Vincent Dumoulin
Perch 2.0: The Bittern Lesson for Bioacoustics
Aug 06, 2025



Abstract:Perch is a performant pre-trained model for bioacoustics. It was trained in supervised fashion, providing both off-the-shelf classification scores for thousands of vocalizing species as well as strong embeddings for transfer learning. In this new release, Perch 2.0, we expand from training exclusively on avian species to a large multi-taxa dataset. The model is trained with self-distillation using a prototype-learning classifier as well as a new source-prediction training criterion. Perch 2.0 obtains state-of-the-art performance on the BirdSet and BEANS benchmarks. It also outperforms specialized marine models on marine transfer learning tasks, despite having almost no marine training data. We present hypotheses as to why fine-grained species classification is a particularly robust pre-training task for bioacoustics.
The Search for Squawk: Agile Modeling in Bioacoustics
May 07, 2025Abstract:Passive acoustic monitoring (PAM) has shown great promise in helping ecologists understand the health of animal populations and ecosystems. However, extracting insights from millions of hours of audio recordings requires the development of specialized recognizers. This is typically a challenging task, necessitating large amounts of training data and machine learning expertise. In this work, we introduce a general, scalable and data-efficient system for developing recognizers for novel bioacoustic problems in under an hour. Our system consists of several key components that tackle problems in previous bioacoustic workflows: 1) highly generalizable acoustic embeddings pre-trained for birdsong classification minimize data hunger; 2) indexed audio search allows the efficient creation of classifier training datasets, and 3) precomputation of embeddings enables an efficient active learning loop, improving classifier quality iteratively with minimal wait time. Ecologists employed our system in three novel case studies: analyzing coral reef health through unidentified sounds; identifying juvenile Hawaiian bird calls to quantify breeding success and improve endangered species monitoring; and Christmas Island bird occupancy modeling. We augment the case studies with simulated experiments which explore the range of design decisions in a structured way and help establish best practices. Altogether these experiments showcase our system's scalability, efficiency, and generalizability, enabling scientists to quickly address new bioacoustic challenges.
Capturing Individual Human Preferences with Reward Features
Mar 21, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback usually models preferences using a reward model that does not distinguish between people. We argue that this is unlikely to be a good design choice in contexts with high potential for disagreement, like in the training of large language models. We propose a method to specialise a reward model to a person or group of people. Our approach builds on the observation that individual preferences can be captured as a linear combination of a set of general reward features. We show how to learn such features and subsequently use them to quickly adapt the reward model to a specific individual, even if their preferences are not reflected in the training data. We present experiments with large language models comparing the proposed architecture with a non-adaptive reward model and also adaptive counterparts, including models that do in-context personalisation. Depending on how much disagreement there is in the training data, our model either significantly outperforms the baselines or matches their performance with a simpler architecture and more stable training.
Are we making progress in unlearning? Findings from the first NeurIPS unlearning competition
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:We present the findings of the first NeurIPS competition on unlearning, which sought to stimulate the development of novel algorithms and initiate discussions on formal and robust evaluation methodologies. The competition was highly successful: nearly 1,200 teams from across the world participated, and a wealth of novel, imaginative solutions with different characteristics were contributed. In this paper, we analyze top solutions and delve into discussions on benchmarking unlearning, which itself is a research problem. The evaluation methodology we developed for the competition measures forgetting quality according to a formal notion of unlearning, while incorporating model utility for a holistic evaluation. We analyze the effectiveness of different instantiations of this evaluation framework vis-a-vis the associated compute cost, and discuss implications for standardizing evaluation. We find that the ranking of leading methods remains stable under several variations of this framework, pointing to avenues for reducing the cost of evaluation. Overall, our findings indicate progress in unlearning, with top-performing competition entries surpassing existing algorithms under our evaluation framework. We analyze trade-offs made by different algorithms and strengths or weaknesses in terms of generalizability to new datasets, paving the way for advancing both benchmarking and algorithm development in this important area.
Data Selection for Transfer Unlearning
May 16, 2024Abstract:As deep learning models are becoming larger and data-hungrier, there are growing ethical, legal and technical concerns over use of data: in practice, agreements on data use may change over time, rendering previously-used training data impermissible for training purposes. These issues have driven increased attention to machine unlearning: removing "the influence of" a subset of training data from a trained model. In this work, we advocate for a relaxed definition of unlearning that does not address privacy applications but targets a scenario where a data owner withdraws permission of use of their data for training purposes. In this context, we consider the important problem of \emph{transfer unlearning} where a pretrained model is transferred to a target dataset that contains some "non-static" data that may need to be unlearned in the future. We propose a new method that uses a mechanism for selecting relevant examples from an auxiliary "static" dataset, and finetunes on the selected data instead of "non-static" target data; addressing all unlearning requests ahead of time. We also adapt a recent relaxed definition of unlearning to our problem setting and demonstrate that our approach is an exact transfer unlearner according to it, while being highly efficient (amortized). We find that our method outperforms the gold standard "exact unlearning" (finetuning on only the "static" portion of the target dataset) on several datasets, especially for small "static" sets, sometimes approaching an upper bound for test accuracy. We also analyze factors influencing the accuracy boost obtained by data selection.
Leveraging tropical reef, bird and unrelated sounds for superior transfer learning in marine bioacoustics
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:Machine learning has the potential to revolutionize passive acoustic monitoring (PAM) for ecological assessments. However, high annotation and compute costs limit the field's efficacy. Generalizable pretrained networks can overcome these costs, but high-quality pretraining requires vast annotated libraries, limiting its current applicability primarily to bird taxa. Here, we identify the optimum pretraining strategy for a data-deficient domain using coral reef bioacoustics. We assemble ReefSet, a large annotated library of reef sounds, though modest compared to bird libraries at 2% of the sample count. Through testing few-shot transfer learning performance, we observe that pretraining on bird audio provides notably superior generalizability compared to pretraining on ReefSet or unrelated audio alone. However, our key findings show that cross-domain mixing which leverages bird, reef and unrelated audio during pretraining maximizes reef generalizability. SurfPerch, our pretrained network, provides a strong foundation for automated analysis of marine PAM data with minimal annotation and compute costs.
BIRB: A Generalization Benchmark for Information Retrieval in Bioacoustics
Dec 13, 2023



Abstract:The ability for a machine learning model to cope with differences in training and deployment conditions--e.g. in the presence of distribution shift or the generalization to new classes altogether--is crucial for real-world use cases. However, most empirical work in this area has focused on the image domain with artificial benchmarks constructed to measure individual aspects of generalization. We present BIRB, a complex benchmark centered on the retrieval of bird vocalizations from passively-recorded datasets given focal recordings from a large citizen science corpus available for training. We propose a baseline system for this collection of tasks using representation learning and a nearest-centroid search. Our thorough empirical evaluation and analysis surfaces open research directions, suggesting that BIRB fills the need for a more realistic and complex benchmark to drive progress on robustness to distribution shifts and generalization of ML models.
A density estimation perspective on learning from pairwise human preferences
Nov 30, 2023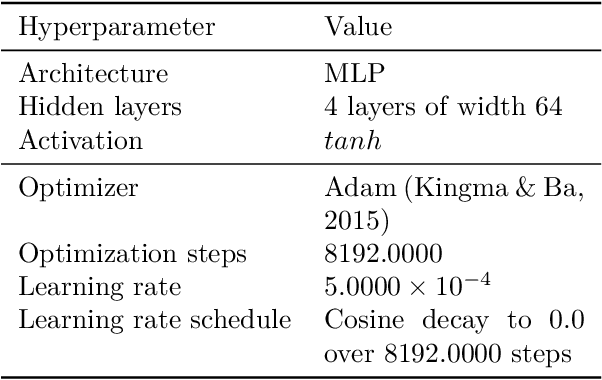


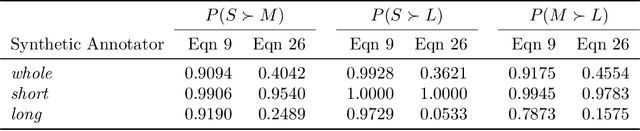
Abstract:Learning from human feedback (LHF) -- and in particular learning from pairwise preferences -- has recently become a crucial ingredient in training large language models (LLMs), and has been the subject of much research. Most recent works frame it as a reinforcement learning problem, where a reward function is learned from pairwise preference data and the LLM is treated as a policy which is adapted to maximize the rewards, often under additional regularization constraints. We propose an alternative interpretation which centers on the generative process for pairwise preferences and treats LHF as a density estimation problem. We provide theoretical and empirical results showing that for a family of generative processes defined via preference behavior distribution equations, training a reward function on pairwise preferences effectively models an annotator's implicit preference distribution. Finally, we discuss and present findings on "annotator misspecification" -- failure cases where wrong modeling assumptions are made about annotator behavior, resulting in poorly-adapted models -- suggesting that approaches that learn from pairwise human preferences could have trouble learning from a population of annotators with diverse viewpoints.
Active learning for fast and slow modeling attacks on Arbiter PUFs
Aug 25, 2023Abstract:Modeling attacks, in which an adversary uses machine learning techniques to model a hardware-based Physically Unclonable Function (PUF) pose a great threat to the viability of these hardware security primitives. In most modeling attacks, a random subset of challenge-response-pairs (CRPs) are used as the labeled data for the machine learning algorithm. Here, for the arbiter-PUF, a delay based PUF which may be viewed as a linear threshold function with random weights (due to manufacturing imperfections), we investigate the role of active learning in Support Vector Machine (SVM) learning. We focus on challenge selection to help SVM algorithm learn ``fast'' and learn ``slow''. Our methods construct challenges rather than relying on a sample pool of challenges as in prior work. Using active learning to learn ``fast'' (less CRPs revealed, higher accuracies) may help manufacturers learn the manufactured PUFs more efficiently, or may form a more powerful attack when the attacker may query the PUF for CRPs at will. Using active learning to select challenges from which learning is ``slow'' (low accuracy despite a large number of revealed CRPs) may provide a basis for slowing down attackers who are limited to overhearing CRPs.
In Search for a Generalizable Method for Source Free Domain Adaptation
Feb 13, 2023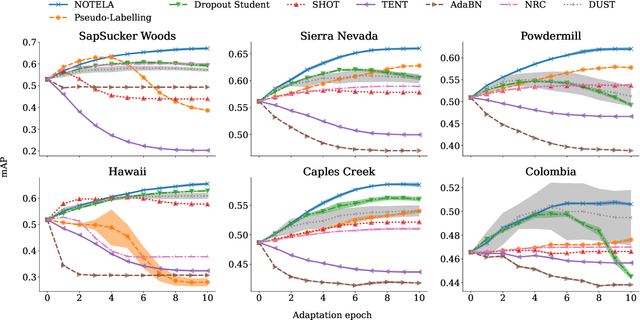
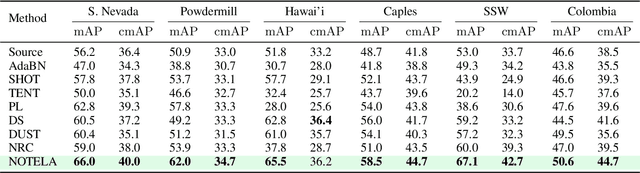
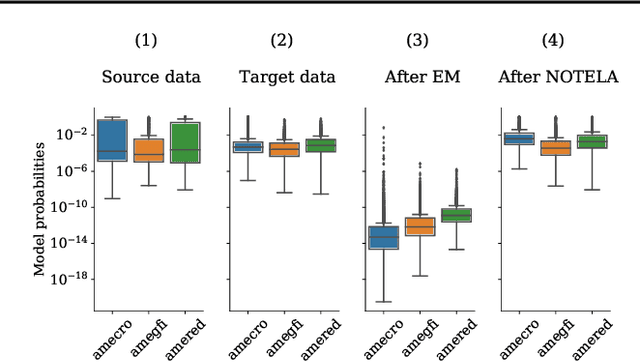
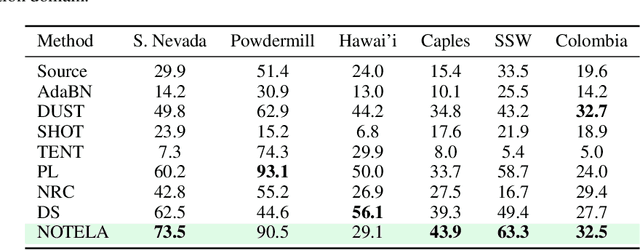
Abstract:Source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) is compelling because it allows adapting an off-the-shelf model to a new domain using only unlabelled data. In this work, we apply existing SFDA techniques to a challenging set of naturally-occurring distribution shifts in bioacoustics, which are very different from the ones commonly studied in computer vision. We find existing methods perform differently relative to each other than observed in vision benchmarks, and sometimes perform worse than no adaptation at all. We propose a new simple method which outperforms the existing methods on our new shifts while exhibiting strong performance on a range of vision datasets. Our findings suggest that existing SFDA methods are not as generalizable as previously thought and that considering diverse modalities can be a useful avenue for designing more robust models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge