating the robustness of our proposed approach.
Unified Cross-Modal Attention-Mixer Based Structural-Functional Connectomics Fusion for Neuropsychiatric Disorder Diagnosis
May 21, 2025Abstract:Gaining insights into the structural and functional mechanisms of the brain has been a longstanding focus in neuroscience research, particularly in the context of understanding and treating neuropsychiatric disorders such as Schizophrenia (SZ). Nevertheless, most of the traditional multimodal deep learning approaches fail to fully leverage the complementary characteristics of structural and functional connectomics data to enhance diagnostic performance. To address this issue, we proposed ConneX, a multimodal fusion method that integrates cross-attention mechanism and multilayer perceptron (MLP)-Mixer for refined feature fusion. Modality-specific backbone graph neural networks (GNNs) were firstly employed to obtain feature representation for each modality. A unified cross-modal attention network was then introduced to fuse these embeddings by capturing intra- and inter-modal interactions, while MLP-Mixer layers refined global and local features, leveraging higher-order dependencies for end-to-end classification with a multi-head joint loss. Extensive evaluations demonstrated improved performance on two distinct clinical datasets, highlighting the robustness of our proposed framework.
LLM-Enabled Style and Content Regularization for Personalized Text-to-Image Generation
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:The personalized text-to-image generation has rapidly advanced with the emergence of Stable Diffusion. Existing methods, which typically fine-tune models using embedded identifiers, often struggle with insufficient stylization and inaccurate image content due to reduced textual controllability. In this paper, we propose style refinement and content preservation strategies. The style refinement strategy leverages the semantic information of visual reasoning prompts and reference images to optimize style embeddings, allowing a more precise and consistent representation of style information. The content preservation strategy addresses the content bias problem by preserving the model's generalization capabilities, ensuring enhanced textual controllability without compromising stylization. Experimental results verify that our approach achieves superior performance in generating consistent and personalized text-to-image outputs.
FashionDPO:Fine-tune Fashion Outfit Generation Model using Direct Preference Optimization
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Personalized outfit generation aims to construct a set of compatible and personalized fashion items as an outfit. Recently, generative AI models have received widespread attention, as they can generate fashion items for users to complete an incomplete outfit or create a complete outfit. However, they have limitations in terms of lacking diversity and relying on the supervised learning paradigm. Recognizing this gap, we propose a novel framework FashionDPO, which fine-tunes the fashion outfit generation model using direct preference optimization. This framework aims to provide a general fine-tuning approach to fashion generative models, refining a pre-trained fashion outfit generation model using automatically generated feedback, without the need to design a task-specific reward function. To make sure that the feedback is comprehensive and objective, we design a multi-expert feedback generation module which covers three evaluation perspectives, \ie quality, compatibility and personalization. Experiments on two established datasets, \ie iFashion and Polyvore-U, demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework in enhancing the model's ability to align with users' personalized preferences while adhering to fashion compatibility principles. Our code and model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/Yzcreator/FashionDPO.
Analysis of the MICCAI Brain Tumor Segmentation -- Metastases (BraTS-METS) 2025 Lighthouse Challenge: Brain Metastasis Segmentation on Pre- and Post-treatment MRI
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Despite continuous advancements in cancer treatment, brain metastatic disease remains a significant complication of primary cancer and is associated with an unfavorable prognosis. One approach for improving diagnosis, management, and outcomes is to implement algorithms based on artificial intelligence for the automated segmentation of both pre- and post-treatment MRI brain images. Such algorithms rely on volumetric criteria for lesion identification and treatment response assessment, which are still not available in clinical practice. Therefore, it is critical to establish tools for rapid volumetric segmentations methods that can be translated to clinical practice and that are trained on high quality annotated data. The BraTS-METS 2025 Lighthouse Challenge aims to address this critical need by establishing inter-rater and intra-rater variability in dataset annotation by generating high quality annotated datasets from four individual instances of segmentation by neuroradiologists while being recorded on video (two instances doing "from scratch" and two instances after AI pre-segmentation). This high-quality annotated dataset will be used for testing phase in 2025 Lighthouse challenge and will be publicly released at the completion of the challenge. The 2025 Lighthouse challenge will also release the 2023 and 2024 segmented datasets that were annotated using an established pipeline of pre-segmentation, student annotation, two neuroradiologists checking, and one neuroradiologist finalizing the process. It builds upon its previous edition by including post-treatment cases in the dataset. Using these high-quality annotated datasets, the 2025 Lighthouse challenge plans to test benchmark algorithms for automated segmentation of pre-and post-treatment brain metastases (BM), trained on diverse and multi-institutional datasets of MRI images obtained from patients with brain metastases.
SURGEON: Memory-Adaptive Fully Test-Time Adaptation via Dynamic Activation Sparsity
Mar 26, 2025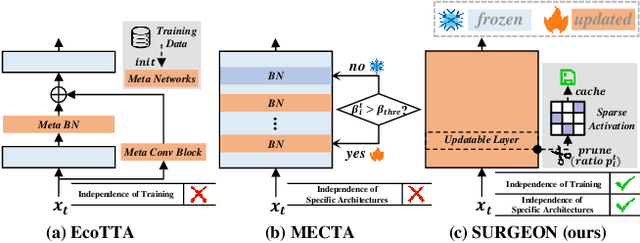
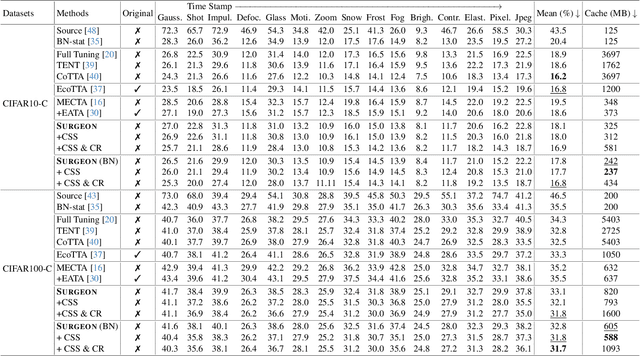
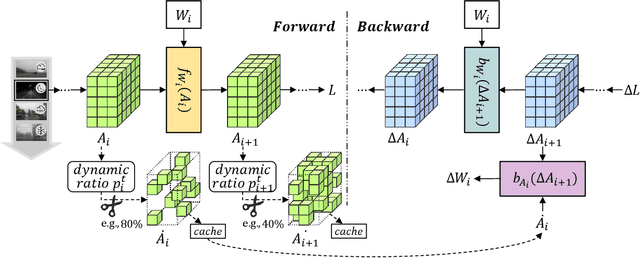
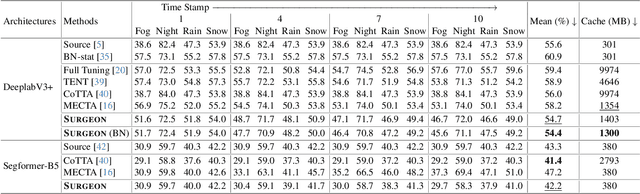
Abstract:Despite the growing integration of deep models into mobile terminals, the accuracy of these models declines significantly due to various deployment interferences. Test-time adaptation (TTA) has emerged to improve the performance of deep models by adapting them to unlabeled target data online. Yet, the significant memory cost, particularly in resource-constrained terminals, impedes the effective deployment of most backward-propagation-based TTA methods. To tackle memory constraints, we introduce SURGEON, a method that substantially reduces memory cost while preserving comparable accuracy improvements during fully test-time adaptation (FTTA) without relying on specific network architectures or modifications to the original training procedure. Specifically, we propose a novel dynamic activation sparsity strategy that directly prunes activations at layer-specific dynamic ratios during adaptation, allowing for flexible control of learning ability and memory cost in a data-sensitive manner. Among this, two metrics, Gradient Importance and Layer Activation Memory, are considered to determine the layer-wise pruning ratios, reflecting accuracy contribution and memory efficiency, respectively. Experimentally, our method surpasses the baselines by not only reducing memory usage but also achieving superior accuracy, delivering SOTA performance across diverse datasets, architectures, and tasks.
Analyzing the Role of Permutation Invariance in Linear Mode Connectivity
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:It was empirically observed in Entezari et al. (2021) that when accounting for the permutation invariance of neural networks, there is likely no loss barrier along the linear interpolation between two SGD solutions -- a phenomenon known as linear mode connectivity (LMC) modulo permutation. This phenomenon has sparked significant attention due to both its theoretical interest and practical relevance in applications such as model merging. In this paper, we provide a fine-grained analysis of this phenomenon for two-layer ReLU networks under a teacher-student setup. We show that as the student network width $m$ increases, the LMC loss barrier modulo permutation exhibits a {\bf double descent} behavior. Particularly, when $m$ is sufficiently large, the barrier decreases to zero at a rate $O(m^{-1/2})$. Notably, this rate does not suffer from the curse of dimensionality and demonstrates how substantial permutation can reduce the LMC loss barrier. Moreover, we observe a sharp transition in the sparsity of GD/SGD solutions when increasing the learning rate and investigate how this sparsity preference affects the LMC loss barrier modulo permutation. Experiments on both synthetic and MNIST datasets corroborate our theoretical predictions and reveal a similar trend for more complex network architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge