Shibiao Xu
SE-EE Tradeoff in Pinching-Antenna Systems: Waveguide Multiplexing or Waveguide Switching?
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:The spectral and energy efficiency (SE-EE) trade-off in pinching-antenna systems (PASS) is investigated in this paper. In particular, two practical operating protocols, namely waveguide multiplexing (WM) and waveguide switching (WS), are considered. A multi-objective optimization problem (MOOP) is formulated to jointly optimize the baseband and pinching beamforming for maximizing the achievable SE and EE, which is then converted into a single-objective problem via the ε-constraint method. For WM, the problem is decomposed within the alternating-optimization framework, where the baseband beamforming is optimized using the successive convex approximation, and the pinching beamforming is updated through the particle swarm optimization. For WS, due to the time-division transmission and interference-free nature, the pinching beamforming in each time slot is first adjusted to maximize the served user channel gain, followed by the baseband power allocation. Simulation results demonstrate that 1) PASS outperforms conventional antennas by mitigating large-scale path losses; 2) WS leads to a higher maximum achievable EE by activating a single RF chain, whereas WM yields a higher SE upper bound by serving all users concurrently; and 3) increasing the number of users substantially enhances SE under WM, whereas WS shows more pronounced benefits in low-signal-to-noise ratio regimes.
CurriFlow: Curriculum-Guided Depth Fusion with Optical Flow-Based Temporal Alignment for 3D Semantic Scene Completion
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Semantic Scene Completion (SSC) aims to infer complete 3D geometry and semantics from monocular images, serving as a crucial capability for camera-based perception in autonomous driving. However, existing SSC methods relying on temporal stacking or depth projection often lack explicit motion reasoning and struggle with occlusions and noisy depth supervision. We propose CurriFlow, a novel semantic occupancy prediction framework that integrates optical flow-based temporal alignment with curriculum-guided depth fusion. CurriFlow employs a multi-level fusion strategy to align segmentation, visual, and depth features across frames using pre-trained optical flow, thereby improving temporal consistency and dynamic object understanding. To enhance geometric robustness, a curriculum learning mechanism progressively transitions from sparse yet accurate LiDAR depth to dense but noisy stereo depth during training, ensuring stable optimization and seamless adaptation to real-world deployment. Furthermore, semantic priors from the Segment Anything Model (SAM) provide category-agnostic supervision, strengthening voxel-level semantic learning and spatial consistency. Experiments on the SemanticKITTI benchmark demonstrate that CurriFlow achieves state-of-the-art performance with a mean IoU of 16.9, validating the effectiveness of our motion-guided and curriculum-aware design for camera-based 3D semantic scene completion.
3D-MoRe: Unified Modal-Contextual Reasoning for Embodied Question Answering
Jul 16, 2025
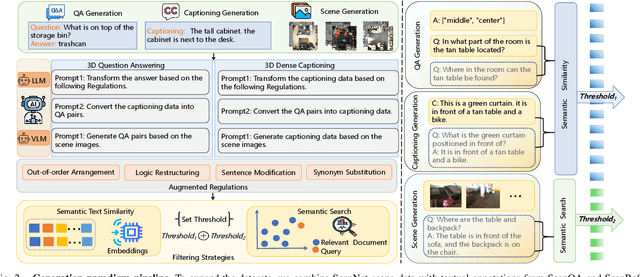


Abstract:With the growing need for diverse and scalable data in indoor scene tasks, such as question answering and dense captioning, we propose 3D-MoRe, a novel paradigm designed to generate large-scale 3D-language datasets by leveraging the strengths of foundational models. The framework integrates key components, including multi-modal embedding, cross-modal interaction, and a language model decoder, to process natural language instructions and 3D scene data. This approach facilitates enhanced reasoning and response generation in complex 3D environments. Using the ScanNet 3D scene dataset, along with text annotations from ScanQA and ScanRefer, 3D-MoRe generates 62,000 question-answer (QA) pairs and 73,000 object descriptions across 1,513 scenes. We also employ various data augmentation techniques and implement semantic filtering to ensure high-quality data. Experiments on ScanQA demonstrate that 3D-MoRe significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, with the CIDEr score improving by 2.15\%. Similarly, on ScanRefer, our approach achieves a notable increase in CIDEr@0.5 by 1.84\%, highlighting its effectiveness in both tasks. Our code and generated datasets will be publicly released to benefit the community, and both can be accessed on the https://3D-MoRe.github.io.
SAMamba: Adaptive State Space Modeling with Hierarchical Vision for Infrared Small Target Detection
May 29, 2025Abstract:Infrared small target detection (ISTD) is vital for long-range surveillance in military, maritime, and early warning applications. ISTD is challenged by targets occupying less than 0.15% of the image and low distinguishability from complex backgrounds. Existing deep learning methods often suffer from information loss during downsampling and inefficient global context modeling. This paper presents SAMamba, a novel framework integrating SAM2's hierarchical feature learning with Mamba's selective sequence modeling. Key innovations include: (1) A Feature Selection Adapter (FS-Adapter) for efficient natural-to-infrared domain adaptation via dual-stage selection (token-level with a learnable task embedding and channel-wise adaptive transformations); (2) A Cross-Channel State-Space Interaction (CSI) module for efficient global context modeling with linear complexity using selective state space modeling; and (3) A Detail-Preserving Contextual Fusion (DPCF) module that adaptively combines multi-scale features with a gating mechanism to balance high-resolution and low-resolution feature contributions. SAMamba addresses core ISTD challenges by bridging the domain gap, maintaining fine-grained details, and efficiently modeling long-range dependencies. Experiments on NUAA-SIRST, IRSTD-1k, and NUDT-SIRST datasets show SAMamba significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, especially in challenging scenarios with heterogeneous backgrounds and varying target scales. Code: https://github.com/zhengshuchen/SAMamba.
Movable-Element STARS-Assisted Near-Field Wideband Communications
May 25, 2025Abstract:A novel movable-element simultaneously transmitting and reflecting surface (ME-STARS)-assisted near-field wideband communication framework is proposed. In particular, the position of each STARS element can be adjusted to combat the significant wideband beam squint issue in the near field instead of using costly true-time delay components. Four practical ME-STARS element movement modes are proposed, namely region-based (RB), horizontal-based (HB), vertical-based (VB), and diagonal-based (DB) modes. Based on this, a near-field wideband multi-user downlink communication scenario is considered, where a sum rate maximization problem is formulated by jointly optimizing the base station (BS) precoding, ME-STARS beamforming, and element positions. To solve this intractable problem, a two-layer algorithm is developed. For the inner layer, the block coordinate descent optimization framework is utilized to solve the BS precoding and ME-STARS beamforming in an iterative manner. For the outer layer, the particle swarm optimization-based heuristic search method is employed to determine the desired element positions. Numerical results show that:1) the ME-STARSs can effectively address the beam squint for near-field wideband communications compared to conventional STARSs with fixed element positions; 2) the RB mode achieves the most efficient beam squint effect mitigation, while the DB mode achieves the best trade-off between performance gain and hardware overhead; and 3) an increase in the number of ME-STARS elements or BS subcarriers substantially improves the system performance.
FDBPL: Faster Distillation-Based Prompt Learning for Region-Aware Vision-Language Models Adaptation
May 23, 2025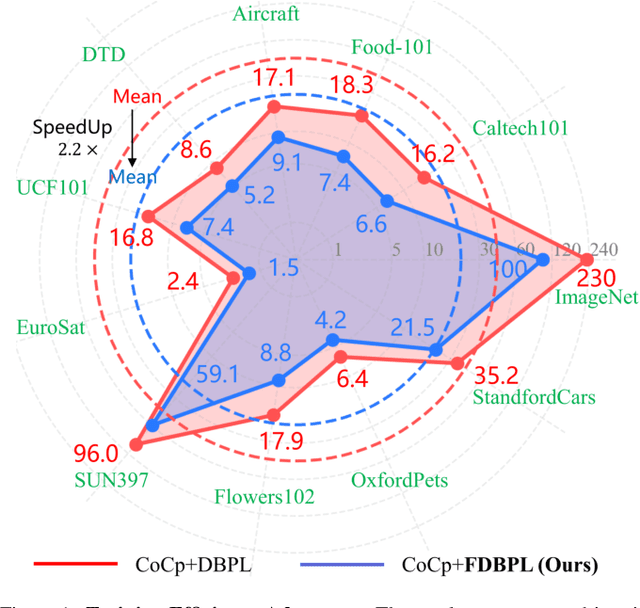
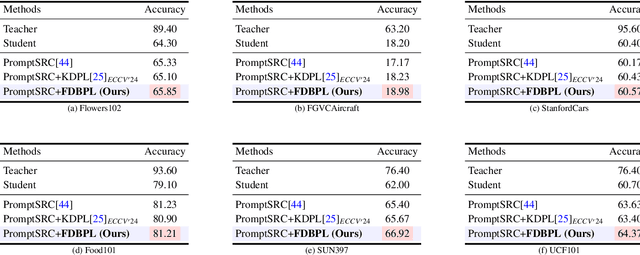
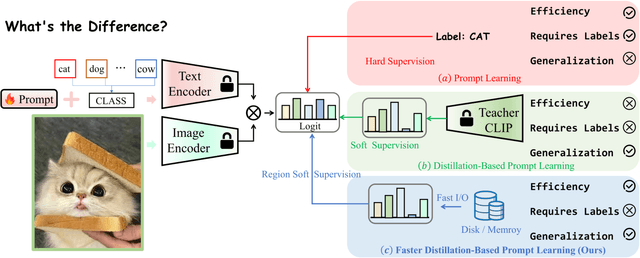
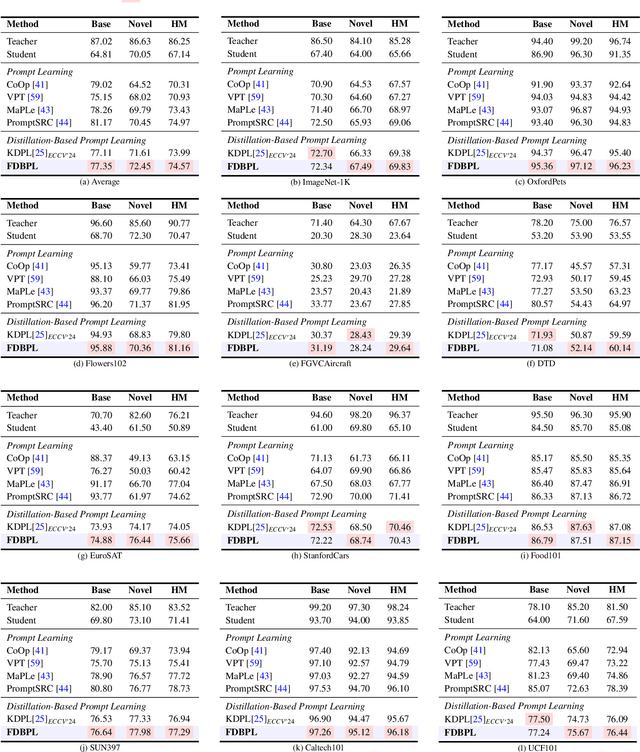
Abstract:Prompt learning as a parameter-efficient method that has been widely adopted to adapt Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to downstream tasks. While hard-prompt design requires domain expertise and iterative optimization, soft-prompt methods rely heavily on task-specific hard labels, limiting their generalization to unseen categories. Recent popular distillation-based prompt learning methods improve generalization by exploiting larger teacher VLMs and unsupervised knowledge transfer, yet their repetitive teacher model online inference sacrifices the inherent training efficiency advantage of prompt learning. In this paper, we propose {{\large {\textbf{F}}}}aster {{\large {\textbf{D}}}}istillation-{{\large {\textbf{B}}}}ased {{\large {\textbf{P}}}}rompt {{\large {\textbf{L}}}}earning (\textbf{FDBPL}), which addresses these issues by sharing soft supervision contexts across multiple training stages and implementing accelerated I/O. Furthermore, FDBPL introduces a region-aware prompt learning paradigm with dual positive-negative prompt spaces to fully exploit randomly cropped regions that containing multi-level information. We propose a positive-negative space mutual learning mechanism based on similarity-difference learning, enabling student CLIP models to recognize correct semantics while learning to reject weakly related concepts, thereby improving zero-shot performance. Unlike existing distillation-based prompt learning methods that sacrifice parameter efficiency for generalization, FDBPL maintains dual advantages of parameter efficiency and strong downstream generalization. Comprehensive evaluations across 11 datasets demonstrate superior performance in base-to-new generalization, cross-dataset transfer, and robustness tests, achieving $2.2\times$ faster training speed.
Image Recognition with Online Lightweight Vision Transformer: A Survey
May 06, 2025Abstract:The Transformer architecture has achieved significant success in natural language processing, motivating its adaptation to computer vision tasks. Unlike convolutional neural networks, vision transformers inherently capture long-range dependencies and enable parallel processing, yet lack inductive biases and efficiency benefits, facing significant computational and memory challenges that limit its real-world applicability. This paper surveys various online strategies for generating lightweight vision transformers for image recognition, focusing on three key areas: Efficient Component Design, Dynamic Network, and Knowledge Distillation. We evaluate the relevant exploration for each topic on the ImageNet-1K benchmark, analyzing trade-offs among precision, parameters, throughput, and more to highlight their respective advantages, disadvantages, and flexibility. Finally, we propose future research directions and potential challenges in the lightweighting of vision transformers with the aim of inspiring further exploration and providing practical guidance for the community. Project Page: https://github.com/ajxklo/Lightweight-VIT
CAE-DFKD: Bridging the Transferability Gap in Data-Free Knowledge Distillation
Apr 30, 2025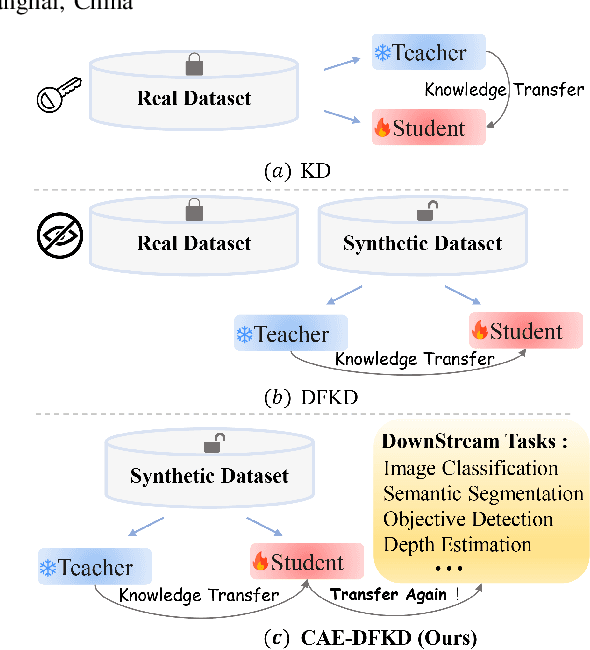
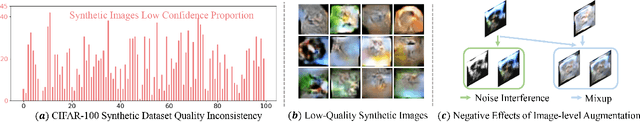
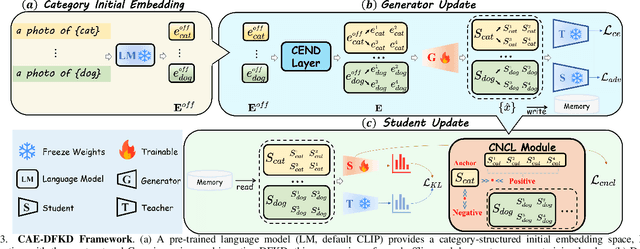
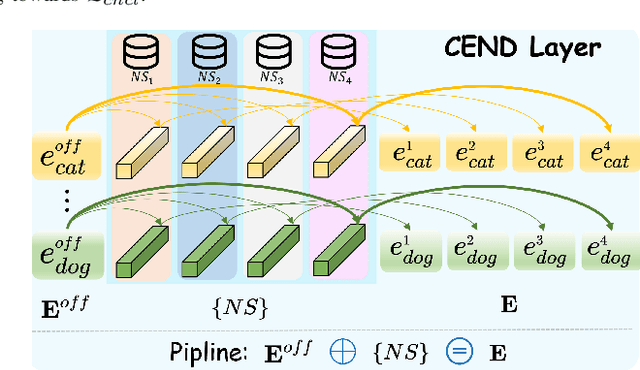
Abstract:Data-Free Knowledge Distillation (DFKD) enables the knowledge transfer from the given pre-trained teacher network to the target student model without access to the real training data. Existing DFKD methods focus primarily on improving image recognition performance on associated datasets, often neglecting the crucial aspect of the transferability of learned representations. In this paper, we propose Category-Aware Embedding Data-Free Knowledge Distillation (CAE-DFKD), which addresses at the embedding level the limitations of previous rely on image-level methods to improve model generalization but fail when directly applied to DFKD. The superiority and flexibility of CAE-DFKD are extensively evaluated, including: \textit{\textbf{i.)}} Significant efficiency advantages resulting from altering the generator training paradigm; \textit{\textbf{ii.)}} Competitive performance with existing DFKD state-of-the-art methods on image recognition tasks; \textit{\textbf{iii.)}} Remarkable transferability of data-free learned representations demonstrated in downstream tasks.
Pinching-Antenna Systems (PASS)-enabled Secure Wireless Communications
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:A novel pinching-antenna systems (PASS)-enabled secure wireless communication framework is proposed. By dynamically adjusting the positions of dielectric particles, namely pinching antennas (PAs), along the waveguides, PASS introduces a novel concept of pinching beamforming to enhance the performance of physical layer security. A fundamental PASS-enabled secure communication system is considered with one legitimate user and one eavesdropper. Both single-waveguide and multiple-waveguide scenarios are studied. 1) For the single-waveguide scenario, the secrecy rate (SR) maximization is formulated to optimize the pinching beamforming. A PA-wise successive tuning (PAST) algorithm is proposed, which ensures constructive signal superposition at the legitimate user while inducing a destructive legitimate signal at the eavesdropper. 2) For the multiple-waveguide scenario, artificial noise (AN) is employed to further improve secrecy performance. A pair of practical transmission architectures are developed: waveguide division (WD) and waveguide multiplexing (WM). The key difference lies in whether each waveguide carries a single type of signal or a mixture of signals with baseband beamforming. For the SR maximization problem under the WD case, a two-stage algorithm is developed, where the pinching beamforming is designed with the PAST algorithm and the baseband power allocation among AN and legitimate signals is solved using successive convex approximation (SCA). For the WM case, an alternating optimization algorithm is developed, where the baseband beamforming is optimized with SCA and the pinching beamforming is designed employing particle swarm optimization.
Focus on Local: Finding Reliable Discriminative Regions for Visual Place Recognition
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Visual Place Recognition (VPR) is aimed at predicting the location of a query image by referencing a database of geotagged images. For VPR task, often fewer discriminative local regions in an image produce important effects while mundane background regions do not contribute or even cause perceptual aliasing because of easy overlap. However, existing methods lack precisely modeling and full exploitation of these discriminative regions. In this paper, we propose the Focus on Local (FoL) approach to stimulate the performance of image retrieval and re-ranking in VPR simultaneously by mining and exploiting reliable discriminative local regions in images and introducing pseudo-correlation supervision. First, we design two losses, Extraction-Aggregation Spatial Alignment Loss (SAL) and Foreground-Background Contrast Enhancement Loss (CEL), to explicitly model reliable discriminative local regions and use them to guide the generation of global representations and efficient re-ranking. Second, we introduce a weakly-supervised local feature training strategy based on pseudo-correspondences obtained from aggregating global features to alleviate the lack of local correspondences ground truth for the VPR task. Third, we suggest an efficient re-ranking pipeline that is efficiently and precisely based on discriminative region guidance. Finally, experimental results show that our FoL achieves the state-of-the-art on multiple VPR benchmarks in both image retrieval and re-ranking stages and also significantly outperforms existing two-stage VPR methods in terms of computational efficiency. Code and models are available at https://github.com/chenshunpeng/FoL
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge