Tingting Zhu
VQ-DSC-R: Robust Vector Quantized-Enabled Digital Semantic Communication With OFDM Transmission
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Digital mapping of semantic features is essential for achieving interoperability between semantic communication and practical digital infrastructure. However, current research efforts predominantly concentrate on analog semantic communication with simplified channel models. To bridge these gaps, we develop a robust vector quantized-enabled digital semantic communication (VQ-DSC-R) system built upon orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) transmission. Our work encompasses the framework design of VQ-DSC-R, followed by a comprehensive optimization study. Firstly, we design a Swin Transformer-based backbone for hierarchical semantic feature extraction, integrated with VQ modules that map the features into a shared semantic quantized codebook (SQC) for efficient index transmission. Secondly, we propose a differentiable vector quantization with adaptive noise-variance (ANDVQ) scheme to mitigate quantization errors in SQC, which dynamically adjusts the quantization process using K-nearest neighbor statistics, while exponential moving average mechanism stabilizes SQC training. Thirdly, for robust index transmission over multipath fading channel and noise, we develop a conditional diffusion model (CDM) to refine channel state information, and design an attention-based module to dynamically adapt to channel noise. The entire VQ-DSC-R system is optimized via a three-stage training strategy. Extensive experiments demonstrate superiority of VQ-DSC-R over benchmark schemes, achieving high compression ratios and robust performance in practical scenarios.
From Generative Engines to Actionable Simulators: The Imperative of Physical Grounding in World Models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:A world model is an AI system that simulates how an environment evolves under actions, enabling planning through imagined futures rather than reactive perception. Current world models, however, suffer from visual conflation: the mistaken assumption that high-fidelity video generation implies an understanding of physical and causal dynamics. We show that while modern models excel at predicting pixels, they frequently violate invariant constraints, fail under intervention, and break down in safety-critical decision-making. This survey argues that visual realism is an unreliable proxy for world understanding. Instead, effective world models must encode causal structure, respect domain-specific constraints, and remain stable over long horizons. We propose a reframing of world models as actionable simulators rather than visual engines, emphasizing structured 4D interfaces, constraint-aware dynamics, and closed-loop evaluation. Using medical decision-making as an epistemic stress test, where trial-and-error is impossible and errors are irreversible, we demonstrate that a world model's value is determined not by how realistic its rollouts appear, but by its ability to support counterfactual reasoning, intervention planning, and robust long-horizon foresight.
SurvBench: A Standardised Preprocessing Pipeline for Multi-Modal Electronic Health Record Survival Analysis
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Electronic health record (EHR) data present tremendous opportunities for advancing survival analysis through deep learning, yet reproducibility remains severely constrained by inconsistent preprocessing methodologies. We present SurvBench, a comprehensive, open-source preprocessing pipeline that transforms raw PhysioNet datasets into standardised, model-ready tensors for multi-modal survival analysis. SurvBench provides data loaders for three major critical care databases, MIMIC-IV, eICU, and MC-MED, supporting diverse modalities including time-series vitals, static demographics, ICD diagnosis codes, and radiology reports. The pipeline implements rigorous data quality controls, patient-level splitting to prevent data leakage, explicit missingness tracking, and standardised temporal aggregation. SurvBench handles both single-risk (e.g., in-hospital mortality) and competing-risks scenarios (e.g., multiple discharge outcomes). The outputs are compatible with pycox library packages and implementations of standard statistical and deep learning models. By providing reproducible, configuration-driven preprocessing with comprehensive documentation, SurvBench addresses the "preprocessing gap" that has hindered fair comparison of deep learning survival models, enabling researchers to focus on methodological innovation rather than data engineering.
Think Consistently, Reason Efficiently: Energy-Based Calibration for Implicit Chain-of-Thought
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong reasoning capabilities through \emph{Chain-of-Thought} (CoT) prompting, which enables step-by-step intermediate reasoning. However, explicit CoT methods rely on discrete token-level reasoning processes that are prone to error propagation and limited by vocabulary expressiveness, often resulting in rigid and inconsistent reasoning trajectories. Recent research has explored implicit or continuous reasoning in latent spaces, allowing models to perform internal reasoning before generating explicit output. Although such approaches alleviate some limitations of discrete CoT, they generally lack explicit mechanisms to enforce consistency among reasoning steps, leading to divergent reasoning paths and unstable outcomes. To address this issue, we propose EBM-CoT, an Energy-Based Chain-of-Thought Calibration framework that refines latent thought representations through an energy-based model (EBM). Our method dynamically adjusts latent reasoning trajectories toward lower-energy, high-consistency regions in the embedding space, improving both reasoning accuracy and consistency without modifying the base language model. Extensive experiments across mathematical, commonsense, and symbolic reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed framework significantly enhances the consistency and efficiency of multi-step reasoning in LLMs.
BioX-Bridge: Model Bridging for Unsupervised Cross-Modal Knowledge Transfer across Biosignals
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Biosignals offer valuable insights into the physiological states of the human body. Although biosignal modalities differ in functionality, signal fidelity, sensor comfort, and cost, they are often intercorrelated, reflecting the holistic and interconnected nature of human physiology. This opens up the possibility of performing the same tasks using alternative biosignal modalities, thereby improving the accessibility, usability, and adaptability of health monitoring systems. However, the limited availability of large labeled datasets presents challenges for training models tailored to specific tasks and modalities of interest. Unsupervised cross-modal knowledge transfer offers a promising solution by leveraging knowledge from an existing modality to support model training for a new modality. Existing methods are typically based on knowledge distillation, which requires running a teacher model alongside student model training, resulting in high computational and memory overhead. This challenge is further exacerbated by the recent development of foundation models that demonstrate superior performance and generalization across tasks at the cost of large model sizes. To this end, we explore a new framework for unsupervised cross-modal knowledge transfer of biosignals by training a lightweight bridge network to align the intermediate representations and enable information flow between foundation models and across modalities. Specifically, we introduce an efficient strategy for selecting alignment positions where the bridge should be constructed, along with a flexible prototype network as the bridge architecture. Extensive experiments across multiple biosignal modalities, tasks, and datasets show that BioX-Bridge reduces the number of trainable parameters by 88--99\% while maintaining or even improving transfer performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Bridging Data Gaps of Rare Conditions in ICU: A Multi-Disease Adaptation Approach for Clinical Prediction
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:Artificial Intelligence has revolutionised critical care for common conditions. Yet, rare conditions in the intensive care unit (ICU), including recognised rare diseases and low-prevalence conditions in the ICU, remain underserved due to data scarcity and intra-condition heterogeneity. To bridge such gaps, we developed KnowRare, a domain adaptation-based deep learning framework for predicting clinical outcomes for rare conditions in the ICU. KnowRare mitigates data scarcity by initially learning condition-agnostic representations from diverse electronic health records through self-supervised pre-training. It addresses intra-condition heterogeneity by selectively adapting knowledge from clinically similar conditions with a developed condition knowledge graph. Evaluated on two ICU datasets across five clinical prediction tasks (90-day mortality, 30-day readmission, ICU mortality, remaining length of stay, and phenotyping), KnowRare consistently outperformed existing state-of-the-art models. Additionally, KnowRare demonstrated superior predictive performance compared to established ICU scoring systems, including APACHE IV and IV-a. Case studies further demonstrated KnowRare's flexibility in adapting its parameters to accommodate dataset-specific and task-specific characteristics, its generalisation to common conditions under limited data scenarios, and its rationality in selecting source conditions. These findings highlight KnowRare's potential as a robust and practical solution for supporting clinical decision-making and improving care for rare conditions in the ICU.
SurvUnc: A Meta-Model Based Uncertainty Quantification Framework for Survival Analysis
May 20, 2025Abstract:Survival analysis, which estimates the probability of event occurrence over time from censored data, is fundamental in numerous real-world applications, particularly in high-stakes domains such as healthcare and risk assessment. Despite advances in numerous survival models, quantifying the uncertainty of predictions from these models remains underexplored and challenging. The lack of reliable uncertainty quantification limits the interpretability and trustworthiness of survival models, hindering their adoption in clinical decision-making and other sensitive applications. To bridge this gap, in this work, we introduce SurvUnc, a novel meta-model based framework for post-hoc uncertainty quantification for survival models. SurvUnc introduces an anchor-based learning strategy that integrates concordance knowledge into meta-model optimization, leveraging pairwise ranking performance to estimate uncertainty effectively. Notably, our framework is model-agnostic, ensuring compatibility with any survival model without requiring modifications to its architecture or access to its internal parameters. Especially, we design a comprehensive evaluation pipeline tailored to this critical yet overlooked problem. Through extensive experiments on four publicly available benchmarking datasets and five representative survival models, we demonstrate the superiority of SurvUnc across multiple evaluation scenarios, including selective prediction, misprediction detection, and out-of-domain detection. Our results highlight the effectiveness of SurvUnc in enhancing model interpretability and reliability, paving the way for more trustworthy survival predictions in real-world applications.
Towards deployment-centric multimodal AI beyond vision and language
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Multimodal artificial intelligence (AI) integrates diverse types of data via machine learning to improve understanding, prediction, and decision-making across disciplines such as healthcare, science, and engineering. However, most multimodal AI advances focus on models for vision and language data, while their deployability remains a key challenge. We advocate a deployment-centric workflow that incorporates deployment constraints early to reduce the likelihood of undeployable solutions, complementing data-centric and model-centric approaches. We also emphasise deeper integration across multiple levels of multimodality and multidisciplinary collaboration to significantly broaden the research scope beyond vision and language. To facilitate this approach, we identify common multimodal-AI-specific challenges shared across disciplines and examine three real-world use cases: pandemic response, self-driving car design, and climate change adaptation, drawing expertise from healthcare, social science, engineering, science, sustainability, and finance. By fostering multidisciplinary dialogue and open research practices, our community can accelerate deployment-centric development for broad societal impact.
DynaGraph: Interpretable Multi-Label Prediction from EHRs via Dynamic Graph Learning and Contrastive Augmentation
Mar 28, 2025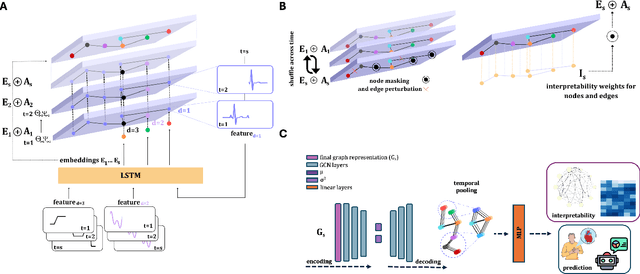
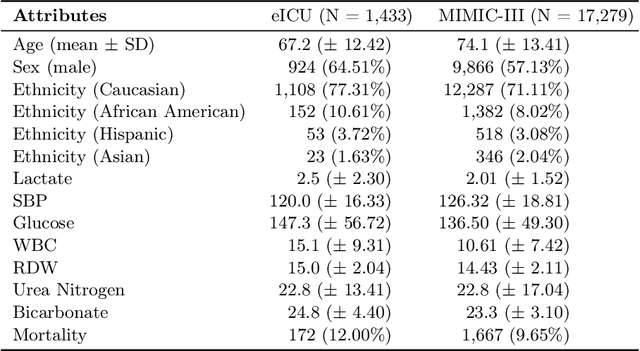
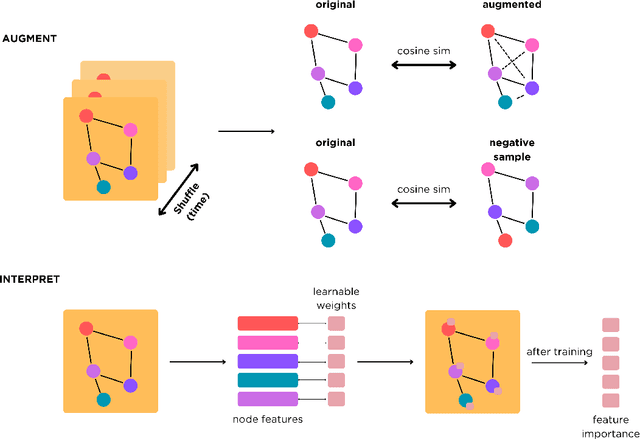
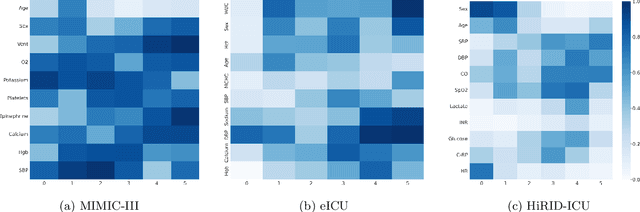
Abstract:Learning from longitudinal electronic health records is limited if it does not capture the temporal trajectories of the patient's state in a clinical setting. Graph models allow us to capture the hidden dependencies of the multivariate time-series when the graphs are constructed in a similar dynamic manner. Previous dynamic graph models require a pre-defined and/or static graph structure, which is unknown in most cases, or they only capture the spatial relations between the features. Furthermore in healthcare, the interpretability of the model is an essential requirement to build trust with clinicians. In addition to previously proposed attention mechanisms, there has not been an interpretable dynamic graph framework for data from multivariate electronic health records (EHRs). Here, we propose DynaGraph, an end-to-end interpretable contrastive graph model that learns the dynamics of multivariate time-series EHRs as part of optimisation. We validate our model in four real-world clinical datasets, ranging from primary care to secondary care settings with broad demographics, in challenging settings where tasks are imbalanced and multi-labelled. Compared to state-of-the-art models, DynaGraph achieves significant improvements in balanced accuracy and sensitivity over the nearest complex competitors in time-series or dynamic graph modelling across three ICU and one primary care datasets. Through a pseudo-attention approach to graph construction, our model also indicates the importance of clinical covariates over time, providing means for clinical validation.
AnchorInv: Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning of Physiological Signals via Representation Space Guided Inversion
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Deep learning models have demonstrated exceptional performance in a variety of real-world applications. These successes are often attributed to strong base models that can generalize to novel tasks with limited supporting data while keeping prior knowledge intact. However, these impressive results are based on the availability of a large amount of high-quality data, which is often lacking in specialized biomedical applications. In such fields, models are usually developed with limited data that arrive incrementally with novel categories. This requires the model to adapt to new information while preserving existing knowledge. Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) methods offer a promising approach to addressing these challenges, but they also depend on strong base models that face the same aforementioned limitations. To overcome these constraints, we propose AnchorInv following the straightforward and efficient buffer-replay strategy. Instead of selecting and storing raw data, AnchorInv generates synthetic samples guided by anchor points in the feature space. This approach protects privacy and regularizes the model for adaptation. When evaluated on three public physiological time series datasets, AnchorInv exhibits efficient knowledge forgetting prevention and improved adaptation to novel classes, surpassing state-of-the-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge