Otilia Stretcu
Agile Deliberation: Concept Deliberation for Subjective Visual Classification
Dec 11, 2025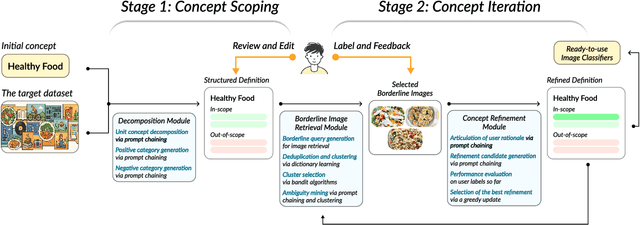
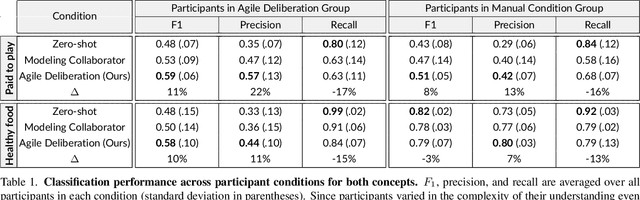
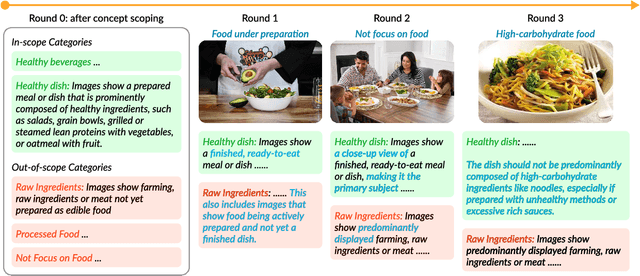
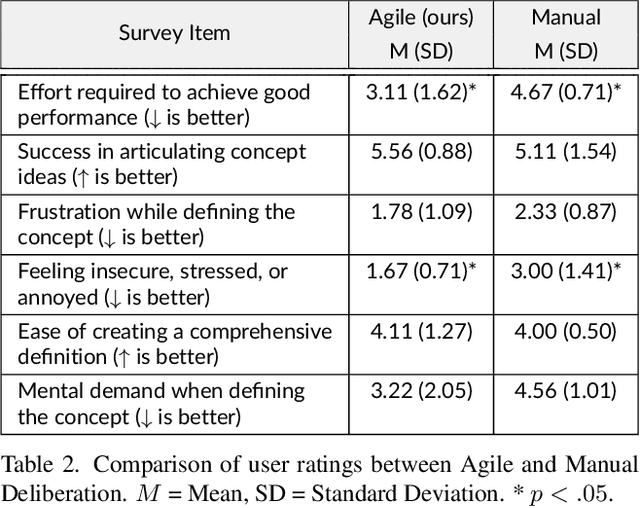
Abstract:From content moderation to content curation, applications requiring vision classifiers for visual concepts are rapidly expanding. Existing human-in-the-loop approaches typically assume users begin with a clear, stable concept understanding to be able to provide high-quality supervision. In reality, users often start with a vague idea and must iteratively refine it through "concept deliberation", a practice we uncovered through structured interviews with content moderation experts. We operationalize the common strategies in deliberation used by real content moderators into a human-in-the-loop framework called "Agile Deliberation" that explicitly supports evolving and subjective concepts. The system supports users in defining the concept for themselves by exposing them to borderline cases. The system does this with two deliberation stages: (1) concept scoping, which decomposes the initial concept into a structured hierarchy of sub-concepts, and (2) concept iteration, which surfaces semantically borderline examples for user reflection and feedback to iteratively align an image classifier with the user's evolving intent. Since concept deliberation is inherently subjective and interactive, we painstakingly evaluate the framework through 18 user sessions, each 1.5h long, rather than standard benchmarking datasets. We find that Agile Deliberation achieves 7.5% higher F1 scores than automated decomposition baselines and more than 3% higher than manual deliberation, while participants reported clearer conceptual understanding and lower cognitive effort.
The Search for Squawk: Agile Modeling in Bioacoustics
May 07, 2025Abstract:Passive acoustic monitoring (PAM) has shown great promise in helping ecologists understand the health of animal populations and ecosystems. However, extracting insights from millions of hours of audio recordings requires the development of specialized recognizers. This is typically a challenging task, necessitating large amounts of training data and machine learning expertise. In this work, we introduce a general, scalable and data-efficient system for developing recognizers for novel bioacoustic problems in under an hour. Our system consists of several key components that tackle problems in previous bioacoustic workflows: 1) highly generalizable acoustic embeddings pre-trained for birdsong classification minimize data hunger; 2) indexed audio search allows the efficient creation of classifier training datasets, and 3) precomputation of embeddings enables an efficient active learning loop, improving classifier quality iteratively with minimal wait time. Ecologists employed our system in three novel case studies: analyzing coral reef health through unidentified sounds; identifying juvenile Hawaiian bird calls to quantify breeding success and improve endangered species monitoring; and Christmas Island bird occupancy modeling. We augment the case studies with simulated experiments which explore the range of design decisions in a structured way and help establish best practices. Altogether these experiments showcase our system's scalability, efficiency, and generalizability, enabling scientists to quickly address new bioacoustic challenges.
Modeling Collaborator: Enabling Subjective Vision Classification With Minimal Human Effort via LLM Tool-Use
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:From content moderation to wildlife conservation, the number of applications that require models to recognize nuanced or subjective visual concepts is growing. Traditionally, developing classifiers for such concepts requires substantial manual effort measured in hours, days, or even months to identify and annotate data needed for training. Even with recently proposed Agile Modeling techniques, which enable rapid bootstrapping of image classifiers, users are still required to spend 30 minutes or more of monotonous, repetitive data labeling just to train a single classifier. Drawing on Fiske's Cognitive Miser theory, we propose a new framework that alleviates manual effort by replacing human labeling with natural language interactions, reducing the total effort required to define a concept by an order of magnitude: from labeling 2,000 images to only 100 plus some natural language interactions. Our framework leverages recent advances in foundation models, both large language models and vision-language models, to carve out the concept space through conversation and by automatically labeling training data points. Most importantly, our framework eliminates the need for crowd-sourced annotations. Moreover, our framework ultimately produces lightweight classification models that are deployable in cost-sensitive scenarios. Across 15 subjective concepts and across 2 public image classification datasets, our trained models outperform traditional Agile Modeling as well as state-of-the-art zero-shot classification models like ALIGN, CLIP, CuPL, and large visual question-answering models like PaLI-X.
Scaling Up LLM Reviews for Google Ads Content Moderation
Feb 07, 2024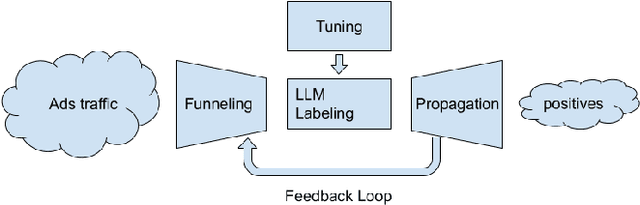
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are powerful tools for content moderation, but their inference costs and latency make them prohibitive for casual use on large datasets, such as the Google Ads repository. This study proposes a method for scaling up LLM reviews for content moderation in Google Ads. First, we use heuristics to select candidates via filtering and duplicate removal, and create clusters of ads for which we select one representative ad per cluster. We then use LLMs to review only the representative ads. Finally, we propagate the LLM decisions for the representative ads back to their clusters. This method reduces the number of reviews by more than 3 orders of magnitude while achieving a 2x recall compared to a baseline non-LLM model. The success of this approach is a strong function of the representations used in clustering and label propagation; we found that cross-modal similarity representations yield better results than uni-modal representations.
Visual Program Distillation: Distilling Tools and Programmatic Reasoning into Vision-Language Models
Dec 05, 2023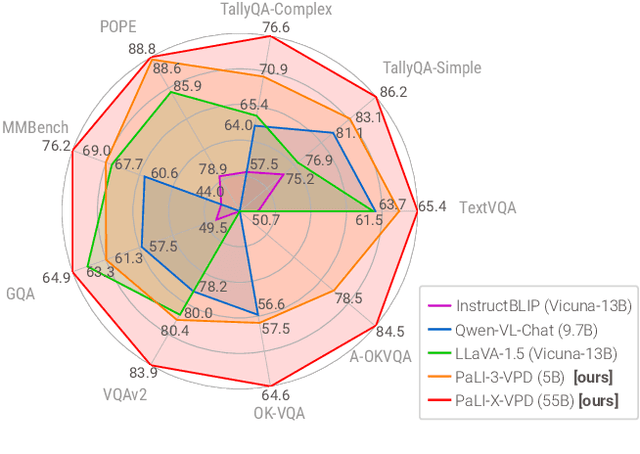
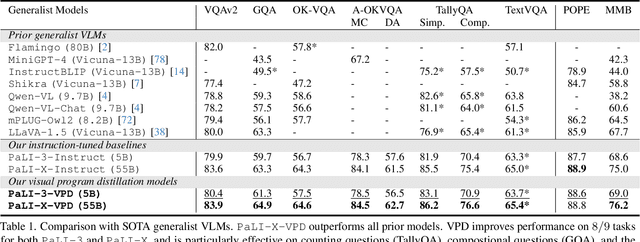
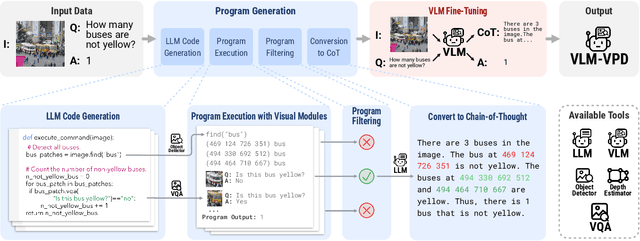
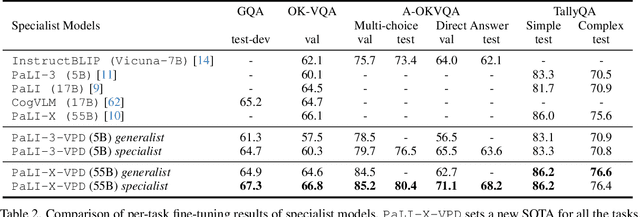
Abstract:Solving complex visual tasks such as "Who invented the musical instrument on the right?" involves a composition of skills: understanding space, recognizing instruments, and also retrieving prior knowledge. Recent work shows promise by decomposing such tasks using a large language model (LLM) into an executable program that invokes specialized vision models. However, generated programs are error-prone: they omit necessary steps, include spurious ones, and are unable to recover when the specialized models give incorrect outputs. Moreover, they require loading multiple models, incurring high latency and computation costs. We propose Visual Program Distillation (VPD), an instruction tuning framework that produces a vision-language model (VLM) capable of solving complex visual tasks with a single forward pass. VPD distills the reasoning ability of LLMs by using them to sample multiple candidate programs, which are then executed and verified to identify a correct one. It translates each correct program into a language description of the reasoning steps, which are then distilled into a VLM. Extensive experiments show that VPD improves the VLM's ability to count, understand spatial relations, and reason compositionally. Our VPD-trained PaLI-X outperforms all prior VLMs, achieving state-of-the-art performance across complex vision tasks, including MMBench, OK-VQA, A-OKVQA, TallyQA, POPE, and Hateful Memes. An evaluation with human annotators also confirms that VPD improves model response factuality and consistency. Finally, experiments on content moderation demonstrate that VPD is also helpful for adaptation to real-world applications with limited data.
Agile Modeling: Image Classification with Domain Experts in the Loop
Feb 25, 2023

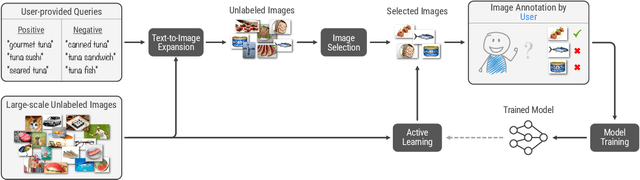
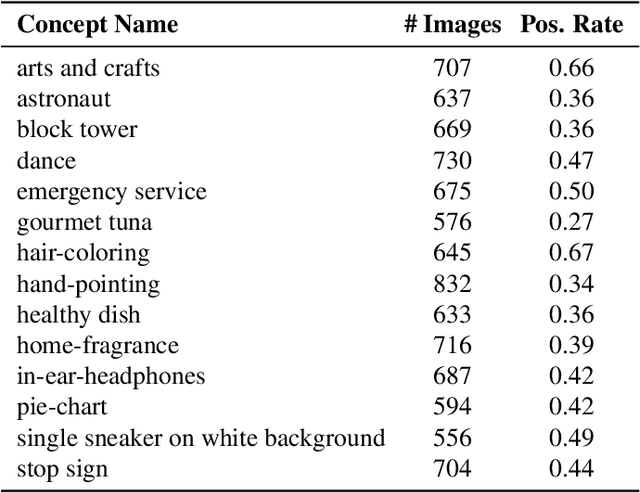
Abstract:Machine learning is not readily accessible to domain experts from many fields, blocked by issues ranging from data mining to model training. We argue that domain experts should be at the center of the modeling process, and we introduce the "Agile Modeling" problem: the process of turning any visual concept from an idea into a well-trained ML classifier through a human-in-the-loop interaction driven by the domain expert in a way that minimizes domain expert time. We propose a solution to the problem that enables domain experts to create classifiers in real-time and build upon recent advances in image-text co-embeddings such as CLIP or ALIGN to implement it. We show the feasibility of this solution through live experiments with 14 domain experts, each modeling their own concept. Finally, we compare a domain expert driven process with the traditional crowdsourcing paradigm and find that difficult concepts see pronounced improvements with domain experts.
Benchmarking Robustness to Adversarial Image Obfuscations
Jan 30, 2023



Abstract:Automated content filtering and moderation is an important tool that allows online platforms to build striving user communities that facilitate cooperation and prevent abuse. Unfortunately, resourceful actors try to bypass automated filters in a bid to post content that violate platform policies and codes of conduct. To reach this goal, these malicious actors may obfuscate policy violating images (e.g. overlay harmful images by carefully selected benign images or visual patterns) to prevent machine learning models from reaching the correct decision. In this paper, we invite researchers to tackle this specific issue and present a new image benchmark. This benchmark, based on ImageNet, simulates the type of obfuscations created by malicious actors. It goes beyond ImageNet-$\textrm{C}$ and ImageNet-$\bar{\textrm{C}}$ by proposing general, drastic, adversarial modifications that preserve the original content intent. It aims to tackle a more common adversarial threat than the one considered by $\ell_p$-norm bounded adversaries. We evaluate 33 pretrained models on the benchmark and train models with different augmentations, architectures and training methods on subsets of the obfuscations to measure generalization. We hope this benchmark will encourage researchers to test their models and methods and try to find new approaches that are more robust to these obfuscations.
Coarse-to-Fine Curriculum Learning
Jun 08, 2021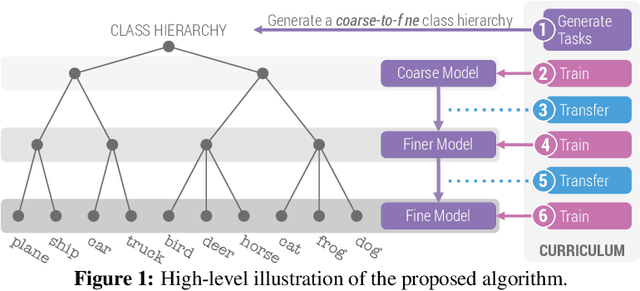
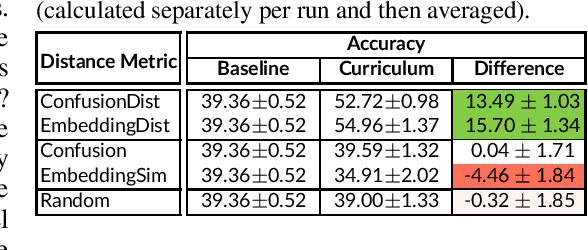
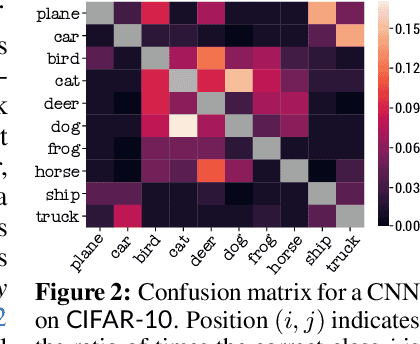
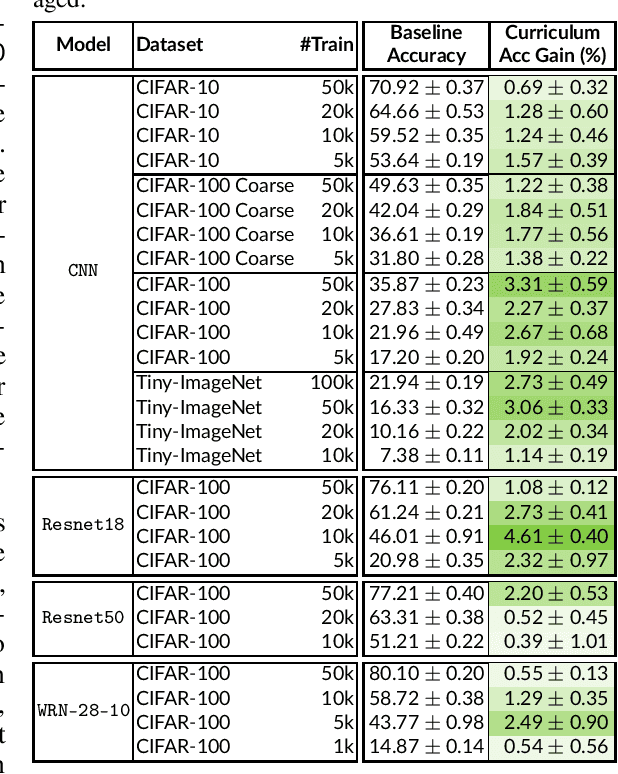
Abstract:When faced with learning challenging new tasks, humans often follow sequences of steps that allow them to incrementally build up the necessary skills for performing these new tasks. However, in machine learning, models are most often trained to solve the target tasks directly.Inspired by human learning, we propose a novel curriculum learning approach which decomposes challenging tasks into sequences of easier intermediate goals that are used to pre-train a model before tackling the target task. We focus on classification tasks, and design the intermediate tasks using an automatically constructed label hierarchy. We train the model at each level of the hierarchy, from coarse labels to fine labels, transferring acquired knowledge across these levels. For instance, the model will first learn to distinguish animals from objects, and then use this acquired knowledge when learning to classify among more fine-grained classes such as cat, dog, car, and truck. Most existing curriculum learning algorithms for supervised learning consist of scheduling the order in which the training examples are presented to the model. In contrast, our approach focuses on the output space of the model. We evaluate our method on several established datasets and show significant performance gains especially on classification problems with many labels. We also evaluate on a new synthetic dataset which allows us to study multiple aspects of our method.
Modeling Task Effects on Meaning Representation in the Brain via Zero-Shot MEG Prediction
Sep 17, 2020

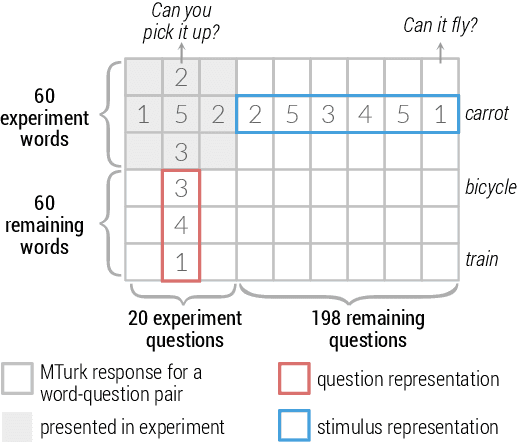

Abstract:How meaning is represented in the brain is still one of the big open questions in neuroscience. Does a word (e.g., bird) always have the same representation, or does the task under which the word is processed alter its representation (answering "can you eat it?" versus "can it fly?")? The brain activity of subjects who read the same word while performing different semantic tasks has been shown to differ across tasks. However, it is still not understood how the task itself contributes to this difference. In the current work, we study Magnetoencephalography (MEG) brain recordings of participants tasked with answering questions about concrete nouns. We investigate the effect of the task (i.e. the question being asked) on the processing of the concrete noun by predicting the millisecond-resolution MEG recordings as a function of both the semantics of the noun and the task. Using this approach, we test several hypotheses about the task-stimulus interactions by comparing the zero-shot predictions made by these hypotheses for novel tasks and nouns not seen during training. We find that incorporating the task semantics significantly improves the prediction of MEG recordings, across participants. The improvement occurs 475-550ms after the participants first see the word, which corresponds to what is considered to be the ending time of semantic processing for a word. These results suggest that only the end of semantic processing of a word is task-dependent, and pose a challenge for future research to formulate new hypotheses for earlier task effects as a function of the task and stimuli.
Competence-based Curriculum Learning for Neural Machine Translation
Mar 26, 2019



Abstract:Current state-of-the-art NMT systems use large neural networks that are not only slow to train, but also often require many heuristics and optimization tricks, such as specialized learning rate schedules and large batch sizes. This is undesirable as it requires extensive hyperparameter tuning. In this paper, we propose a curriculum learning framework for NMT that reduces training time, reduces the need for specialized heuristics or large batch sizes, and results in overall better performance. Our framework consists of a principled way of deciding which training samples are shown to the model at different times during training, based on the estimated difficulty of a sample and the current competence of the model. Filtering training samples in this manner prevents the model from getting stuck in bad local optima, making it converge faster and reach a better solution than the common approach of uniformly sampling training examples. Furthermore, the proposed method can be easily applied to existing NMT models by simply modifying their input data pipelines. We show that our framework can help improve the training time and the performance of both recurrent neural network models and Transformers, achieving up to a 70% decrease in training time, while at the same time obtaining accuracy improvements of up to 2.2 BLEU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge