Xingyu Zhao
Shattered Compositionality: Counterintuitive Learning Dynamics of Transformers for Arithmetic
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often exhibit unexpected errors or unintended behavior, even at scale. While recent work reveals the discrepancy between LLMs and humans in skill compositions, the learning dynamics of skill compositions and the underlying cause of non-human behavior remain elusive. In this study, we investigate the mechanism of learning dynamics by training transformers on synthetic arithmetic tasks. Through extensive ablations and fine-grained diagnostic metrics, we discover that transformers do not reliably build skill compositions according to human-like sequential rules. Instead, they often acquire skills in reverse order or in parallel, which leads to unexpected mixing errors especially under distribution shifts--a phenomenon we refer to as shattered compositionality. To explain these behaviors, we provide evidence that correlational matching to the training data, rather than causal or procedural composition, shapes learning dynamics. We further show that shattered compositionality persists in modern LLMs and is not mitigated by pure model scaling or scratchpad-based reasoning. Our results reveal a fundamental mismatch between a model's learning behavior and desired skill compositions, with implications for reasoning reliability, out-of-distribution robustness, and alignment.
Quantifying and Bridging the Fidelity Gap: A Decisive-Feature Approach to Comparing Synthetic and Real Imagery
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Virtual testing using synthetic data has become a cornerstone of autonomous vehicle (AV) safety assurance. Despite progress in improving visual realism through advanced simulators and generative AI, recent studies reveal that pixel-level fidelity alone does not ensure reliable transfer from simulation to the real world. What truly matters is whether the system-under-test (SUT) bases its decisions on the same causal evidence in both real and simulated environments - not just whether images "look real" to humans. This paper addresses the lack of such a behavior-grounded fidelity measure by introducing Decisive Feature Fidelity (DFF), a new SUT-specific metric that extends the existing fidelity spectrum to capture mechanism parity - the agreement in causal evidence underlying the SUT's decisions across domains. DFF leverages explainable-AI (XAI) methods to identify and compare the decisive features driving the SUT's outputs for matched real-synthetic pairs. We further propose practical estimators based on counterfactual explanations, along with a DFF-guided calibration scheme to enhance simulator fidelity. Experiments on 2126 matched KITTI-VirtualKITTI2 pairs demonstrate that DFF reveals discrepancies overlooked by conventional output-value fidelity. Furthermore, results show that DFF-guided calibration improves decisive-feature and input-level fidelity without sacrificing output value fidelity across diverse SUTs.
Uncertainty-Aware Measurement of Scenario Suite Representativeness for Autonomous Systems
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Assuring the trustworthiness and safety of AI systems, e.g., autonomous vehicles (AV), depends critically on the data-related safety properties, e.g., representativeness, completeness, etc., of the datasets used for their training and testing. Among these properties, this paper focuses on representativeness-the extent to which the scenario-based data used for training and testing, reflect the operational conditions that the system is designed to operate safely in, i.e., Operational Design Domain (ODD) or expected to encounter, i.e., Target Operational Domain (TOD). We propose a probabilistic method that quantifies representativeness by comparing the statistical distribution of features encoded by the scenario suites with the corresponding distribution of features representing the TOD, acknowledging that the true TOD distribution is unknown, as it can only be inferred from limited data. We apply an imprecise Bayesian method to handle limited data and uncertain priors. The imprecise Bayesian formulation produces interval-valued, uncertainty-aware estimates of representativeness, rather than a single value. We present a numerical example comparing the distributions of the scenario suite and the inferred TOD across operational categories-weather, road type, time of day, etc., under dependencies and prior uncertainty. We estimate representativeness locally (between categories) and globally as an interval.
Fragile by Design: On the Limits of Adversarial Defenses in Personalized Generation
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Personalized AI applications such as DreamBooth enable the generation of customized content from user images, but also raise significant privacy concerns, particularly the risk of facial identity leakage. Recent defense mechanisms like Anti-DreamBooth attempt to mitigate this risk by injecting adversarial perturbations into user photos to prevent successful personalization. However, we identify two critical yet overlooked limitations of these methods. First, the adversarial examples often exhibit perceptible artifacts such as conspicuous patterns or stripes, making them easily detectable as manipulated content. Second, the perturbations are highly fragile, as even a simple, non-learned filter can effectively remove them, thereby restoring the model's ability to memorize and reproduce user identity. To investigate this vulnerability, we propose a novel evaluation framework, AntiDB_Purify, to systematically evaluate existing defenses under realistic purification threats, including both traditional image filters and adversarial purification. Results reveal that none of the current methods maintains their protective effectiveness under such threats. These findings highlight that current defenses offer a false sense of security and underscore the urgent need for more imperceptible and robust protections to safeguard user identity in personalized generation.
OBJVanish: Physically Realizable Text-to-3D Adv. Generation of LiDAR-Invisible Objects
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:LiDAR-based 3D object detectors are fundamental to autonomous driving, where failing to detect objects poses severe safety risks. Developing effective 3D adversarial attacks is essential for thoroughly testing these detection systems and exposing their vulnerabilities before real-world deployment. However, existing adversarial attacks that add optimized perturbations to 3D points have two critical limitations: they rarely cause complete object disappearance and prove difficult to implement in physical environments. We introduce the text-to-3D adversarial generation method, a novel approach enabling physically realizable attacks that can generate 3D models of objects truly invisible to LiDAR detectors and be easily realized in the real world. Specifically, we present the first empirical study that systematically investigates the factors influencing detection vulnerability by manipulating the topology, connectivity, and intensity of individual pedestrian 3D models and combining pedestrians with multiple objects within the CARLA simulation environment. Building on the insights, we propose the physically-informed text-to-3D adversarial generation (Phy3DAdvGen) that systematically optimizes text prompts by iteratively refining verbs, objects, and poses to produce LiDAR-invisible pedestrians. To ensure physical realizability, we construct a comprehensive object pool containing 13 3D models of real objects and constrain Phy3DAdvGen to generate 3D objects based on combinations of objects in this set. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach can generate 3D pedestrians that evade six state-of-the-art (SOTA) LiDAR 3D detectors in both CARLA simulation and physical environments, thereby highlighting vulnerabilities in safety-critical applications.
Tailored Teaching with Balanced Difficulty: Elevating Reasoning in Multimodal Chain-of-Thought via Prompt Curriculum
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The effectiveness of Multimodal Chain-of-Thought (MCoT) prompting is often limited by the use of randomly or manually selected examples. These examples fail to account for both model-specific knowledge distributions and the intrinsic complexity of the tasks, resulting in suboptimal and unstable model performance. To address this, we propose a novel framework inspired by the pedagogical principle of "tailored teaching with balanced difficulty". We reframe prompt selection as a prompt curriculum design problem: constructing a well ordered set of training examples that align with the model's current capabilities. Our approach integrates two complementary signals: (1) model-perceived difficulty, quantified through prediction disagreement in an active learning setup, capturing what the model itself finds challenging; and (2) intrinsic sample complexity, which measures the inherent difficulty of each question-image pair independently of any model. By jointly analyzing these signals, we develop a difficulty-balanced sampling strategy that ensures the selected prompt examples are diverse across both dimensions. Extensive experiments conducted on five challenging benchmarks and multiple popular Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate that our method yields substantial and consistent improvements and greatly reduces performance discrepancies caused by random sampling, providing a principled and robust approach for enhancing multimodal reasoning.
On the Need for a Statistical Foundation in Scenario-Based Testing of Autonomous Vehicles
May 04, 2025Abstract:Scenario-based testing has emerged as a common method for autonomous vehicles (AVs) safety, offering a more efficient alternative to mile-based testing by focusing on high-risk scenarios. However, fundamental questions persist regarding its stopping rules, residual risk estimation, debug effectiveness, and the impact of simulation fidelity on safety claims. This paper argues that a rigorous statistical foundation is essential to address these challenges and enable rigorous safety assurance. By drawing parallels between AV testing and traditional software testing methodologies, we identify shared research gaps and reusable solutions. We propose proof-of-concept models to quantify the probability of failure per scenario (pfs) and evaluate testing effectiveness under varying conditions. Our analysis reveals that neither scenario-based nor mile-based testing universally outperforms the other. Furthermore, we introduce Risk Estimation Fidelity (REF), a novel metric to certify the alignment of synthetic and real-world testing outcomes, ensuring simulation-based safety claims are statistically defensible.
Sensing-Then-Beamforming: Robust Transmission Design for RIS-Empowered Integrated Sensing and Covert Communication
Apr 18, 2025



Abstract:Traditional covert communication often relies on the knowledge of the warden's channel state information, which is inherently challenging to obtain due to the non-cooperative nature and potential mobility of the warden. The integration of sensing and communication technology provides a promising solution by enabling the legitimate transmitter to sense and track the warden, thereby enhancing transmission covertness. In this paper, we develop a framework for sensing-then-beamforming in reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-empowered integrated sensing and covert communication (ISCC) systems, where the transmitter (Alice) estimates and tracks the mobile aerial warden's channel using sensing echo signals while simultaneously sending covert information to multiple legitimate users (Bobs) with the assistance of RIS, under the surveillance of the warden (Willie). Considering channel estimation errors, we formulate a robust non-convex optimization problem that jointly designs the communication beamformers, the sensing signal covariance matrix at Alice, and the phase shifts at the RIS to maximize the covert sum rate of Bobs while satisfying the constraints related to covert communication, sensing, transmitter power, and the unit modulus of the RIS elements. To solve this complex problem, we develop an efficient algorithm using alternating optimization, successive convex approximation, S-procedure, sequential rank-one constraint relaxation, and semidefinite relaxation techniques. Numerical results confirm the convergence of the proposed algorithm and demonstrate its effectiveness in tracking the warden's channel while ensuring robust covert transmission. Furthermore, the results highlight the advantages of using RIS to enhance the covert transmission rate compared to baseline schemes, and also illustrate the intricate trade-off between communication and sensing in ISCC systems.
Movable Antenna Enhanced Downlink Multi-User Integrated Sensing and Communication System
Mar 28, 2025



Abstract:This work investigates the potential of exploiting movable antennas (MAs) to enhance the performance of a multi-user downlink integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system. Specifically, we formulate an optimization problem to maximize the transmit beampattern gain for sensing while simultaneously meeting each user's communication requirement by jointly optimizing antenna positions and beamforming design. The problem formulated is highly non-convex and involves multivariate-coupled constraints. To address these challenges, we introduce a series of auxiliary random variables and transform the original problem into an augmented Lagrangian problem. A double-loop algorithm based on a penalty dual decomposition framework is then developed to solve the problem. Numerical results validate the effectiveness of the proposed design, demonstrating its superiority over MA designs based on successive convex approximation optimization and other baseline approaches in ISAC systems. The results also highlight the advantages of MAs in achieving better sensing performance and improved beam control, especially for sparse arrays with large apertures.
Scalable Trajectory-User Linking with Dual-Stream Representation Networks
Mar 19, 2025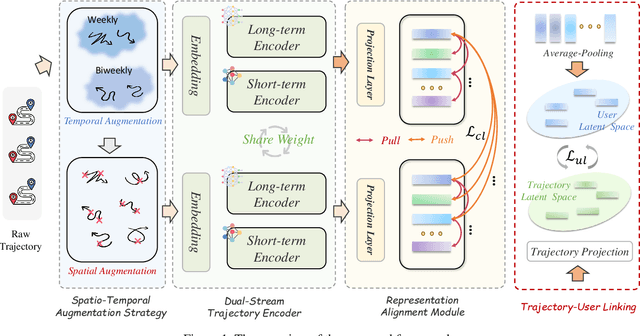
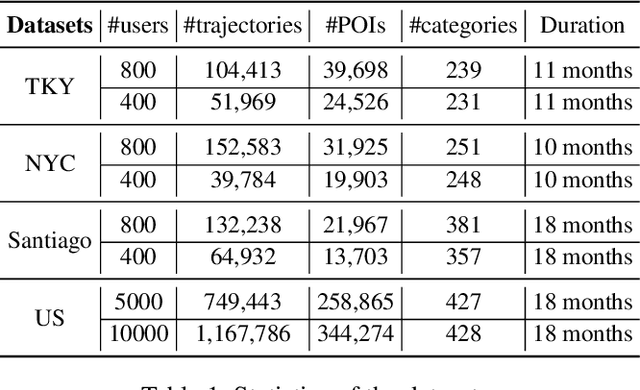
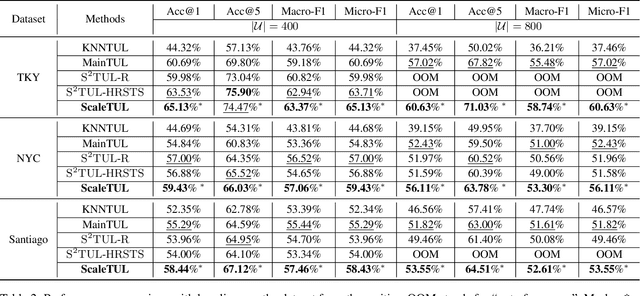
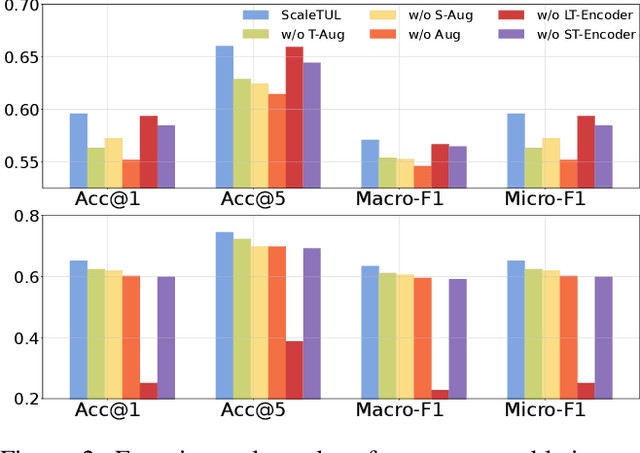
Abstract:Trajectory-user linking (TUL) aims to match anonymous trajectories to the most likely users who generated them, offering benefits for a wide range of real-world spatio-temporal applications. However, existing TUL methods are limited by high model complexity and poor learning of the effective representations of trajectories, rendering them ineffective in handling large-scale user trajectory data. In this work, we propose a novel $\underline{Scal}$abl$\underline{e}$ Trajectory-User Linking with dual-stream representation networks for large-scale $\underline{TUL}$ problem, named ScaleTUL. Specifically, ScaleTUL generates two views using temporal and spatial augmentations to exploit supervised contrastive learning framework to effectively capture the irregularities of trajectories. In each view, a dual-stream trajectory encoder, consisting of a long-term encoder and a short-term encoder, is designed to learn unified trajectory representations that fuse different temporal-spatial dependencies. Then, a TUL layer is used to associate the trajectories with the corresponding users in the representation space using a two-stage training model. Experimental results on check-in mobility datasets from three real-world cities and the nationwide U.S. demonstrate the superiority of ScaleTUL over state-of-the-art baselines for large-scale TUL tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge