Moritz Wirth
Towards Deep Active Learning in Avian Bioacoustics
Jun 26, 2024

Abstract:Passive acoustic monitoring (PAM) in avian bioacoustics enables cost-effective and extensive data collection with minimal disruption to natural habitats. Despite advancements in computational avian bioacoustics, deep learning models continue to encounter challenges in adapting to diverse environments in practical PAM scenarios. This is primarily due to the scarcity of annotations, which requires labor-intensive efforts from human experts. Active learning (AL) reduces annotation cost and speed ups adaption to diverse scenarios by querying the most informative instances for labeling. This paper outlines a deep AL approach, introduces key challenges, and conducts a small-scale pilot study.
BirdSet: A Multi-Task Benchmark for Classification in Avian Bioacoustics
Mar 15, 2024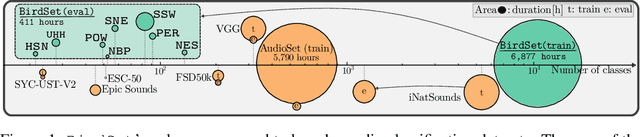
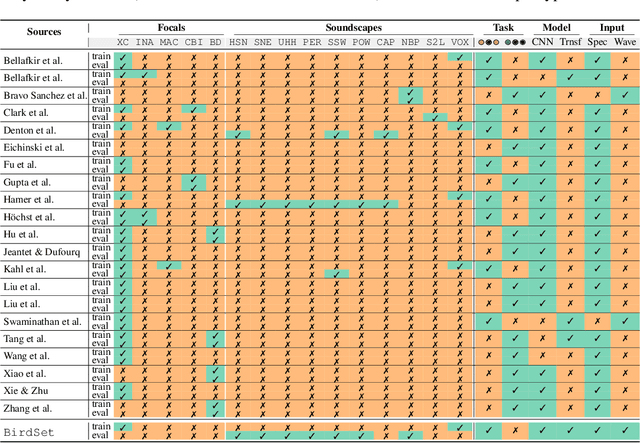

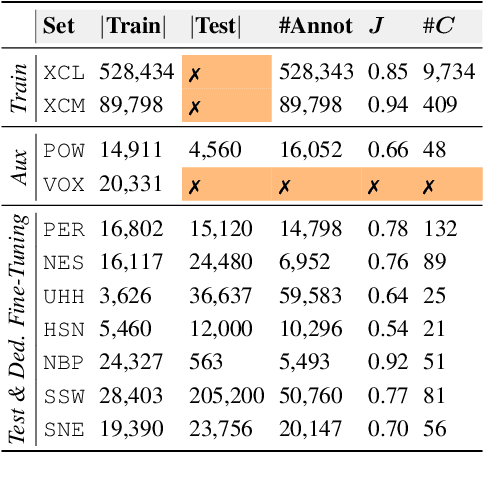
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) models have emerged as a powerful tool in avian bioacoustics to diagnose environmental health and biodiversity. However, inconsistencies in research pose notable challenges hindering progress in this domain. Reliable DL models need to analyze bird calls flexibly across various species and environments to fully harness the potential of bioacoustics in a cost-effective passive acoustic monitoring scenario. Data fragmentation and opacity across studies complicate a comprehensive evaluation of general model performance. To overcome these challenges, we present the BirdSet benchmark, a unified framework consolidating research efforts with a holistic approach for classifying bird vocalizations in avian bioacoustics. BirdSet harmonizes open-source bird recordings into a curated dataset collection. This unified approach provides an in-depth understanding of model performance and identifies potential shortcomings across different tasks. By establishing baseline results of current models, BirdSet aims to facilitate comparability, guide subsequent data collection, and increase accessibility for newcomers to avian bioacoustics.
Active Bird2Vec: Towards End-to-End Bird Sound Monitoring with Transformers
Aug 14, 2023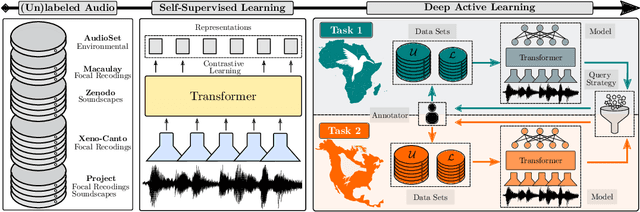
Abstract:We propose a shift towards end-to-end learning in bird sound monitoring by combining self-supervised (SSL) and deep active learning (DAL). Leveraging transformer models, we aim to bypass traditional spectrogram conversions, enabling direct raw audio processing. ActiveBird2Vec is set to generate high-quality bird sound representations through SSL, potentially accelerating the assessment of environmental changes and decision-making processes for wind farms. Additionally, we seek to utilize the wide variety of bird vocalizations through DAL, reducing the reliance on extensively labeled datasets by human experts. We plan to curate a comprehensive set of tasks through Huggingface Datasets, enhancing future comparability and reproducibility of bioacoustic research. A comparative analysis between various transformer models will be conducted to evaluate their proficiency in bird sound recognition tasks. We aim to accelerate the progression of avian bioacoustic research and contribute to more effective conservation strategies.
ActiveGLAE: A Benchmark for Deep Active Learning with Transformers
Jun 16, 2023Abstract:Deep active learning (DAL) seeks to reduce annotation costs by enabling the model to actively query instance annotations from which it expects to learn the most. Despite extensive research, there is currently no standardized evaluation protocol for transformer-based language models in the field of DAL. Diverse experimental settings lead to difficulties in comparing research and deriving recommendations for practitioners. To tackle this challenge, we propose the ActiveGLAE benchmark, a comprehensive collection of data sets and evaluation guidelines for assessing DAL. Our benchmark aims to facilitate and streamline the evaluation process of novel DAL strategies. Additionally, we provide an extensive overview of current practice in DAL with transformer-based language models. We identify three key challenges - data set selection, model training, and DAL settings - that pose difficulties in comparing query strategies. We establish baseline results through an extensive set of experiments as a reference point for evaluating future work. Based on our findings, we provide guidelines for researchers and practitioners.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge