Scott Mahlke
SNIP: An Adaptive Mixed Precision Framework for Subbyte Large Language Model Training
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Training large language models (LLMs) efficiently while preserving model quality poses significant challenges, particularly with subbyte precision supported by state-of-the-art GPUs. Current mixed-precision training approaches either apply uniform precision to all GEMM operations or rely on heuristic-based methods that fail to generalize during training, leading to suboptimal convergence and instability. To address these challenges, this paper introduces SNIP, a fine-grained adaptive mixed-precision training framework for LLM pretraining that supports subbyte precision. SNIP periodically collects statistics on activations, gradients, and optimizer states to assess the precision loss impact on model quality. We define two key metrics: loss divergence in the forward pass, caused by quantization-induced increases in training loss, and weight divergence in the backward pass, which measures error propagation through gradients affecting model updates. These metrics guide an Integer Linear Programming (ILP) problem that systematically optimizes layerwise precision to minimize overall quality loss while meeting efficiency targets. Experiments on 1B, 3B, 7B and 70B Llama-like models demonstrate that SNIP consistently outperforms existing baselines, reducing FLOPs by up to 80% while preserving model quality across different model sizes and training phases with minimal computational overhead.
LSM-GNN: Large-scale Storage-based Multi-GPU GNN Training by Optimizing Data Transfer Scheme
Jul 21, 2024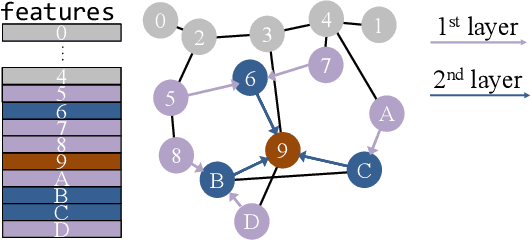
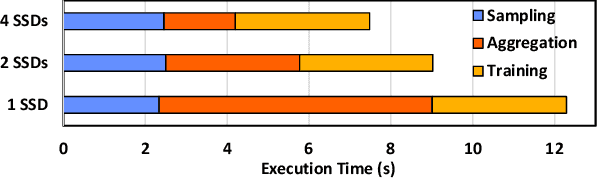
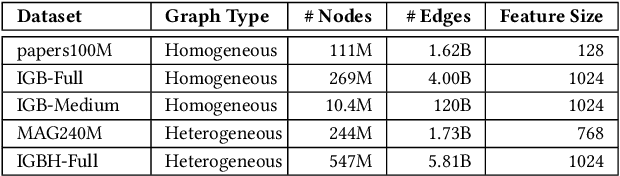
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are widely used today in recommendation systems, fraud detection, and node/link classification tasks. Real world GNNs continue to scale in size and require a large memory footprint for storing graphs and embeddings that often exceed the memory capacities of the target GPUs used for training. To address limited memory capacities, traditional GNN training approaches use graph partitioning and sharding techniques to scale up across multiple GPUs within a node and/or scale out across multiple nodes. However, this approach suffers from the high computational costs of graph partitioning algorithms and inefficient communication across GPUs. To address these overheads, we propose Large-scale Storage-based Multi-GPU GNN framework (LSM-GNN), a storagebased approach to train GNN models that utilizes a novel communication layer enabling GPU software caches to function as a system-wide shared cache with low overheads.LSM-GNN incorporates a hybrid eviction policy that intelligently manages cache space by using both static and dynamic node information to significantly enhance cache performance. Furthermore, we introduce the Preemptive Victim-buffer Prefetcher (PVP), a mechanism for prefetching node feature data from a Victim Buffer located in CPU pinned-memory to further reduce the pressure on the storage devices. Experimental results show that despite the lower compute capabilities and memory capacities, LSM-GNN in a single node with two GPUs offers superior performance over two-node-four-GPU Dist-DGL baseline and provides up to 3.75x speed up on end-to-end epoch time while running large-scale GNN training
Rethinking Numerical Representations for Deep Neural Networks
Aug 07, 2018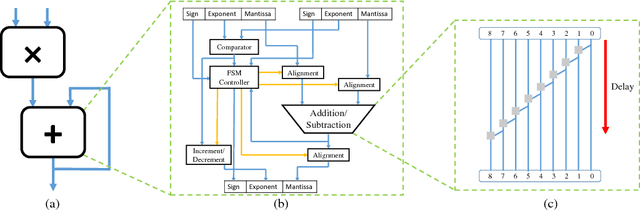
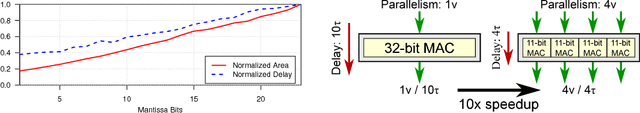
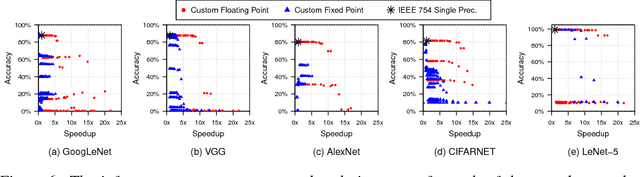
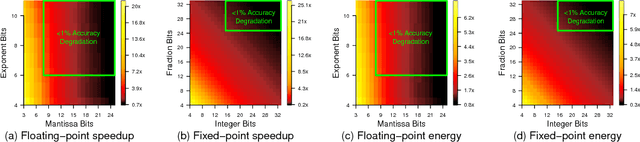
Abstract:With ever-increasing computational demand for deep learning, it is critical to investigate the implications of the numeric representation and precision of DNN model weights and activations on computational efficiency. In this work, we explore unconventional narrow-precision floating-point representations as it relates to inference accuracy and efficiency to steer the improved design of future DNN platforms. We show that inference using these custom numeric representations on production-grade DNNs, including GoogLeNet and VGG, achieves an average speedup of 7.6x with less than 1% degradation in inference accuracy relative to a state-of-the-art baseline platform representing the most sophisticated hardware using single-precision floating point. To facilitate the use of such customized precision, we also present a novel technique that drastically reduces the time required to derive the optimal precision configuration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge