Guangyu Zhu
SE-EE Tradeoff in Pinching-Antenna Systems: Waveguide Multiplexing or Waveguide Switching?
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:The spectral and energy efficiency (SE-EE) trade-off in pinching-antenna systems (PASS) is investigated in this paper. In particular, two practical operating protocols, namely waveguide multiplexing (WM) and waveguide switching (WS), are considered. A multi-objective optimization problem (MOOP) is formulated to jointly optimize the baseband and pinching beamforming for maximizing the achievable SE and EE, which is then converted into a single-objective problem via the ε-constraint method. For WM, the problem is decomposed within the alternating-optimization framework, where the baseband beamforming is optimized using the successive convex approximation, and the pinching beamforming is updated through the particle swarm optimization. For WS, due to the time-division transmission and interference-free nature, the pinching beamforming in each time slot is first adjusted to maximize the served user channel gain, followed by the baseband power allocation. Simulation results demonstrate that 1) PASS outperforms conventional antennas by mitigating large-scale path losses; 2) WS leads to a higher maximum achievable EE by activating a single RF chain, whereas WM yields a higher SE upper bound by serving all users concurrently; and 3) increasing the number of users substantially enhances SE under WM, whereas WS shows more pronounced benefits in low-signal-to-noise ratio regimes.
Movable-Element STARS-Assisted Near-Field Wideband Communications
May 25, 2025Abstract:A novel movable-element simultaneously transmitting and reflecting surface (ME-STARS)-assisted near-field wideband communication framework is proposed. In particular, the position of each STARS element can be adjusted to combat the significant wideband beam squint issue in the near field instead of using costly true-time delay components. Four practical ME-STARS element movement modes are proposed, namely region-based (RB), horizontal-based (HB), vertical-based (VB), and diagonal-based (DB) modes. Based on this, a near-field wideband multi-user downlink communication scenario is considered, where a sum rate maximization problem is formulated by jointly optimizing the base station (BS) precoding, ME-STARS beamforming, and element positions. To solve this intractable problem, a two-layer algorithm is developed. For the inner layer, the block coordinate descent optimization framework is utilized to solve the BS precoding and ME-STARS beamforming in an iterative manner. For the outer layer, the particle swarm optimization-based heuristic search method is employed to determine the desired element positions. Numerical results show that:1) the ME-STARSs can effectively address the beam squint for near-field wideband communications compared to conventional STARSs with fixed element positions; 2) the RB mode achieves the most efficient beam squint effect mitigation, while the DB mode achieves the best trade-off between performance gain and hardware overhead; and 3) an increase in the number of ME-STARS elements or BS subcarriers substantially improves the system performance.
Pinching-Antenna Systems (PASS)-enabled Secure Wireless Communications
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:A novel pinching-antenna systems (PASS)-enabled secure wireless communication framework is proposed. By dynamically adjusting the positions of dielectric particles, namely pinching antennas (PAs), along the waveguides, PASS introduces a novel concept of pinching beamforming to enhance the performance of physical layer security. A fundamental PASS-enabled secure communication system is considered with one legitimate user and one eavesdropper. Both single-waveguide and multiple-waveguide scenarios are studied. 1) For the single-waveguide scenario, the secrecy rate (SR) maximization is formulated to optimize the pinching beamforming. A PA-wise successive tuning (PAST) algorithm is proposed, which ensures constructive signal superposition at the legitimate user while inducing a destructive legitimate signal at the eavesdropper. 2) For the multiple-waveguide scenario, artificial noise (AN) is employed to further improve secrecy performance. A pair of practical transmission architectures are developed: waveguide division (WD) and waveguide multiplexing (WM). The key difference lies in whether each waveguide carries a single type of signal or a mixture of signals with baseband beamforming. For the SR maximization problem under the WD case, a two-stage algorithm is developed, where the pinching beamforming is designed with the PAST algorithm and the baseband power allocation among AN and legitimate signals is solved using successive convex approximation (SCA). For the WM case, an alternating optimization algorithm is developed, where the baseband beamforming is optimized with SCA and the pinching beamforming is designed employing particle swarm optimization.
Pinching-Antenna System (PASS)-enabled Multicast Communications
Feb 23, 2025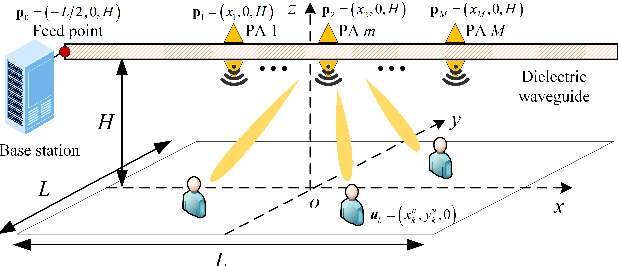
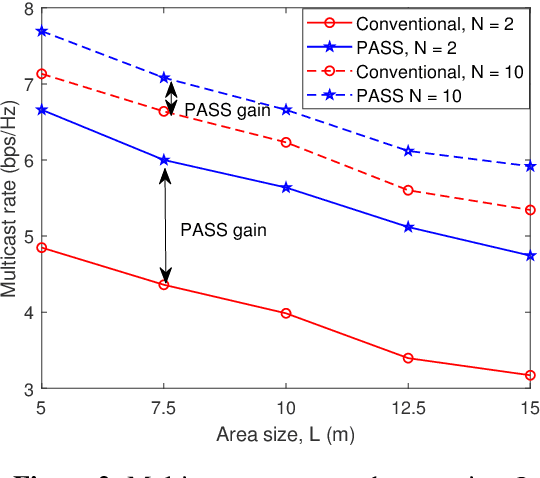
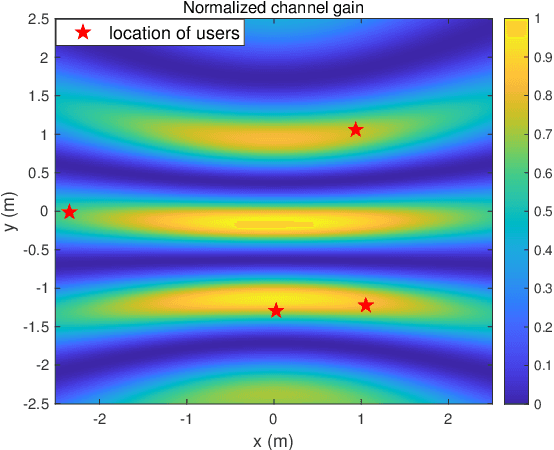
Abstract:Pinching-antenna system (PASS) is a novel flexible-antenna technology, which employs long-spread waveguides to convey signals with negligible path loss and pinching antennas (PAs) with adjustable positions to radiate signals from the waveguide into the free space. Therefore, short-distance and strong line-of-sight transmission can be established. In this paper, a novel PASS-enabled multicast communication framework is proposed, where multiple PAs on a single waveguide radiate the broadcast signals to multiple users. The multicast performance maximization problem is formulated to optimize the positions of all PAs. To address this non-convex problem, a particle swarm optimization-based algorithm is developed. Numerical results show that PASS can significantly outperform the conventional multiple-antenna transmission.
STAR-RIS Assisted SWIPT Systems: Active or Passive?
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:A simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surface (STAR-RIS) assisted simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT) system is investigated. Both active and passive STAR-RISs are considered. Passive STAR-RISs can be cost-efficiently fabricated to large aperture sizes with significant near-field regions, but the design flexibility is limited by the coupled phase-shifts. Active STAR-RISs can further amplify signals and have independent phase-shifts, but their aperture sizes are relatively small due to the high cost. To characterize and compare their performance, a power consumption minimization problem is formulated by jointly designing the beamforming at the access point (AP) and the STAR-RIS, subject to both the power and information quality-of-service requirements. To solve the resulting highly-coupled non-convex problem, the original problem is first decomposed into simpler subproblems and then an alternating optimization framework is proposed. For the passive STAR-RIS, the coupled phase-shift constraint is tackled by employing a vector-driven weight penalty method. While for the active STAR-RIS, the independent phase-shift is optimized with AP beamforming via matrix-driven semidefinite programming, and the amplitude matrix is updated using convex optimization techniques in each iteration. Numerical results show that: 1) given the same aperture sizes, the active STAR-RIS exhibits superior performance over the passive one when the aperture size is small, but the performance gap decreases with the increase in aperture size; and 2) given identical power budgets, the passive STAR-RIS is generally preferred, whereas the active STAR-RIS typically suffers performance loss for balancing between the hardware power and the amplification power.
Enhancing User Fairness in Wireless Powered Communication Networks with STAR-RIS
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:A simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surface (STAR-RIS) assisted wireless powered communication network (WPCN) is proposed, where two energy-limited devices first harvest energy from a hybrid access point (HAP) and then use that energy to transmit information back. To fully eliminate the doubly-near-far effect in WPCNs, two STAR-RIS operating protocol-driven transmission strategies, namely energy splitting non-orthogonal multiple access (ES- NOMA) and time switching time division multiple access (TS- TDMA) are proposed. For each strategy, the corresponding optimization problem is formulated to maximize the minimum throughput by jointly optimizing time allocation, user transmit power, active HAP beamforming, and passive STAR-RIS beamforming. For ES-NOMA, the resulting intractable problem is solved via a two-layer algorithm, which exploits the one-dimensional search and block coordinate descent methods in an iterative manner. For TS-TDMA, the optimal active beamforming and passive beamforming are first determined according to the maximum-ratio transmission beamformer. Then, the optimal solution of the time allocation variables is obtained by solving a standard convex problem. Numerical results show that: 1) the STAR-RIS can achieve considerable performance improvements for both strategies compared to the conventional RIS; 2) TS- TDMA is preferred for single-antenna scenarios, whereas ES- NOMA is better suited for multi-antenna scenarios; and 3) the superiority of ES-NOMA over TS-TDMA is enhanced as the number of STAR-RIS elements increases.
Robust Resource Allocation for STAR-RIS Assisted SWIPT Systems
Mar 22, 2024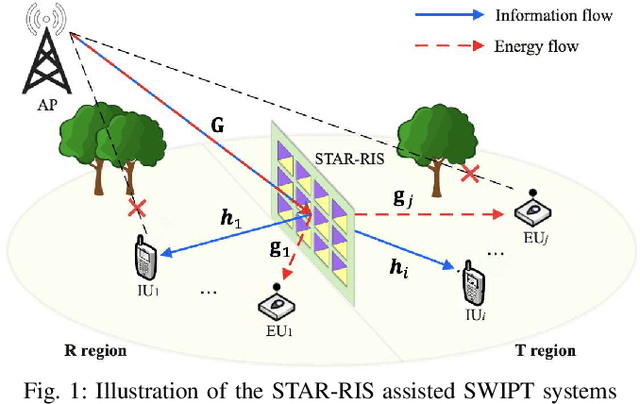
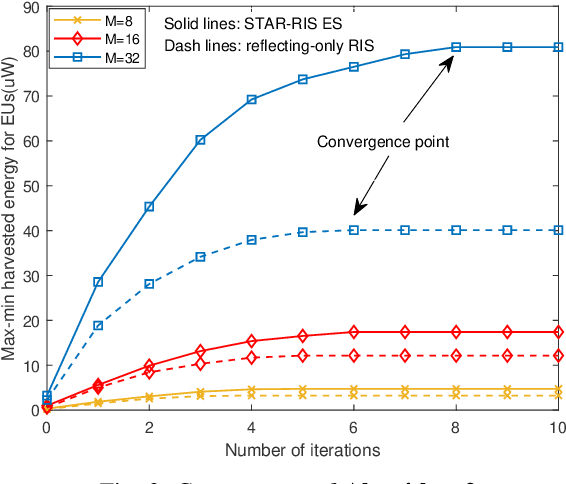
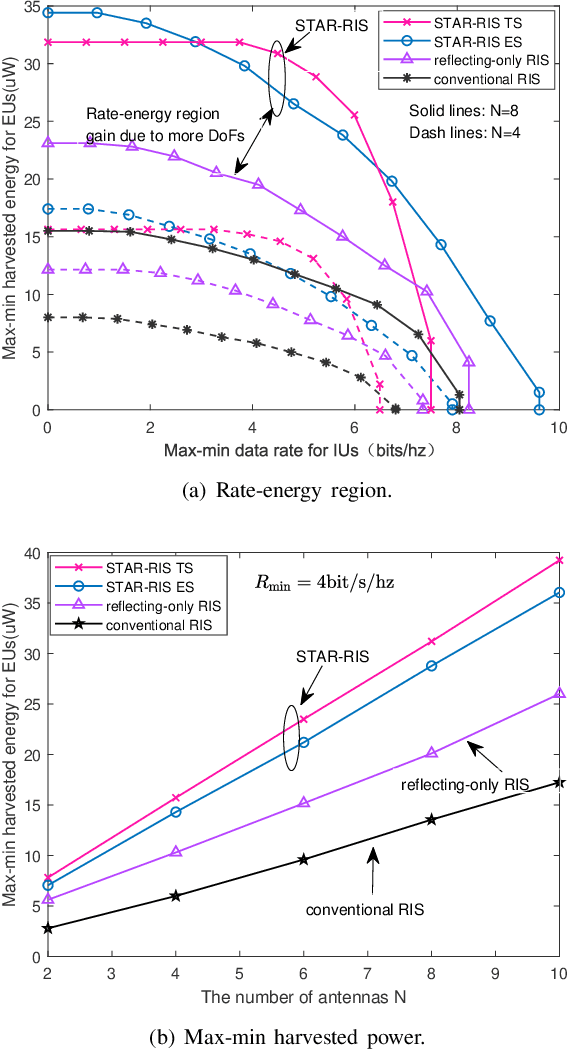
Abstract:A simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surface (STAR-RIS) assisted simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT) system is proposed. More particularly, an STAR-RIS is deployed to assist in the information/power transfer from a multi-antenna access point (AP) to multiple single-antenna information users (IUs) and energy users (EUs), where two practical STAR-RIS operating protocols, namely energy splitting (ES) and time switching (TS), are employed. Under the imperfect channel state information (CSI) condition, a multi-objective optimization problem (MOOP) framework, that simultaneously maximizes the minimum data rate and minimum harvested power, is employed to investigate the fundamental rate-energy trade-off between IUs and EUs. To obtain the optimal robust resource allocation strategy, the MOOP is first transformed into a single-objective optimization problem (SOOP) via the {\epsilon}-constraint method, which is then reformulated by approximating semi-infinite inequality constraints with the S-procedure. For ES, an alternating optimization (AO)-based algorithm is proposed to jointly design AP active beamforming and STAR-RIS passive beamforming, where a penalty method is leveraged in STAR-RIS beamforming design. Furthermore, the developed algorithm is extended to optimize the time allocation policy and beamforming vectors in a two-layer iterative manner for TS. Numerical results reveal that: 1) deploying STAR-RISs achieves a significant performance gain over conventional RISs, especially in terms of harvested power for EUs; 2) the ES protocol obtains a better user fairness performance when focusing only on IUs or EUs, while the TS protocol yields a better balance between IUs and EUs; 3) the imperfect CSI affects IUs more significantly than EUs, whereas TS can confer a more robust design to attenuate these effects.
Hybrid Active-Passive RIS Transmitter Enabled Energy-Efficient Multi-User Communications
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:A novel hybrid active-passive reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) transmitter enabled downlink multi-user communication system is investigated. Specifically, RISs are exploited to serve as transmitter antennas, where each element can flexibly switch between active and passive modes to deliver information to multiple users. The system energy efficiency (EE) maximization problem is formulated by jointly optimizing the RIS element scheduling and beamforming coefficients, as well as the power allocation coefficients, subject to the user's individual rate requirement and the maximum RIS amplification power constraint. Using the Dinkelbach relaxation, the original mixed-integer nonlinear programming problem is transformed into a nonfractional optimization problem with a two-layer structure, which is solved by the alternating optimization approach. In particular, an exhaustive search method is proposed to determine the optimal operating mode for each RIS element. Then, the RIS beamforming and power allocation coefficients are properly designed in an alternating manner. To overcome the potentially high complexity caused by exhaustive searching, we further develop a joint RIS element mode and beamforming optimization scheme by exploiting the Big-M formulation technique. Numerical results validate that: 1) The proposed hybrid RIS scheme yields higher EE than the baseline multi-antenna schemes employing fully active/passive RIS or conventional radio frequency chains; 2) Both proposed algorithms are effective in improving the system performance, especially the latter can achieve precise design of RIS elements with low complexity; and 3) For a fixed-size hybrid RIS, maximum EE can be reaped by setting only a minority of elements to operate in the active mode.
ESFL: Efficient Split Federated Learning over Resource-Constrained Heterogeneous Wireless Devices
Feb 24, 2024



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) allows multiple parties (distributed devices) to train a machine learning model without sharing raw data. How to effectively and efficiently utilize the resources on devices and the central server is a highly interesting yet challenging problem. In this paper, we propose an efficient split federated learning algorithm (ESFL) to take full advantage of the powerful computing capabilities at a central server under a split federated learning framework with heterogeneous end devices (EDs). By splitting the model into different submodels between the server and EDs, our approach jointly optimizes user-side workload and server-side computing resource allocation by considering users' heterogeneity. We formulate the whole optimization problem as a mixed-integer non-linear program, which is an NP-hard problem, and develop an iterative approach to obtain an approximate solution efficiently. Extensive simulations have been conducted to validate the significantly increased efficiency of our ESFL approach compared with standard federated learning, split learning, and splitfed learning.
Efficient Parallel Split Learning over Resource-constrained Wireless Edge Networks
Apr 07, 2023Abstract:The increasingly deeper neural networks hinder the democratization of privacy-enhancing distributed learning, such as federated learning (FL), to resource-constrained devices. To overcome this challenge, in this paper, we advocate the integration of edge computing paradigm and parallel split learning (PSL), allowing multiple client devices to offload substantial training workloads to an edge server via layer-wise model split. By observing that existing PSL schemes incur excessive training latency and large volume of data transmissions, we propose an innovative PSL framework, namely, efficient parallel split learning (EPSL), to accelerate model training. To be specific, EPSL parallelizes client-side model training and reduces the dimension of local gradients for back propagation (BP) via last-layer gradient aggregation, leading to a significant reduction in server-side training and communication latency. Moreover, by considering the heterogeneous channel conditions and computing capabilities at client devices, we jointly optimize subchannel allocation, power control, and cut layer selection to minimize the per-round latency. Simulation results show that the proposed EPSL framework significantly decreases the training latency needed to achieve a target accuracy compared with the state-of-the-art benchmarks, and the tailored resource management and layer split strategy can considerably reduce latency than the counterpart without optimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge