Shuai He
NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image (T2I) generation model quality assessment, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2025. The aim of this challenge is to address the fine-grained quality assessment of text-to-image generation models. This challenge evaluates text-to-image models from two aspects: image-text alignment and image structural distortion detection, and is divided into the alignment track and the structural track. The alignment track uses the EvalMuse-40K, which contains around 40K AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) generated by 20 popular generative models. The alignment track has a total of 371 registered participants. A total of 1,883 submissions are received in the development phase, and 507 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 12 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. The structure track uses the EvalMuse-Structure, which contains 10,000 AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) with corresponding structural distortion mask. A total of 211 participants have registered in the structure track. A total of 1155 submissions are received in the development phase, and 487 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 8 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods in both tracks have demonstrated superior prediction performance on T2I model quality assessment.
Second FRCSyn-onGoing: Winning Solutions and Post-Challenge Analysis to Improve Face Recognition with Synthetic Data
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Synthetic data is gaining increasing popularity for face recognition technologies, mainly due to the privacy concerns and challenges associated with obtaining real data, including diverse scenarios, quality, and demographic groups, among others. It also offers some advantages over real data, such as the large amount of data that can be generated or the ability to customize it to adapt to specific problem-solving needs. To effectively use such data, face recognition models should also be specifically designed to exploit synthetic data to its fullest potential. In order to promote the proposal of novel Generative AI methods and synthetic data, and investigate the application of synthetic data to better train face recognition systems, we introduce the 2nd FRCSyn-onGoing challenge, based on the 2nd Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data (FRCSyn), originally launched at CVPR 2024. This is an ongoing challenge that provides researchers with an accessible platform to benchmark i) the proposal of novel Generative AI methods and synthetic data, and ii) novel face recognition systems that are specifically proposed to take advantage of synthetic data. We focus on exploring the use of synthetic data both individually and in combination with real data to solve current challenges in face recognition such as demographic bias, domain adaptation, and performance constraints in demanding situations, such as age disparities between training and testing, changes in the pose, or occlusions. Very interesting findings are obtained in this second edition, including a direct comparison with the first one, in which synthetic databases were restricted to DCFace and GANDiffFace.
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Short-form UGC Video Quality Assessment: Methods and Results
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Shortform UGC Video Quality Assessment (S-UGC VQA), where various excellent solutions are submitted and evaluated on the collected dataset KVQ from popular short-form video platform, i.e., Kuaishou/Kwai Platform. The KVQ database is divided into three parts, including 2926 videos for training, 420 videos for validation, and 854 videos for testing. The purpose is to build new benchmarks and advance the development of S-UGC VQA. The competition had 200 participants and 13 teams submitted valid solutions for the final testing phase. The proposed solutions achieved state-of-the-art performances for S-UGC VQA. The project can be found at https://github.com/lixinustc/KVQChallenge-CVPR-NTIRE2024.
Second Edition FRCSyn Challenge at CVPR 2024: Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data
Apr 16, 2024



Abstract:Synthetic data is gaining increasing relevance for training machine learning models. This is mainly motivated due to several factors such as the lack of real data and intra-class variability, time and errors produced in manual labeling, and in some cases privacy concerns, among others. This paper presents an overview of the 2nd edition of the Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data (FRCSyn) organized at CVPR 2024. FRCSyn aims to investigate the use of synthetic data in face recognition to address current technological limitations, including data privacy concerns, demographic biases, generalization to novel scenarios, and performance constraints in challenging situations such as aging, pose variations, and occlusions. Unlike the 1st edition, in which synthetic data from DCFace and GANDiffFace methods was only allowed to train face recognition systems, in this 2nd edition we propose new sub-tasks that allow participants to explore novel face generative methods. The outcomes of the 2nd FRCSyn Challenge, along with the proposed experimental protocol and benchmarking contribute significantly to the application of synthetic data to face recognition.
* arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2311.10476
Mask Reference Image Quality Assessment
Mar 19, 2023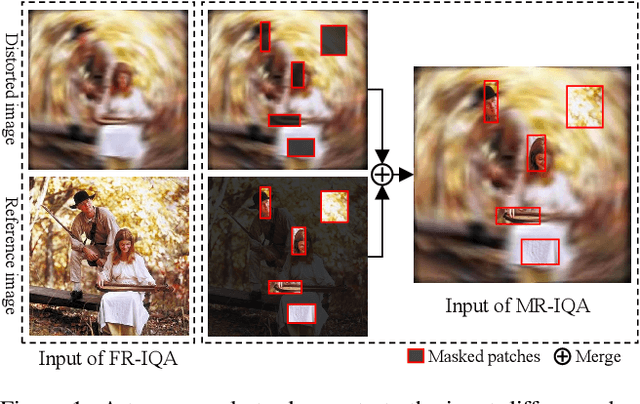
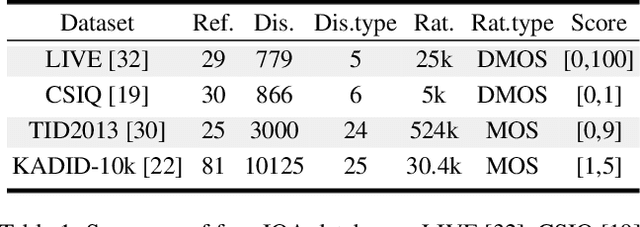
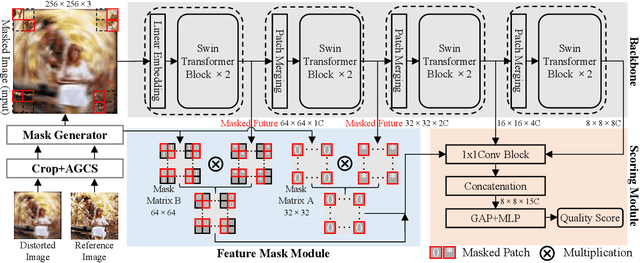
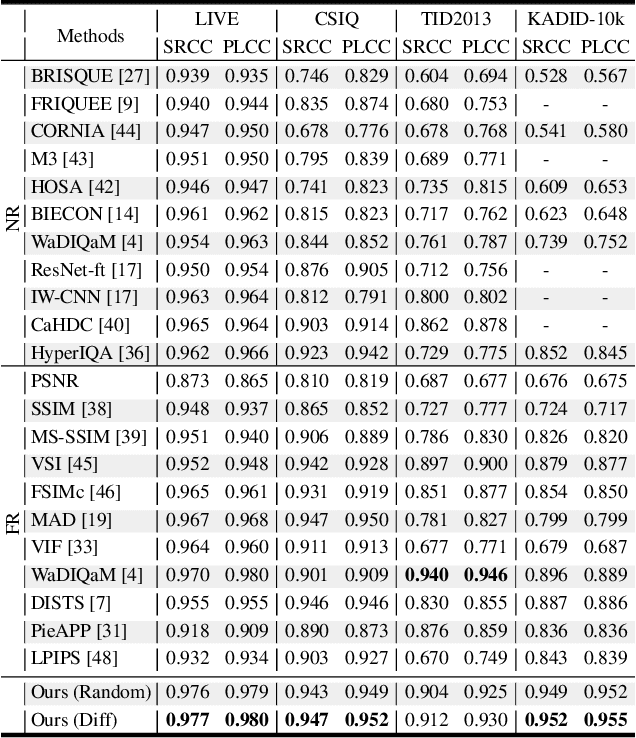
Abstract:Understanding semantic information is an essential step in knowing what is being learned in both full-reference (FR) and no-reference (NR) image quality assessment (IQA) methods. However, especially for many severely distorted images, even if there is an undistorted image as a reference (FR-IQA), it is difficult to perceive the lost semantic and texture information of distorted images directly. In this paper, we propose a Mask Reference IQA (MR-IQA) method that masks specific patches of a distorted image and supplements missing patches with the reference image patches. In this way, our model only needs to input the reconstructed image for quality assessment. First, we design a mask generator to select the best candidate patches from reference images and supplement the lost semantic information in distorted images, thus providing more reference for quality assessment; in addition, the different masked patches imply different data augmentations, which favors model training and reduces overfitting. Second, we provide a Mask Reference Network (MRNet): the dedicated modules can prevent disturbances due to masked patches and help eliminate the patch discontinuity in the reconstructed image. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performances on the benchmark KADID-10k, LIVE and CSIQ datasets and has better generalization performance across datasets. The code and results are available in the supplementary material.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge