Wen-mei Hwu
IRB: Automated Generation of Robust Factuality Benchmarks
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:Static benchmarks for RAG systems often suffer from rapid saturation and require significant manual effort to maintain robustness. To address this, we present IRB, a framework for automatically generating benchmarks to evaluate the factuality of RAG systems. IRB employs a structured generation pipeline utilizing \textit{factual scaffold} and \textit{algorithmic scaffold}. We utilize IRB to construct a benchmark and evaluate frontier LLMs and retrievers. Our results demonstrate that IRB poses a significant challenge for frontier LLMs in the closed-book setting. Furthermore, our evaluation suggests that reasoning LLMs are more reliable, and that improving the retrieval component may yield more cost-effective gains in RAG system correctness than scaling the generator.
VibeTensor: System Software for Deep Learning, Fully Generated by AI Agents
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:VIBETENSOR is an open-source research system software stack for deep learning, generated by LLM-powered coding agents under high-level human guidance. In this paper, "fully generated" refers to code provenance: implementation changes were produced and applied as agent-proposed diffs; validation relied on agent-run builds, tests, and differential checks, without per-change manual diff review. It implements a PyTorch-style eager tensor library with a C++20 core (CPU+CUDA), a torch-like Python overlay via nanobind, and an experimental Node.js/TypeScript interface. Unlike thin bindings, VIBETENSOR includes its own tensor/storage system, schema-lite dispatcher, reverse-mode autograd, CUDA runtime (streams/events/graphs), a stream-ordered caching allocator with diagnostics, and a stable C ABI for dynamically loaded operator plugins. We view this release as a milestone for AI-assisted software engineering: it shows coding agents can generate a coherent deep learning runtime spanning language bindings down to CUDA memory management, validated primarily by builds and tests. We describe the architecture, summarize the workflow used to produce and validate the system, and evaluate the artifact. We report repository scale and test-suite composition, and summarize reproducible microbenchmarks from an accompanying AI-generated kernel suite, including fused attention versus PyTorch SDPA/FlashAttention. We also report end-to-end training sanity checks on 3 small workloads (sequence reversal, ViT, miniGPT) on NVIDIA H100 (Hopper, SM90) and Blackwell-class GPUs; multi-GPU results are Blackwell-only and use an optional CUTLASS-based ring-allreduce plugin gated on CUDA 13+ and sm103a toolchain support. Finally, we discuss failure modes in generated system software, including a "Frankenstein" composition effect where locally correct subsystems interact to yield globally suboptimal performance.
Generalized Neighborhood Attention: Multi-dimensional Sparse Attention at the Speed of Light
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:Many sparse attention mechanisms such as Neighborhood Attention have typically failed to consistently deliver speedup over the self attention baseline. This is largely due to the level of complexity in attention infrastructure, and the rapid evolution of AI hardware architecture. At the same time, many state-of-the-art foundational models, particularly in computer vision, are heavily bound by attention, and need reliable sparsity to escape the O(n^2) complexity. In this paper, we study a class of promising sparse attention mechanisms that focus on locality, and aim to develop a better analytical model of their performance improvements. We first introduce Generalized Neighborhood Attention (GNA), which can describe sliding window, strided sliding window, and blocked attention. We then consider possible design choices in implementing these approaches, and create a simulator that can provide much more realistic speedup upper bounds for any given setting. Finally, we implement GNA on top of a state-of-the-art fused multi-headed attention (FMHA) kernel designed for the NVIDIA Blackwell architecture in CUTLASS. Our implementation can fully realize the maximum speedup theoretically possible in many perfectly block-sparse cases, and achieves an effective utilization of 1.3 petaFLOPs/second in FP16. In addition, we plug various GNA configurations into off-the-shelf generative models, such as Cosmos-7B, HunyuanVideo, and FLUX, and show that it can deliver 28% to 46% end-to-end speedup on B200 without any fine-tuning. We will open source our simulator and Blackwell kernels directly through the NATTEN project.
TBA: Faster Large Language Model Training Using SSD-Based Activation Offloading
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:The growth rate of the GPU memory capacity has not been able to keep up with that of the size of large language models (LLMs), hindering the model training process. In particular, activations -- the intermediate tensors produced during forward propagation and reused in backward propagation -- dominate the GPU memory use. To address this challenge, we propose TBA to efficiently offload activations to high-capacity NVMe SSDs. This approach reduces GPU memory usage without impacting performance by adaptively overlapping data transfers with computation. TBA is compatible with popular deep learning frameworks like PyTorch, Megatron, and DeepSpeed, and it employs techniques such as tensor deduplication, forwarding, and adaptive offloading to further enhance efficiency. We conduct extensive experiments on GPT, BERT, and T5. Results demonstrate that TBA effectively reduces 47% of the activation peak memory usage. At the same time, TBA perfectly overlaps the I/O with the computation and incurs negligible performance overhead. We introduce the recompute-offload-keep (ROK) curve to compare the TBA offloading with other two tensor placement strategies, keeping activations in memory and layerwise full recomputation. We find that TBA achieves better memory savings than layerwise full recomputation while retaining the performance of keeping the activations in memory.
LSM-GNN: Large-scale Storage-based Multi-GPU GNN Training by Optimizing Data Transfer Scheme
Jul 21, 2024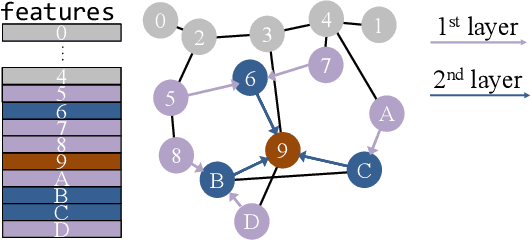
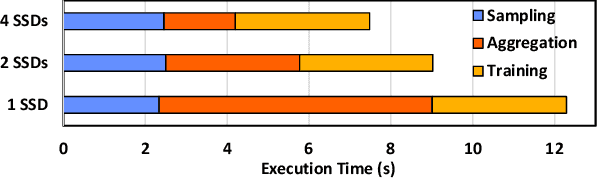
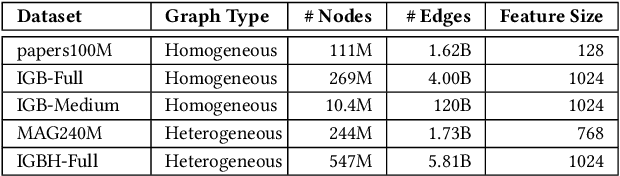
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are widely used today in recommendation systems, fraud detection, and node/link classification tasks. Real world GNNs continue to scale in size and require a large memory footprint for storing graphs and embeddings that often exceed the memory capacities of the target GPUs used for training. To address limited memory capacities, traditional GNN training approaches use graph partitioning and sharding techniques to scale up across multiple GPUs within a node and/or scale out across multiple nodes. However, this approach suffers from the high computational costs of graph partitioning algorithms and inefficient communication across GPUs. To address these overheads, we propose Large-scale Storage-based Multi-GPU GNN framework (LSM-GNN), a storagebased approach to train GNN models that utilizes a novel communication layer enabling GPU software caches to function as a system-wide shared cache with low overheads.LSM-GNN incorporates a hybrid eviction policy that intelligently manages cache space by using both static and dynamic node information to significantly enhance cache performance. Furthermore, we introduce the Preemptive Victim-buffer Prefetcher (PVP), a mechanism for prefetching node feature data from a Victim Buffer located in CPU pinned-memory to further reduce the pressure on the storage devices. Experimental results show that despite the lower compute capabilities and memory capacities, LSM-GNN in a single node with two GPUs offers superior performance over two-node-four-GPU Dist-DGL baseline and provides up to 3.75x speed up on end-to-end epoch time while running large-scale GNN training
Accelerating Sampling and Aggregation Operations in GNN Frameworks with GPU Initiated Direct Storage Accesses
Jun 28, 2023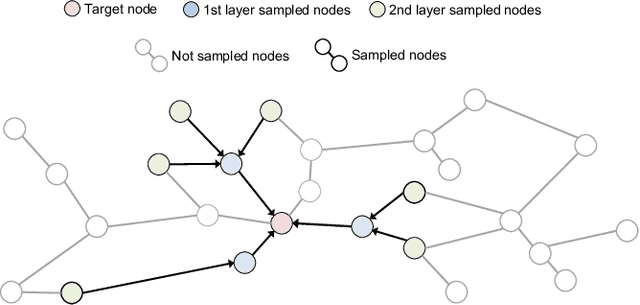
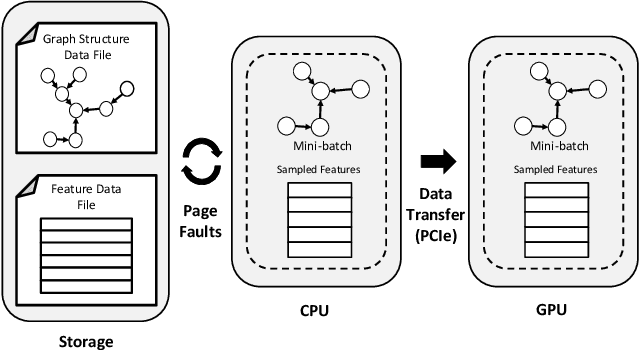
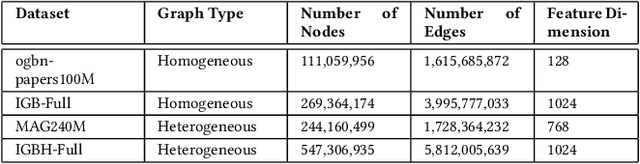
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are emerging as a powerful tool for learning from graph-structured data and performing sophisticated inference tasks in various application domains. Although GNNs have been shown to be effective on modest-sized graphs, training them on large-scale graphs remains a significant challenge due to lack of efficient data access and data movement methods. Existing frameworks for training GNNs use CPUs for graph sampling and feature aggregation, while the training and updating of model weights are executed on GPUs. However, our in-depth profiling shows the CPUs cannot achieve the throughput required to saturate GNN model training throughput, causing gross under-utilization of expensive GPU resources. Furthermore, when the graph and its embeddings do not fit in the CPU memory, the overhead introduced by the operating system, say for handling page-faults, comes in the critical path of execution. To address these issues, we propose the GPU Initiated Direct Storage Access (GIDS) dataloader, to enable GPU-oriented GNN training for large-scale graphs while efficiently utilizing all hardware resources, such as CPU memory, storage, and GPU memory with a hybrid data placement strategy. By enabling GPU threads to fetch feature vectors directly from storage, GIDS dataloader solves the memory capacity problem for GPU-oriented GNN training. Moreover, GIDS dataloader leverages GPU parallelism to tolerate storage latency and eliminates expensive page-fault overhead. Doing so enables us to design novel optimizations for exploiting locality and increasing effective bandwidth for GNN training. Our evaluation using a single GPU on terabyte-scale GNN datasets shows that GIDS dataloader accelerates the overall DGL GNN training pipeline by up to 392X when compared to the current, state-of-the-art DGL dataloader.
IGB: Addressing The Gaps In Labeling, Features, Heterogeneity, and Size of Public Graph Datasets for Deep Learning Research
Feb 27, 2023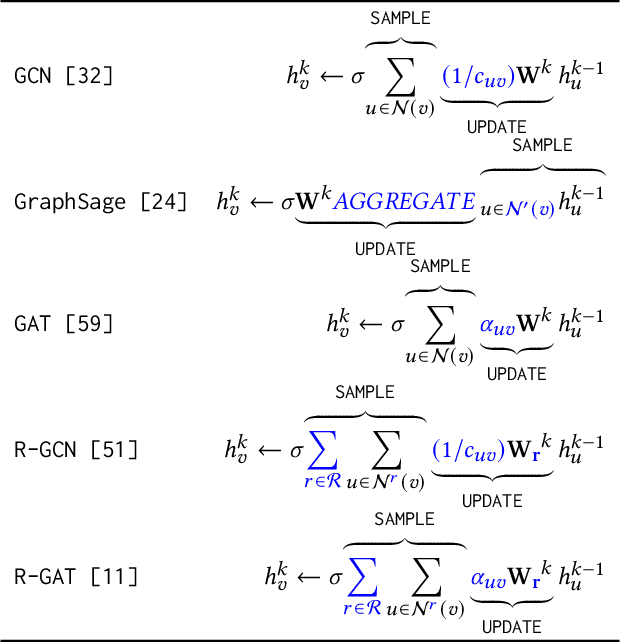
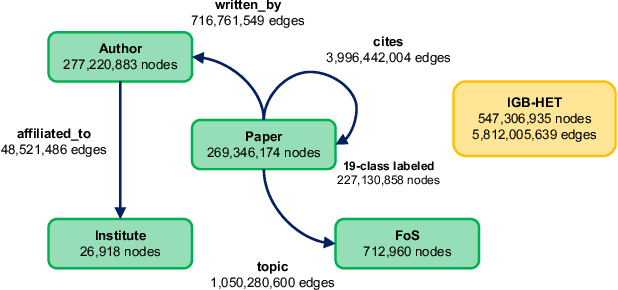
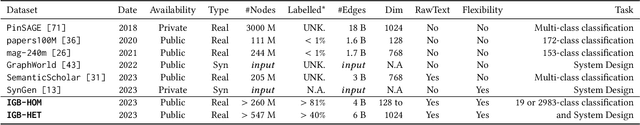
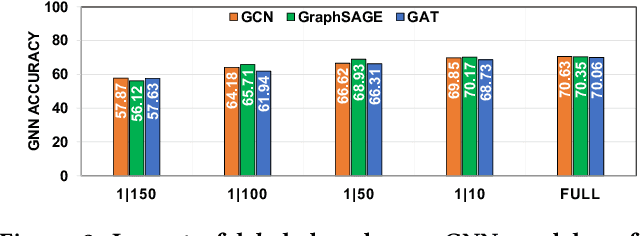
Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have shown high potential for a variety of real-world, challenging applications, but one of the major obstacles in GNN research is the lack of large-scale flexible datasets. Most existing public datasets for GNNs are relatively small, which limits the ability of GNNs to generalize to unseen data. The few existing large-scale graph datasets provide very limited labeled data. This makes it difficult to determine if the GNN model's low accuracy for unseen data is inherently due to insufficient training data or if the model failed to generalize. Additionally, datasets used to train GNNs need to offer flexibility to enable a thorough study of the impact of various factors while training GNN models. In this work, we introduce the Illinois Graph Benchmark (IGB), a research dataset tool that the developers can use to train, scrutinize and systematically evaluate GNN models with high fidelity. IGB includes both homogeneous and heterogeneous graphs of enormous sizes, with more than 40% of their nodes labeled. Compared to the largest graph datasets publicly available, the IGB provides over 162X more labeled data for deep learning practitioners and developers to create and evaluate models with higher accuracy. The IGB dataset is designed to be flexible, enabling the study of various GNN architectures, embedding generation techniques, and analyzing system performance issues. IGB is open-sourced, supports DGL and PyG frameworks, and comes with releases of the raw text that we believe foster emerging language models and GNN research projects. An early public version of IGB is available at https://github.com/IllinoisGraphBenchmark/IGB-Datasets.
PIGEON: Optimizing CUDA Code Generator for End-to-End Training and Inference of Relational Graph Neural Networks
Jan 16, 2023Abstract:Relational graph neural networks (RGNNs) are graph neural networks (GNNs) with dedicated structures for modeling the different types of nodes and/or edges in heterogeneous graphs. While RGNNs have been increasingly adopted in many real-world applications due to their versatility and accuracy, they pose performance and system design challenges due to their inherent computation patterns, gap between the programming interface and kernel APIs, and heavy programming efforts in optimizing kernels caused by their coupling with data layout and heterogeneity. To systematically address these challenges, we propose Pigeon, a novel two-level intermediate representation (IR) and its code generator framework, that (a) represents the key properties of the RGNN models to bridge the gap between the programming interface and kernel APIs, (b) decouples model semantics, data layout, and operators-specific optimization from each other to reduce programming efforts, (c) expresses and leverages optimization opportunities in inter-operator transforms, data layout, and operator-specific schedules. By building on one general matrix multiply (GEMM) template and a node/edge traversal template, Pigeon achieves up to 7.8x speed-up in inference and 5.6x speed-up in training compared with the state-of-the-art public systems in select models, i.e., RGCN, RGAT, HGT, when running heterogeneous graphs provided by Deep Graph Library (DGL) and Open Graph Benchmark (OGB). Pigeon also triggers fewer out-of-memory (OOM) errors. In addition, we propose linear operator fusion and compact materialization to further accelerate the system by up to 2.2x.
Submission-Aware Reviewer Profiling for Reviewer Recommender System
Nov 08, 2022


Abstract:Assigning qualified, unbiased and interested reviewers to paper submissions is vital for maintaining the integrity and quality of the academic publishing system and providing valuable reviews to authors. However, matching thousands of submissions with thousands of potential reviewers within a limited time is a daunting challenge for a conference program committee. Prior efforts based on topic modeling have suffered from losing the specific context that help define the topics in a publication or submission abstract. Moreover, in some cases, topics identified are difficult to interpret. We propose an approach that learns from each abstract published by a potential reviewer the topics studied and the explicit context in which the reviewer studied the topics. Furthermore, we contribute a new dataset for evaluating reviewer matching systems. Our experiments show a significant, consistent improvement in precision when compared with the existing methods. We also use examples to demonstrate why our recommendations are more explainable. The new approach has been deployed successfully at top-tier conferences in the last two years.
Can Language Models Be Specific? How?
Oct 11, 2022

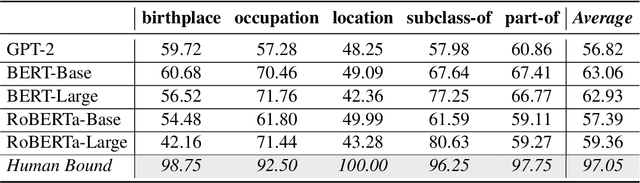
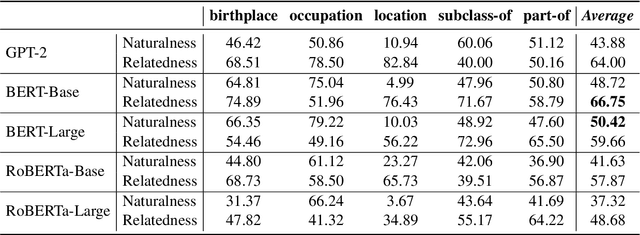
Abstract:A good speaker not only needs to be correct, but also has the ability to be specific when desired, and so are language models. In this paper, we propose to measure how specific the language of pre-trained language models (PLMs) is. To achieve this, we introduce a novel approach to build a benchmark for specificity testing by forming masked token prediction tasks with prompts. For instance, given ``J. K. Rowling was born in [MASK].'', we want to test whether a more specific answer will be better filled in by PLMs, e.g., Yate instead of England. From our evaluations, we show that existing PLMs have only a slight preference for more specific answers. We identify underlying factors affecting the specificity and design two prompt-based methods to improve the specificity. Results show that the specificity of the models can be improved by the proposed methods without additional training. We believe this work can provide new insights for language modeling and encourage the research community to further explore this important but understudied problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge