Longzhao Huang
FDBPL: Faster Distillation-Based Prompt Learning for Region-Aware Vision-Language Models Adaptation
May 23, 2025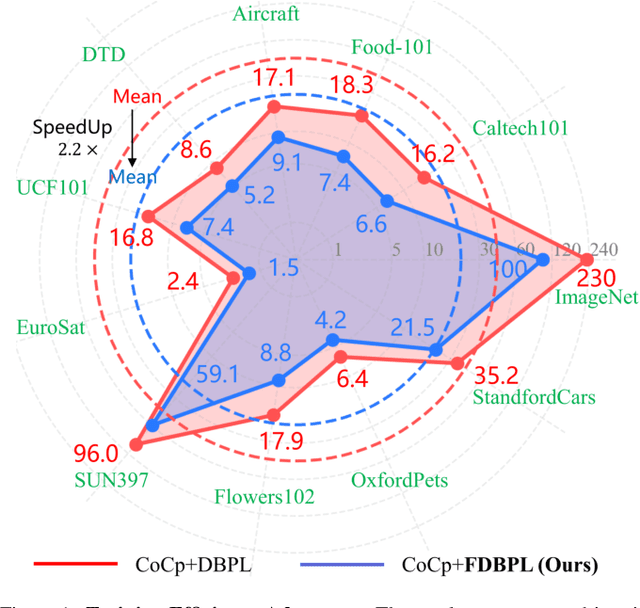
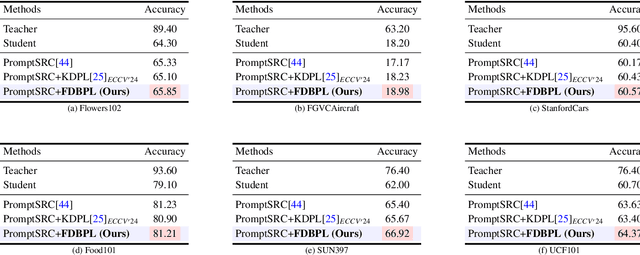
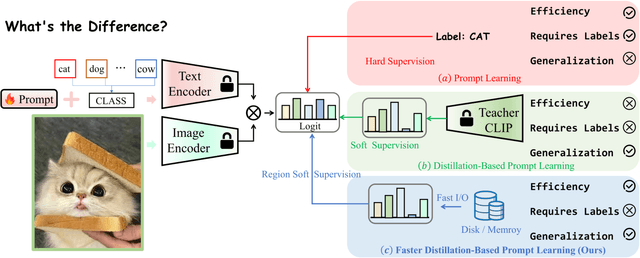
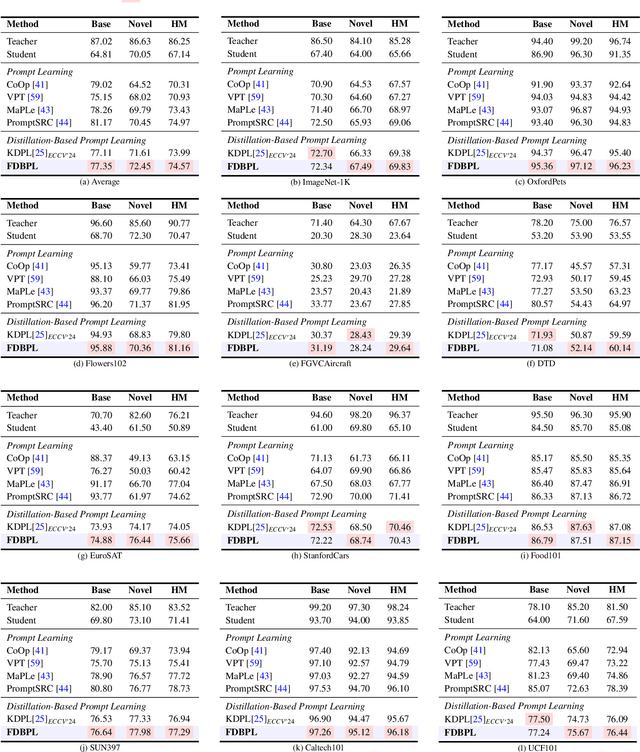
Abstract:Prompt learning as a parameter-efficient method that has been widely adopted to adapt Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to downstream tasks. While hard-prompt design requires domain expertise and iterative optimization, soft-prompt methods rely heavily on task-specific hard labels, limiting their generalization to unseen categories. Recent popular distillation-based prompt learning methods improve generalization by exploiting larger teacher VLMs and unsupervised knowledge transfer, yet their repetitive teacher model online inference sacrifices the inherent training efficiency advantage of prompt learning. In this paper, we propose {{\large {\textbf{F}}}}aster {{\large {\textbf{D}}}}istillation-{{\large {\textbf{B}}}}ased {{\large {\textbf{P}}}}rompt {{\large {\textbf{L}}}}earning (\textbf{FDBPL}), which addresses these issues by sharing soft supervision contexts across multiple training stages and implementing accelerated I/O. Furthermore, FDBPL introduces a region-aware prompt learning paradigm with dual positive-negative prompt spaces to fully exploit randomly cropped regions that containing multi-level information. We propose a positive-negative space mutual learning mechanism based on similarity-difference learning, enabling student CLIP models to recognize correct semantics while learning to reject weakly related concepts, thereby improving zero-shot performance. Unlike existing distillation-based prompt learning methods that sacrifice parameter efficiency for generalization, FDBPL maintains dual advantages of parameter efficiency and strong downstream generalization. Comprehensive evaluations across 11 datasets demonstrate superior performance in base-to-new generalization, cross-dataset transfer, and robustness tests, achieving $2.2\times$ faster training speed.
Generalization Boosted Adapter for Open-Vocabulary Segmentation
Sep 13, 2024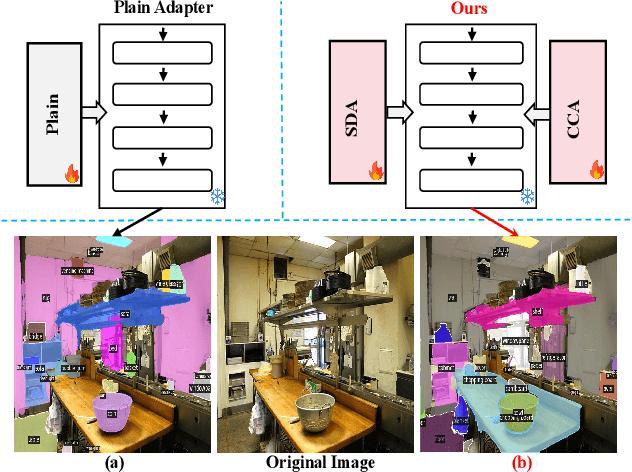
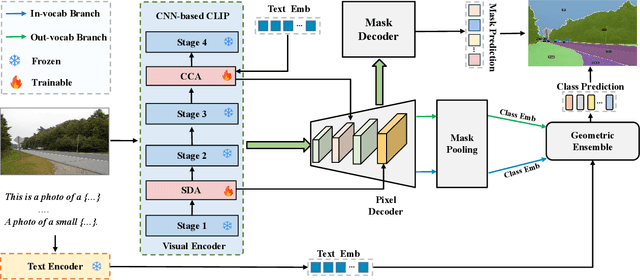
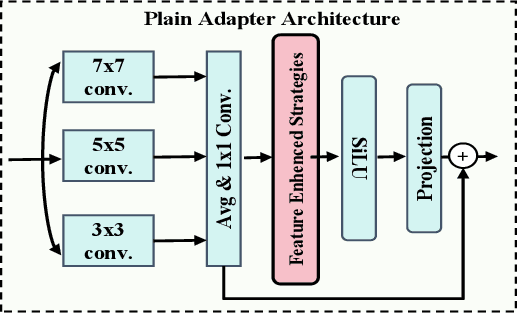
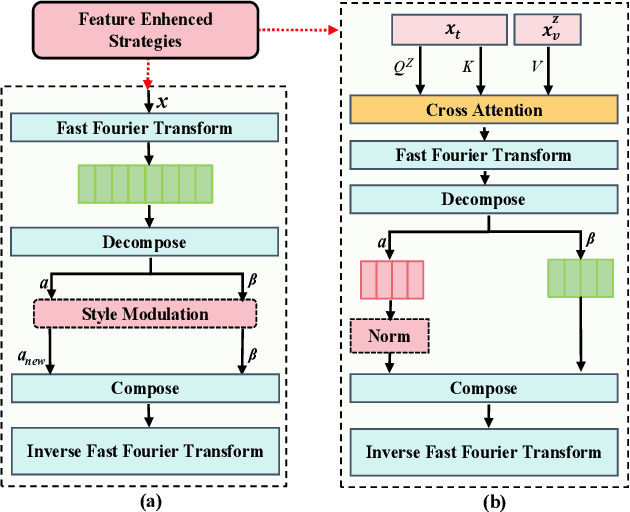
Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable open-vocabulary object recognition capabilities, motivating their adaptation for dense prediction tasks like segmentation. However, directly applying VLMs to such tasks remains challenging due to their lack of pixel-level granularity and the limited data available for fine-tuning, leading to overfitting and poor generalization. To address these limitations, we propose Generalization Boosted Adapter (GBA), a novel adapter strategy that enhances the generalization and robustness of VLMs for open-vocabulary segmentation. GBA comprises two core components: (1) a Style Diversification Adapter (SDA) that decouples features into amplitude and phase components, operating solely on the amplitude to enrich the feature space representation while preserving semantic consistency; and (2) a Correlation Constraint Adapter (CCA) that employs cross-attention to establish tighter semantic associations between text categories and target regions, suppressing irrelevant low-frequency ``noise'' information and avoiding erroneous associations. Through the synergistic effect of the shallow SDA and the deep CCA, GBA effectively alleviates overfitting issues and enhances the semantic relevance of feature representations. As a simple, efficient, and plug-and-play component, GBA can be flexibly integrated into various CLIP-based methods, demonstrating broad applicability and achieving state-of-the-art performance on multiple open-vocabulary segmentation benchmarks.
Gaze Estimation Approach Using Deep Differential Residual Network
Aug 08, 2022

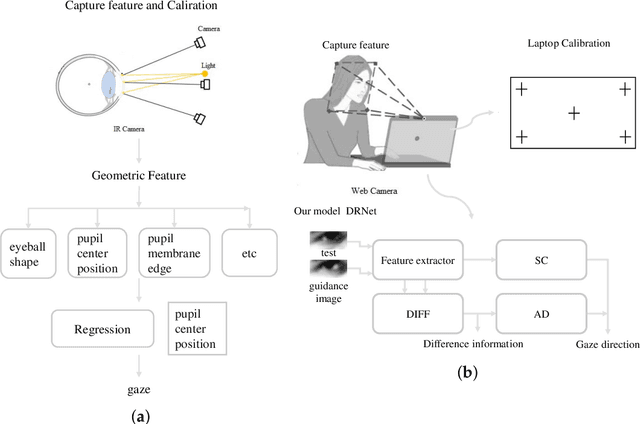
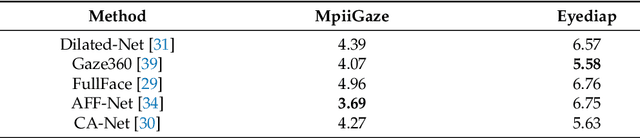
Abstract:Gaze estimation, which is a method to determine where a person is looking at given the person's full face, is a valuable clue for understanding human intention. Similarly to other domains of computer vision, deep learning (DL) methods have gained recognition in the gaze estimation domain. However, there are still gaze calibration problems in the gaze estimation domain, thus preventing existing methods from further improving the performances. An effective solution is to directly predict the difference information of two human eyes, such as the differential network (Diff-Nn). However, this solution results in a loss of accuracy when using only one inference image. We propose a differential residual model (DRNet) combined with a new loss function to make use of the difference information of two eye images. We treat the difference information as auxiliary information. We assess the proposed model (DRNet) mainly using two public datasets (1) MpiiGaze and (2) Eyediap. Considering only the eye features, DRNet outperforms the state-of-the-art gaze estimation methods with $angular-error$ of 4.57 and 6.14 using MpiiGaze and Eyediap datasets, respectively. Furthermore, the experimental results also demonstrate that DRNet is extremely robust to noise images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge