SouYoung Jin
Is Attention All You Need For Actigraphy? Foundation Models of Wearable Accelerometer Data for Mental Health Research
Nov 26, 2024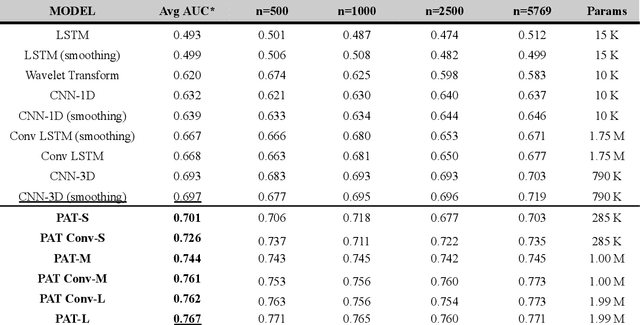
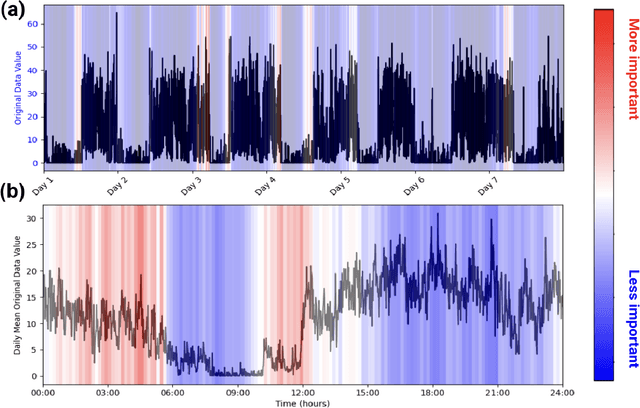
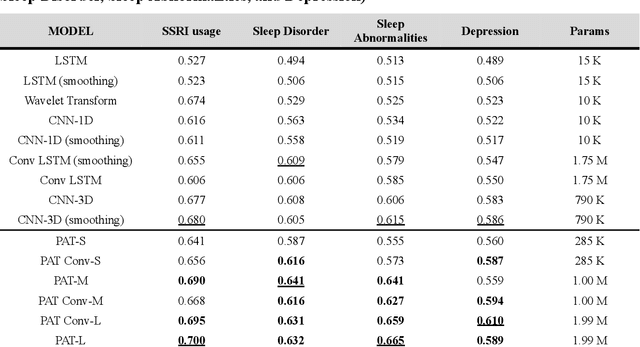
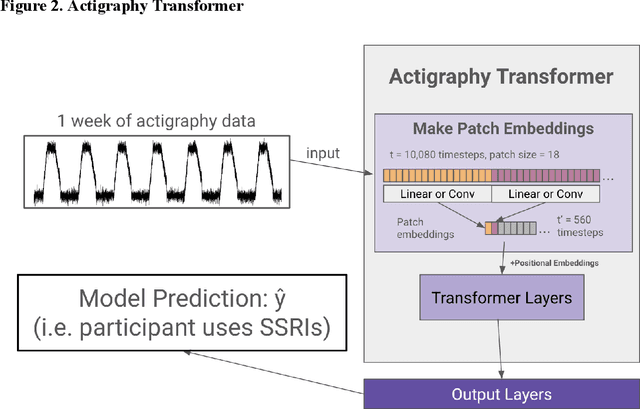
Abstract:Wearable accelerometry (actigraphy) has provided valuable data for clinical insights since the 1970s and is increasingly important as wearable devices continue to become widespread. The effectiveness of actigraphy in research and clinical contexts is heavily dependent on the modeling architecture utilized. To address this, we developed the Pretrained Actigraphy Transformer (PAT)--the first pretrained and fully attention-based model designed specifically to handle actigraphy. PAT was pretrained on actigraphy from 29,307 participants in NHANES, enabling it to deliver state-of-the-art performance when fine-tuned across various actigraphy prediction tasks in the mental health domain, even in data-limited scenarios. For example, when trained to predict benzodiazepine usage using actigraphy from only 500 labeled participants, PAT achieved an 8.8 percentage-point AUC improvement over the best baseline. With fewer than 2 million parameters and built-in model explainability, PAT is robust yet easy to deploy in health research settings. GitHub: https://github.com/njacobsonlab/Pretrained-Actigraphy-Transformer/
Multi-layer Learnable Attention Mask for Multimodal Tasks
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:While the Self-Attention mechanism in the Transformer model has proven to be effective in many domains, we observe that it is less effective in more diverse settings (e.g. multimodality) due to the varying granularity of each token and the high computational demands of lengthy sequences. To address the challenges, we introduce the Learnable Attention Mask (LAM), strategically designed to globally regulate attention maps and prioritize critical tokens within the sequence. Leveraging the Self-Attention module in a BERT-like transformer network, our approach adeptly captures associations between tokens. The extension of the LAM to a multi-layer version accommodates the varied information aspects embedded at each layer of the Transformer network. Comprehensive experimental validation on various datasets, such as MADv2, QVHighlights, ImageNet 1K, and MSRVTT, demonstrates the efficacy of the LAM, exemplifying its ability to enhance model performance while mitigating redundant computations. This pioneering approach presents a significant advancement in enhancing the understanding of complex scenarios, such as in movie understanding.
FT2TF: First-Person Statement Text-To-Talking Face Generation
Dec 09, 2023



Abstract:Talking face generation has gained immense popularity in the computer vision community, with various applications including AR/VR, teleconferencing, digital assistants, and avatars. Traditional methods are mainly audio-driven ones which have to deal with the inevitable resource-intensive nature of audio storage and processing. To address such a challenge, we propose FT2TF - First-Person Statement Text-To-Talking Face Generation, a novel one-stage end-to-end pipeline for talking face generation driven by first-person statement text. Moreover, FT2TF implements accurate manipulation of the facial expressions by altering the corresponding input text. Different from previous work, our model only leverages visual and textual information without any other sources (e.g. audio/landmark/pose) during inference. Extensive experiments are conducted on LRS2 and LRS3 datasets, and results on multi-dimensional evaluation metrics are reported. Both quantitative and qualitative results showcase that FT2TF outperforms existing relevant methods and reaches the state-of-the-art. This achievement highlights our model capability to bridge first-person statements and dynamic face generation, providing insightful guidance for future work.
Learning Human Action Recognition Representations Without Real Humans
Nov 10, 2023



Abstract:Pre-training on massive video datasets has become essential to achieve high action recognition performance on smaller downstream datasets. However, most large-scale video datasets contain images of people and hence are accompanied with issues related to privacy, ethics, and data protection, often preventing them from being publicly shared for reproducible research. Existing work has attempted to alleviate these problems by blurring faces, downsampling videos, or training on synthetic data. On the other hand, analysis on the transferability of privacy-preserving pre-trained models to downstream tasks has been limited. In this work, we study this problem by first asking the question: can we pre-train models for human action recognition with data that does not include real humans? To this end, we present, for the first time, a benchmark that leverages real-world videos with humans removed and synthetic data containing virtual humans to pre-train a model. We then evaluate the transferability of the representation learned on this data to a diverse set of downstream action recognition benchmarks. Furthermore, we propose a novel pre-training strategy, called Privacy-Preserving MAE-Align, to effectively combine synthetic data and human-removed real data. Our approach outperforms previous baselines by up to 5% and closes the performance gap between human and no-human action recognition representations on downstream tasks, for both linear probing and fine-tuning. Our benchmark, code, and models are available at https://github.com/howardzh01/PPMA .
LangNav: Language as a Perceptual Representation for Navigation
Oct 11, 2023



Abstract:We explore the use of language as a perceptual representation for vision-and-language navigation. Our approach uses off-the-shelf vision systems (for image captioning and object detection) to convert an agent's egocentric panoramic view at each time step into natural language descriptions. We then finetune a pretrained language model to select an action, based on the current view and the trajectory history, that would best fulfill the navigation instructions. In contrast to the standard setup which adapts a pretrained language model to work directly with continuous visual features from pretrained vision models, our approach instead uses (discrete) language as the perceptual representation. We explore two use cases of our language-based navigation (LangNav) approach on the R2R vision-and-language navigation benchmark: generating synthetic trajectories from a prompted large language model (GPT-4) with which to finetune a smaller language model; and sim-to-real transfer where we transfer a policy learned on a simulated environment (ALFRED) to a real-world environment (R2R). Our approach is found to improve upon strong baselines that rely on visual features in settings where only a few gold trajectories (10-100) are available, demonstrating the potential of using language as a perceptual representation for navigation tasks.
Cross-Modal Discrete Representation Learning
Jun 10, 2021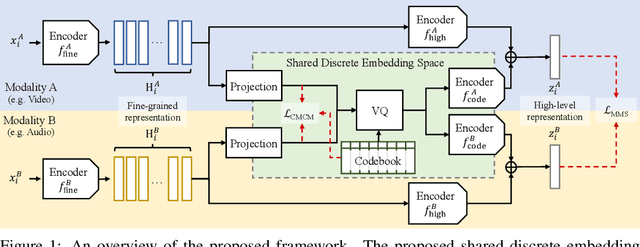
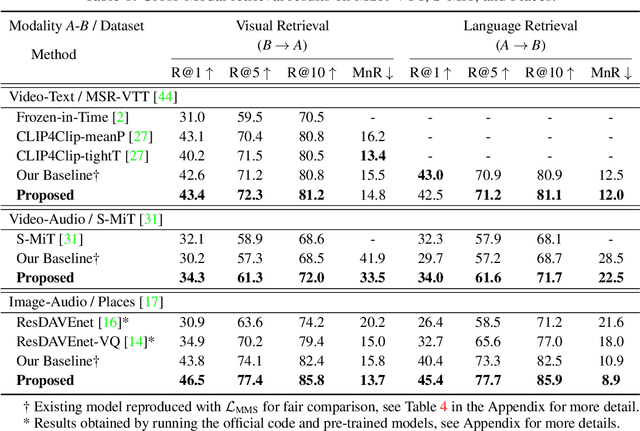
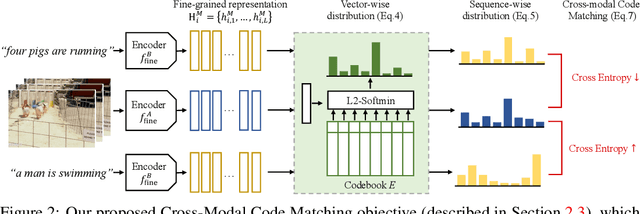
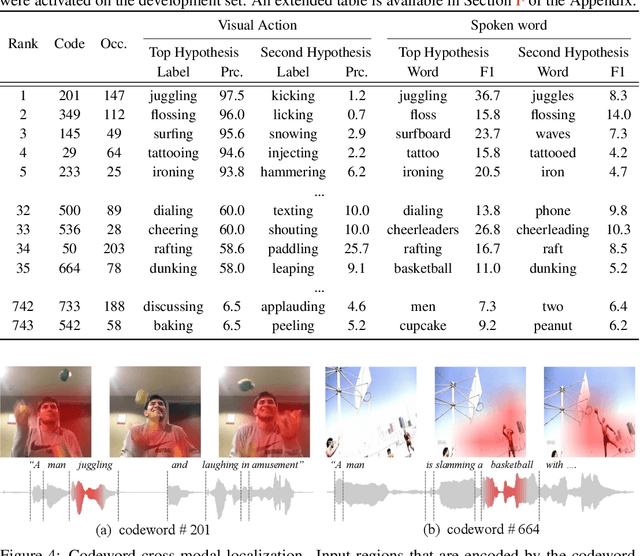
Abstract:Recent advances in representation learning have demonstrated an ability to represent information from different modalities such as video, text, and audio in a single high-level embedding vector. In this work we present a self-supervised learning framework that is able to learn a representation that captures finer levels of granularity across different modalities such as concepts or events represented by visual objects or spoken words. Our framework relies on a discretized embedding space created via vector quantization that is shared across different modalities. Beyond the shared embedding space, we propose a Cross-Modal Code Matching objective that forces the representations from different views (modalities) to have a similar distribution over the discrete embedding space such that cross-modal objects/actions localization can be performed without direct supervision. In our experiments we show that the proposed discretized multi-modal fine-grained representation (e.g., pixel/word/frame) can complement high-level summary representations (e.g., video/sentence/waveform) for improved performance on cross-modal retrieval tasks. We also observe that the discretized representation uses individual clusters to represent the same semantic concept across modalities.
Spoken Moments: Learning Joint Audio-Visual Representations from Video Descriptions
May 10, 2021
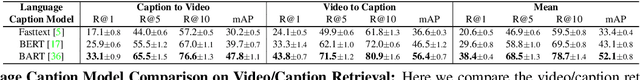
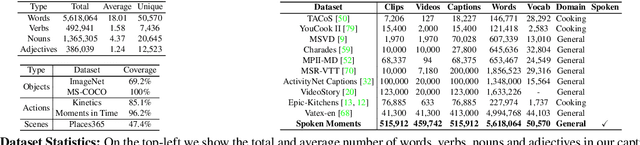
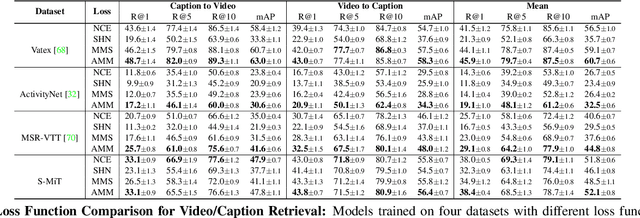
Abstract:When people observe events, they are able to abstract key information and build concise summaries of what is happening. These summaries include contextual and semantic information describing the important high-level details (what, where, who and how) of the observed event and exclude background information that is deemed unimportant to the observer. With this in mind, the descriptions people generate for videos of different dynamic events can greatly improve our understanding of the key information of interest in each video. These descriptions can be captured in captions that provide expanded attributes for video labeling (e.g. actions/objects/scenes/sentiment/etc.) while allowing us to gain new insight into what people find important or necessary to summarize specific events. Existing caption datasets for video understanding are either small in scale or restricted to a specific domain. To address this, we present the Spoken Moments (S-MiT) dataset of 500k spoken captions each attributed to a unique short video depicting a broad range of different events. We collect our descriptions using audio recordings to ensure that they remain as natural and concise as possible while allowing us to scale the size of a large classification dataset. In order to utilize our proposed dataset, we present a novel Adaptive Mean Margin (AMM) approach to contrastive learning and evaluate our models on video/caption retrieval on multiple datasets. We show that our AMM approach consistently improves our results and that models trained on our Spoken Moments dataset generalize better than those trained on other video-caption datasets.
Automatic adaptation of object detectors to new domains using self-training
Apr 15, 2019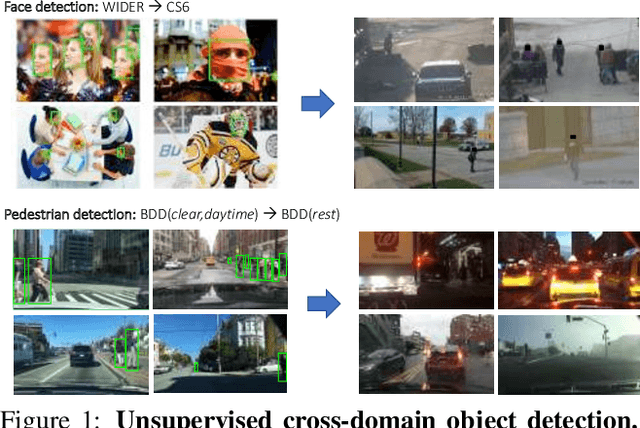
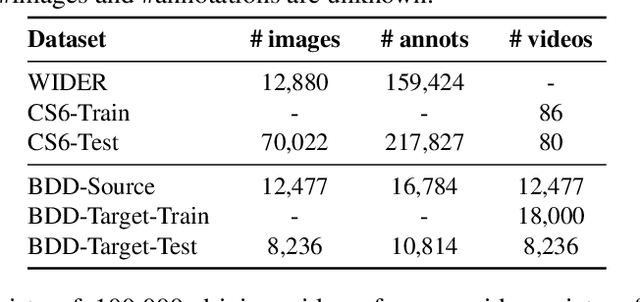

Abstract:This work addresses the unsupervised adaptation of an existing object detector to a new target domain. We assume that a large number of unlabeled videos from this domain are readily available. We automatically obtain labels on the target data by using high-confidence detections from the existing detector, augmented with hard (misclassified) examples acquired by exploiting temporal cues using a tracker. These automatically-obtained labels are then used for re-training the original model. A modified knowledge distillation loss is proposed, and we investigate several ways of assigning soft-labels to the training examples from the target domain. Our approach is empirically evaluated on challenging face and pedestrian detection tasks: a face detector trained on WIDER-Face, which consists of high-quality images crawled from the web, is adapted to a large-scale surveillance data set; a pedestrian detector trained on clear, daytime images from the BDD-100K driving data set is adapted to all other scenarios such as rainy, foggy, night-time. Our results demonstrate the usefulness of incorporating hard examples obtained from tracking, the advantage of using soft-labels via distillation loss versus hard-labels, and show promising performance as a simple method for unsupervised domain adaptation of object detectors, with minimal dependence on hyper-parameters.
Unsupervised Hard Example Mining from Videos for Improved Object Detection
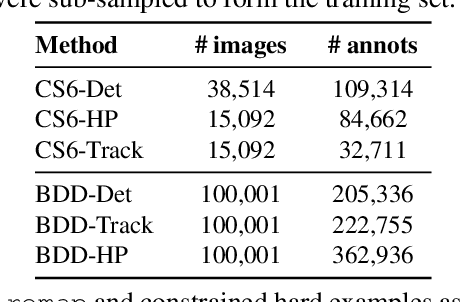
Aug 13, 2018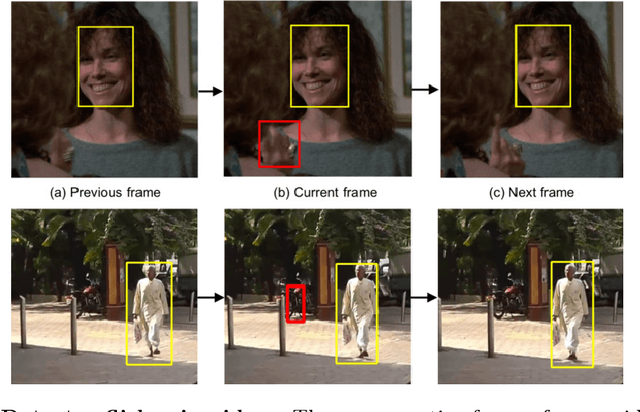


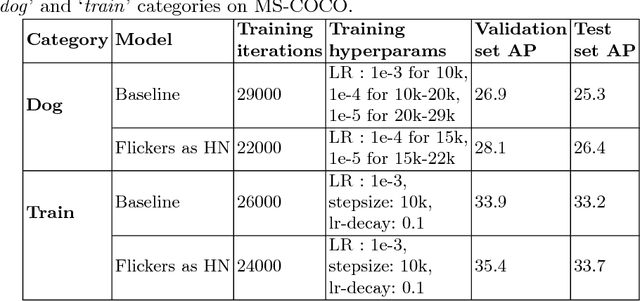
Abstract:Important gains have recently been obtained in object detection by using training objectives that focus on {\em hard negative} examples, i.e., negative examples that are currently rated as positive or ambiguous by the detector. These examples can strongly influence parameters when the network is trained to correct them. Unfortunately, they are often sparse in the training data, and are expensive to obtain. In this work, we show how large numbers of hard negatives can be obtained {\em automatically} by analyzing the output of a trained detector on video sequences. In particular, detections that are {\em isolated in time}, i.e., that have no associated preceding or following detections, are likely to be hard negatives. We describe simple procedures for mining large numbers of such hard negatives (and also hard {\em positives}) from unlabeled video data. Our experiments show that retraining detectors on these automatically obtained examples often significantly improves performance. We present experiments on multiple architectures and multiple data sets, including face detection, pedestrian detection and other object categories.
End-to-end Face Detection and Cast Grouping in Movies Using Erdős-Rényi Clustering
Sep 07, 2017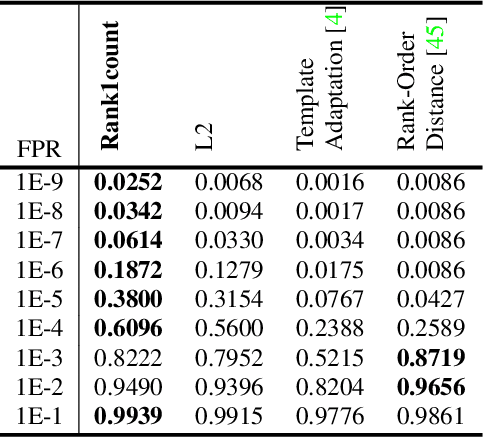

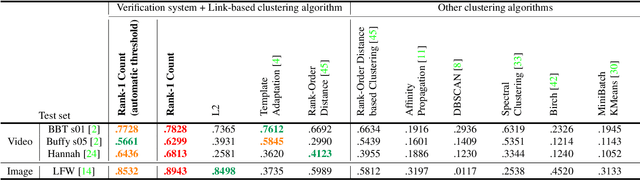
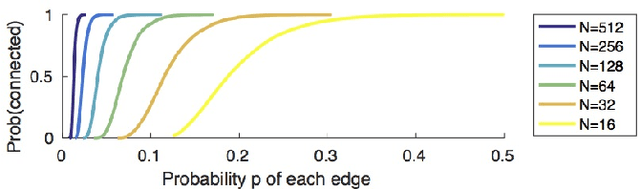
Abstract:We present an end-to-end system for detecting and clustering faces by identity in full-length movies. Unlike works that start with a predefined set of detected faces, we consider the end-to-end problem of detection and clustering together. We make three separate contributions. First, we combine a state-of-the-art face detector with a generic tracker to extract high quality face tracklets. We then introduce a novel clustering method, motivated by the classic graph theory results of Erd\H{o}s and R\'enyi. It is based on the observations that large clusters can be fully connected by joining just a small fraction of their point pairs, while just a single connection between two different people can lead to poor clustering results. This suggests clustering using a verification system with very few false positives but perhaps moderate recall. We introduce a novel verification method, rank-1 counts verification, that has this property, and use it in a link-based clustering scheme. Finally, we define a novel end-to-end detection and clustering evaluation metric allowing us to assess the accuracy of the entire end-to-end system. We present state-of-the-art results on multiple video data sets and also on standard face databases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge