Shiming Zhang
MC-MoE: Mixture Compressor for Mixture-of-Experts LLMs Gains More
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts large language models (MoE-LLMs) marks a significant step forward of language models, however, they encounter two critical challenges in practice: 1) expert parameters lead to considerable memory consumption and loading latency; and 2) the current activated experts are redundant, as many tokens may only require a single expert. Motivated by these issues, we investigate the MoE-LLMs and make two key observations: a) different experts exhibit varying behaviors on activation reconstruction error, routing scores, and activated frequencies, highlighting their differing importance, and b) not all tokens are equally important -- only a small subset is critical. Building on these insights, we propose MC-MoE, a training-free Mixture-Compressor for MoE-LLMs, which leverages the significance of both experts and tokens to achieve an extreme compression. First, to mitigate storage and loading overheads, we introduce Pre-Loading Mixed-Precision Quantization, which formulates the adaptive bit-width allocation as a Linear Programming problem, where the objective function balances multi-factors reflecting the importance of each expert. Additionally, we develop Online Dynamic Pruning, which identifies important tokens to retain and dynamically select activated experts for other tokens during inference to optimize efficiency while maintaining performance. Our MC-MoE integrates static quantization and dynamic pruning to collaboratively achieve extreme compression for MoE-LLMs with less accuracy loss, ensuring an optimal trade-off between performance and efficiency. Extensive experiments confirm the effectiveness of our approach. For instance, at 2.54 bits, MC-MoE compresses 76.6% of the model, with only a 3.8% average accuracy loss. During dynamic inference, we further reduce activated parameters by 15%, with a performance drop of less than 0.6%.
Continual Learning for Smart City: A Survey
Apr 01, 2024Abstract:With the digitization of modern cities, large data volumes and powerful computational resources facilitate the rapid update of intelligent models deployed in smart cities. Continual learning (CL) is a novel machine learning paradigm that constantly updates models to adapt to changing environments, where the learning tasks, data, and distributions can vary over time. Our survey provides a comprehensive review of continual learning methods that are widely used in smart city development. The content consists of three parts: 1) Methodology-wise. We categorize a large number of basic CL methods and advanced CL frameworks in combination with other learning paradigms including graph learning, spatial-temporal learning, multi-modal learning, and federated learning. 2) Application-wise. We present numerous CL applications covering transportation, environment, public health, safety, networks, and associated datasets related to urban computing. 3) Challenges. We discuss current problems and challenges and envision several promising research directions. We believe this survey can help relevant researchers quickly familiarize themselves with the current state of continual learning research used in smart city development and direct them to future research trends.
A Survey of Route Recommendations: Methods, Applications, and Opportunities
Mar 01, 2024



Abstract:Nowadays, with advanced information technologies deployed citywide, large data volumes and powerful computational resources are intelligentizing modern city development. As an important part of intelligent transportation, route recommendation and its applications are widely used, directly influencing citizens` travel habits. Developing smart and efficient travel routes based on big data (possibly multi-modal) has become a central challenge in route recommendation research. Our survey offers a comprehensive review of route recommendation work based on urban computing. It is organized by the following three parts: 1) Methodology-wise. We categorize a large volume of traditional machine learning and modern deep learning methods. Also, we discuss their historical relations and reveal the edge-cutting progress. 2) Application\-wise. We present numerous novel applications related to route commendation within urban computing scenarios. 3) We discuss current problems and challenges and envision several promising research directions. We believe that this survey can help relevant researchers quickly familiarize themselves with the current state of route recommendation research and then direct them to future research trends.
BiLLM: Pushing the Limit of Post-Training Quantization for LLMs
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Pretrained large language models (LLMs) exhibit exceptional general language processing capabilities but come with significant demands on memory and computational resources. As a powerful compression technology, binarization can extremely reduce model weights to a mere 1 bit, lowering the expensive computation and memory requirements. However, existing quantization techniques fall short of maintaining LLM performance under ultra-low bit-widths. In response to this challenge, we present BiLLM, a groundbreaking 1-bit post-training quantization scheme tailored for pretrained LLMs. Based on the weight distribution of LLMs, BiLLM first identifies and structurally selects salient weights, and minimizes the compression loss through an effective binary residual approximation strategy. Moreover, considering the bell-shaped distribution of the non-salient weights, we propose an optimal splitting search to group and binarize them accurately. BiLLM achieving for the first time high-accuracy inference (e.g. 8.41 perplexity on LLaMA2-70B) with only 1.08-bit weights across various LLMs families and evaluation metrics, outperforms SOTA quantization methods of LLM by significant margins. Moreover, BiLLM enables the binarization process of the LLM with 7 billion weights within 0.5 hours on a single GPU, demonstrating satisfactory time efficiency.
Pruning random resistive memory for optimizing analogue AI
Nov 13, 2023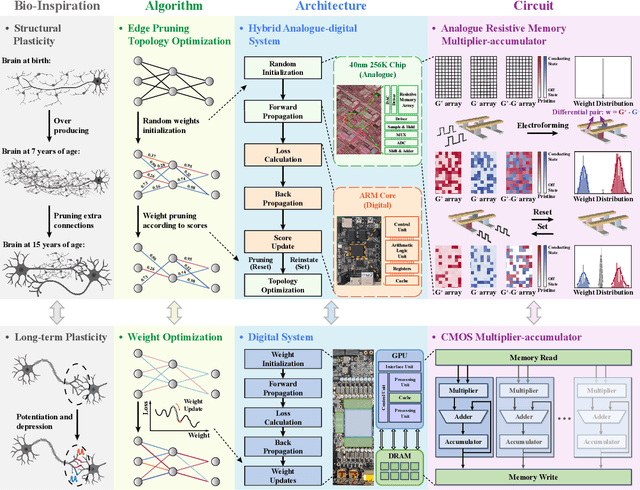
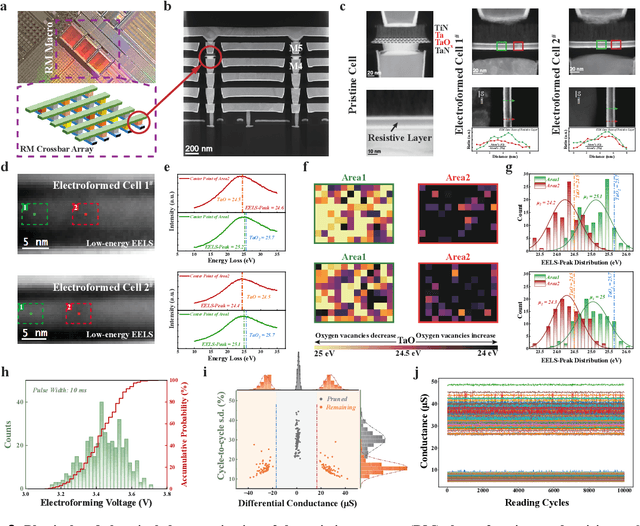
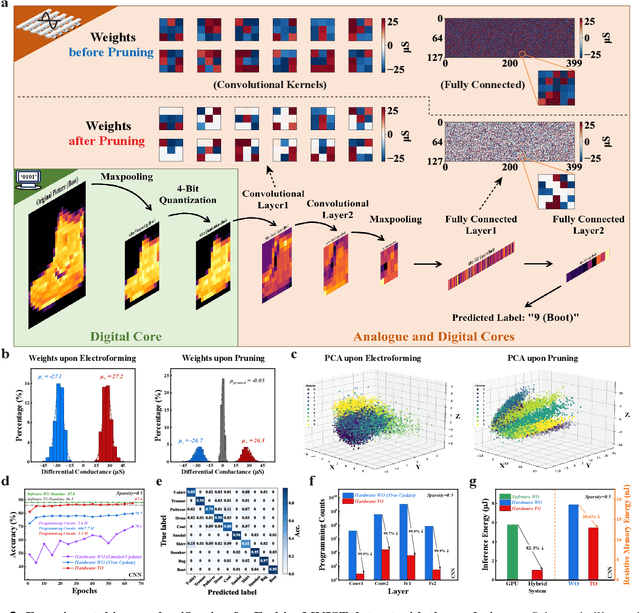
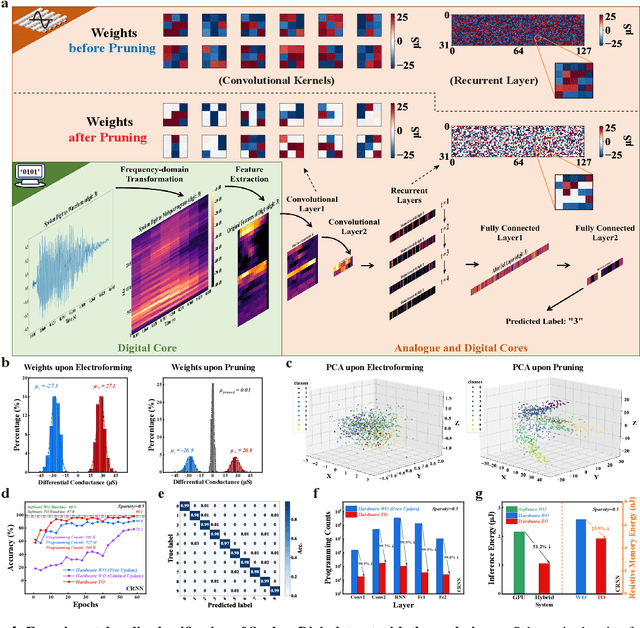
Abstract:The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has been marked by the large language models exhibiting human-like intelligence. However, these models also present unprecedented challenges to energy consumption and environmental sustainability. One promising solution is to revisit analogue computing, a technique that predates digital computing and exploits emerging analogue electronic devices, such as resistive memory, which features in-memory computing, high scalability, and nonvolatility. However, analogue computing still faces the same challenges as before: programming nonidealities and expensive programming due to the underlying devices physics. Here, we report a universal solution, software-hardware co-design using structural plasticity-inspired edge pruning to optimize the topology of a randomly weighted analogue resistive memory neural network. Software-wise, the topology of a randomly weighted neural network is optimized by pruning connections rather than precisely tuning resistive memory weights. Hardware-wise, we reveal the physical origin of the programming stochasticity using transmission electron microscopy, which is leveraged for large-scale and low-cost implementation of an overparameterized random neural network containing high-performance sub-networks. We implemented the co-design on a 40nm 256K resistive memory macro, observing 17.3% and 19.9% accuracy improvements in image and audio classification on FashionMNIST and Spoken digits datasets, as well as 9.8% (2%) improvement in PR (ROC) in image segmentation on DRIVE datasets, respectively. This is accompanied by 82.1%, 51.2%, and 99.8% improvement in energy efficiency thanks to analogue in-memory computing. By embracing the intrinsic stochasticity and in-memory computing, this work may solve the biggest obstacle of analogue computing systems and thus unleash their immense potential for next-generation AI hardware.
Deep Learning in Ultrasound Elastography Imaging
Oct 31, 2020



Abstract:It is known that changes in the mechanical properties of tissues are associated with the onset and progression of certain diseases. Ultrasound elastography is a technique to characterize tissue stiffness using ultrasound imaging either by measuring tissue strain using quasi-static elastography or natural organ pulsation elastography, or by tracing a propagated shear wave induced by a source or a natural vibration using dynamic elastography. In recent years, deep learning has begun to emerge in ultrasound elastography research. In this review, several common deep learning frameworks in the computer vision community, such as multilayer perceptron, convolutional neural network, and recurrent neural network are described. Then, recent advances in ultrasound elastography using such deep learning techniques are revisited in terms of algorithm development and clinical diagnosis. Finally, the current challenges and future developments of deep learning in ultrasound elastography are prospected.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge