Stefan Kahl
BirdSet: A Multi-Task Benchmark for Classification in Avian Bioacoustics
Mar 15, 2024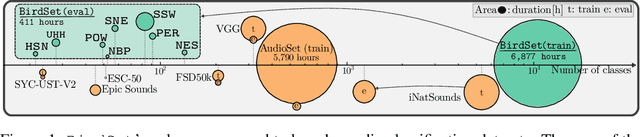
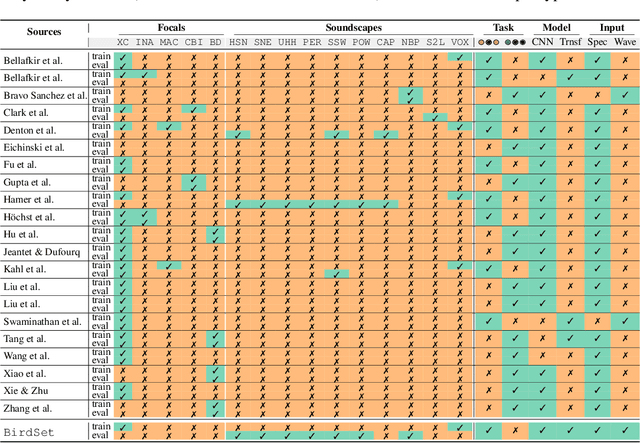

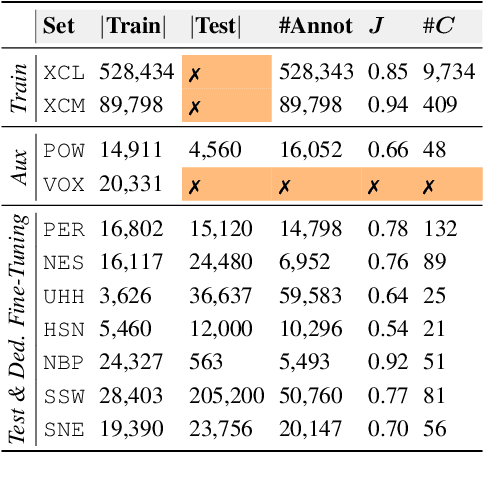
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) models have emerged as a powerful tool in avian bioacoustics to diagnose environmental health and biodiversity. However, inconsistencies in research pose notable challenges hindering progress in this domain. Reliable DL models need to analyze bird calls flexibly across various species and environments to fully harness the potential of bioacoustics in a cost-effective passive acoustic monitoring scenario. Data fragmentation and opacity across studies complicate a comprehensive evaluation of general model performance. To overcome these challenges, we present the BirdSet benchmark, a unified framework consolidating research efforts with a holistic approach for classifying bird vocalizations in avian bioacoustics. BirdSet harmonizes open-source bird recordings into a curated dataset collection. This unified approach provides an in-depth understanding of model performance and identifies potential shortcomings across different tasks. By establishing baseline results of current models, BirdSet aims to facilitate comparability, guide subsequent data collection, and increase accessibility for newcomers to avian bioacoustics.
BIRB: A Generalization Benchmark for Information Retrieval in Bioacoustics
Dec 13, 2023



Abstract:The ability for a machine learning model to cope with differences in training and deployment conditions--e.g. in the presence of distribution shift or the generalization to new classes altogether--is crucial for real-world use cases. However, most empirical work in this area has focused on the image domain with artificial benchmarks constructed to measure individual aspects of generalization. We present BIRB, a complex benchmark centered on the retrieval of bird vocalizations from passively-recorded datasets given focal recordings from a large citizen science corpus available for training. We propose a baseline system for this collection of tasks using representation learning and a nearest-centroid search. Our thorough empirical evaluation and analysis surfaces open research directions, suggesting that BIRB fills the need for a more realistic and complex benchmark to drive progress on robustness to distribution shifts and generalization of ML models.
Feature Embeddings from Large-Scale Acoustic Bird Classifiers Enable Few-Shot Transfer Learning
Jul 12, 2023Abstract:Automated bioacoustic analysis aids understanding and protection of both marine and terrestrial animals and their habitats across extensive spatiotemporal scales, and typically involves analyzing vast collections of acoustic data. With the advent of deep learning models, classification of important signals from these datasets has markedly improved. These models power critical data analyses for research and decision-making in biodiversity monitoring, animal behaviour studies, and natural resource management. However, deep learning models are often data-hungry and require a significant amount of labeled training data to perform well. While sufficient training data is available for certain taxonomic groups (e.g., common bird species), many classes (such as rare and endangered species, many non-bird taxa, and call-type), lack enough data to train a robust model from scratch. This study investigates the utility of feature embeddings extracted from large-scale audio classification models to identify bioacoustic classes other than the ones these models were originally trained on. We evaluate models on diverse datasets, including different bird calls and dialect types, bat calls, marine mammals calls, and amphibians calls. The embeddings extracted from the models trained on bird vocalization data consistently allowed higher quality classification than the embeddings trained on general audio datasets. The results of this study indicate that high-quality feature embeddings from large-scale acoustic bird classifiers can be harnessed for few-shot transfer learning, enabling the learning of new classes from a limited quantity of training data. Our findings reveal the potential for efficient analyses of novel bioacoustic tasks, even in scenarios where available training data is limited to a few samples.
Parsing Birdsong with Deep Audio Embeddings
Aug 20, 2021



Abstract:Monitoring of bird populations has played a vital role in conservation efforts and in understanding biodiversity loss. The automation of this process has been facilitated by both sensing technologies, such as passive acoustic monitoring, and accompanying analytical tools, such as deep learning. However, machine learning models frequently have difficulty generalizing to examples not encountered in the training data. In our work, we present a semi-supervised approach to identify characteristic calls and environmental noise. We utilize several methods to learn a latent representation of audio samples, including a convolutional autoencoder and two pre-trained networks, and group the resulting embeddings for a domain expert to identify cluster labels. We show that our approach can improve classification precision and provide insight into the latent structure of environmental acoustic datasets.
Recognizing Birds from Sound - The 2018 BirdCLEF Baseline System
Apr 19, 2018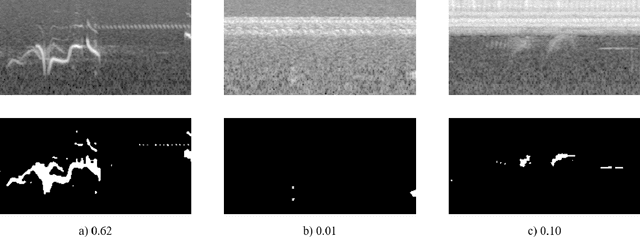
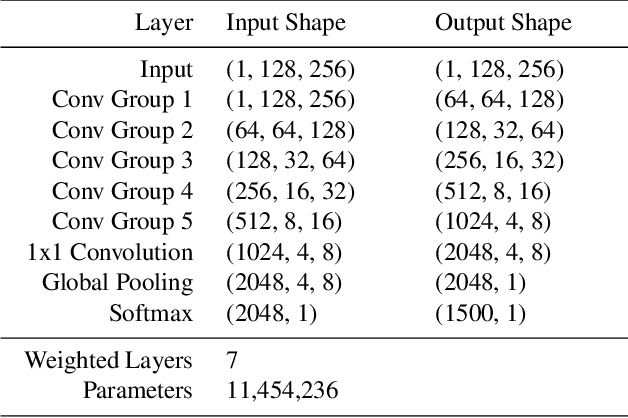
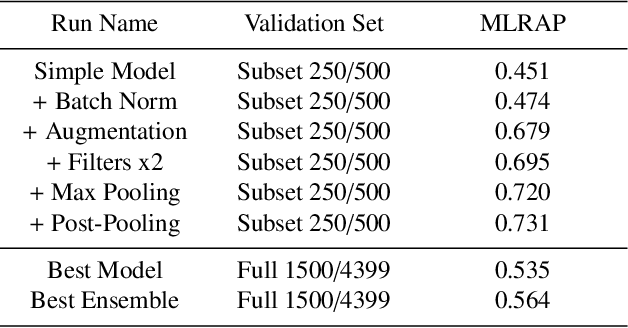
Abstract:Reliable identification of bird species in recorded audio files would be a transformative tool for researchers, conservation biologists, and birders. In recent years, artificial neural networks have greatly improved the detection quality of machine learning systems for bird species recognition. We present a baseline system using convolutional neural networks. We publish our code base as reference for participants in the 2018 LifeCLEF bird identification task and discuss our experiments and potential improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge